Deunsol Jung
Locality-Aware Zero-Shot Human-Object Interaction Detection
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent methods for zero-shot Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection typically leverage the generalization ability of large Vision-Language Model (VLM), i.e., CLIP, on unseen categories, showing impressive results on various zero-shot settings. However, existing methods struggle to adapt CLIP representations for human-object pairs, as CLIP tends to overlook fine-grained information necessary for distinguishing interactions. To address this issue, we devise, LAIN, a novel zero-shot HOI detection framework enhancing the locality and interaction awareness of CLIP representations. The locality awareness, which involves capturing fine-grained details and the spatial structure of individual objects, is achieved by aggregating the information and spatial priors of adjacent neighborhood patches. The interaction awareness, which involves identifying whether and how a human is interacting with an object, is achieved by capturing the interaction pattern between the human and the object. By infusing locality and interaction awareness into CLIP representation, LAIN captures detailed information about the human-object pairs. Our extensive experiments on existing benchmarks show that LAIN outperforms previous methods on various zero-shot settings, demonstrating the importance of locality and interaction awareness for effective zero-shot HOI detection.
Burst Image Super-Resolution with Base Frame Selection
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Burst image super-resolution has been a topic of active research in recent years due to its ability to obtain a high-resolution image by using complementary information between multiple frames in the burst. In this work, we explore using burst shots with non-uniform exposures to confront real-world practical scenarios by introducing a new benchmark dataset, dubbed Non-uniformly Exposed Burst Image (NEBI), that includes the burst frames at varying exposure times to obtain a broader range of irradiance and motion characteristics within a scene. As burst shots with non-uniform exposures exhibit varying levels of degradation, fusing information of the burst shots into the first frame as a base frame may not result in optimal image quality. To address this limitation, we propose a Frame Selection Network (FSN) for non-uniform scenarios. This network seamlessly integrates into existing super-resolution methods in a plug-and-play manner with low computational costs. The comparative analysis reveals the effectiveness of the nonuniform setting for the practical scenario and our FSN on synthetic-/real- NEBI datasets.
Activity Grammars for Temporal Action Segmentation
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:Sequence prediction on temporal data requires the ability to understand compositional structures of multi-level semantics beyond individual and contextual properties. The task of temporal action segmentation, which aims at translating an untrimmed activity video into a sequence of action segments, remains challenging for this reason. This paper addresses the problem by introducing an effective activity grammar to guide neural predictions for temporal action segmentation. We propose a novel grammar induction algorithm that extracts a powerful context-free grammar from action sequence data. We also develop an efficient generalized parser that transforms frame-level probability distributions into a reliable sequence of actions according to the induced grammar with recursive rules. Our approach can be combined with any neural network for temporal action segmentation to enhance the sequence prediction and discover its compositional structure. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves temporal action segmentation in terms of both performance and interpretability on two standard benchmarks, Breakfast and 50 Salads.
Relational Context Learning for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Apr 11, 2023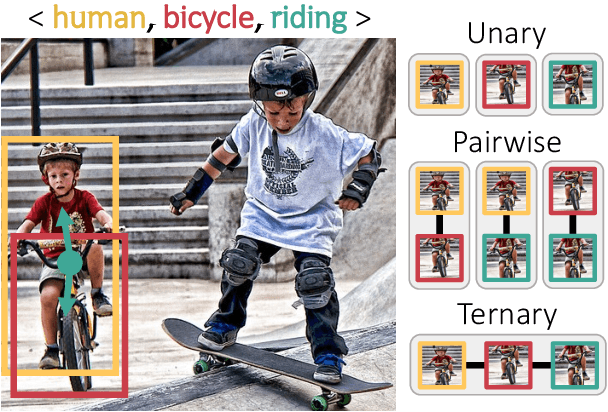
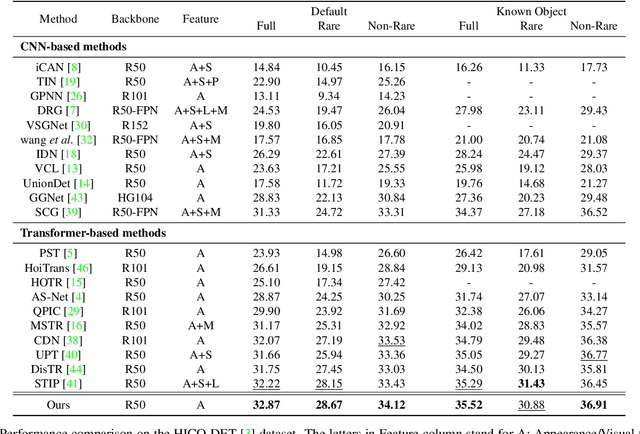
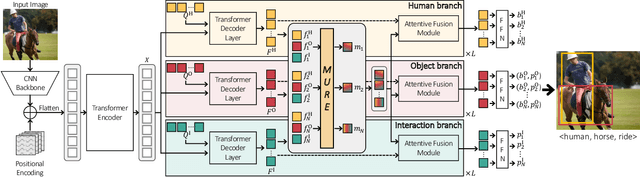
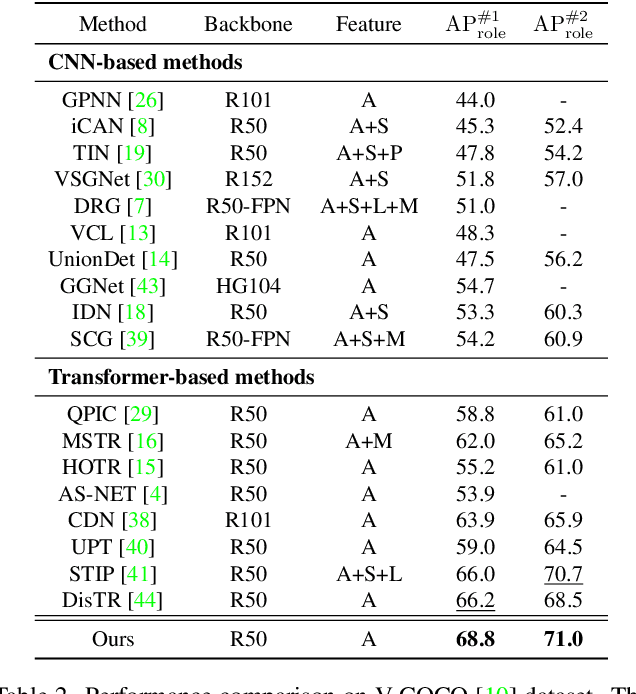
Abstract:Recent state-of-the-art methods for HOI detection typically build on transformer architectures with two decoder branches, one for human-object pair detection and the other for interaction classification. Such disentangled transformers, however, may suffer from insufficient context exchange between the branches and lead to a lack of context information for relational reasoning, which is critical in discovering HOI instances. In this work, we propose the multiplex relation network (MUREN) that performs rich context exchange between three decoder branches using unary, pairwise, and ternary relations of human, object, and interaction tokens. The proposed method learns comprehensive relational contexts for discovering HOI instances, achieving state-of-the-art performance on two standard benchmarks for HOI detection, HICO-DET and V-COCO.
Devil's on the Edges: Selective Quad Attention for Scene Graph Generation
Apr 07, 2023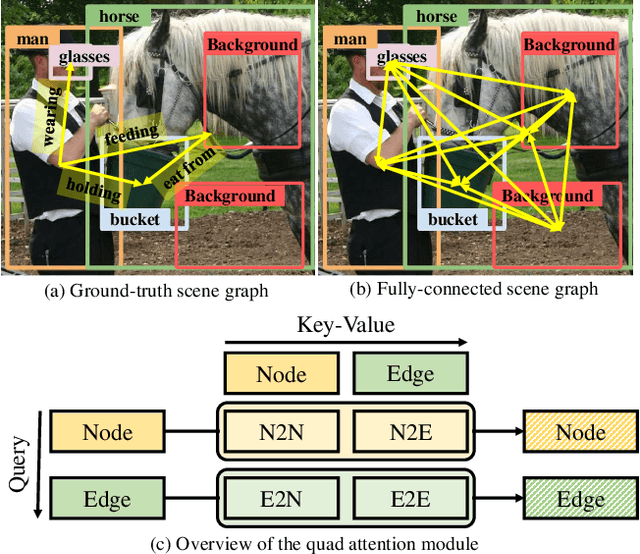
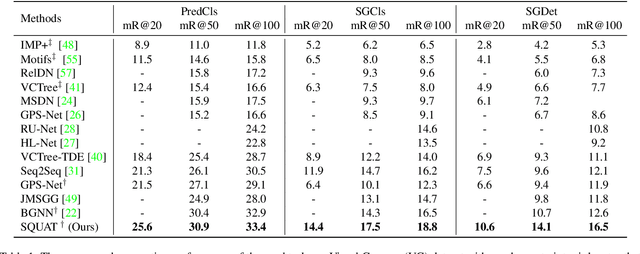
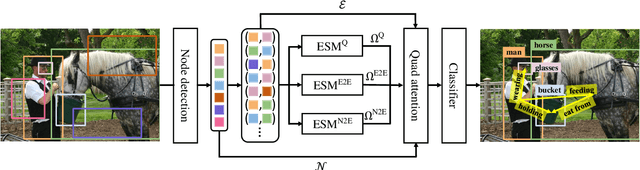
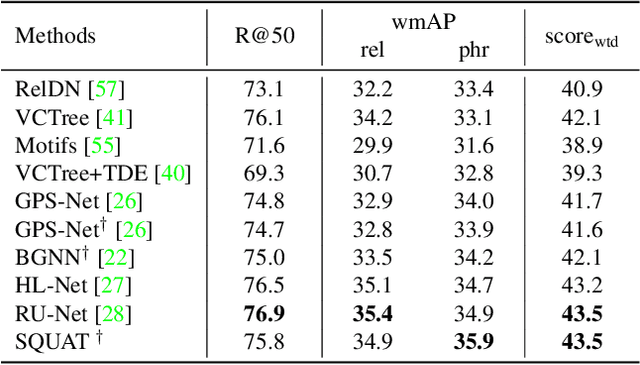
Abstract:Scene graph generation aims to construct a semantic graph structure from an image such that its nodes and edges respectively represent objects and their relationships. One of the major challenges for the task lies in the presence of distracting objects and relationships in images; contextual reasoning is strongly distracted by irrelevant objects or backgrounds and, more importantly, a vast number of irrelevant candidate relations. To tackle the issue, we propose the Selective Quad Attention Network (SQUAT) that learns to select relevant object pairs and disambiguate them via diverse contextual interactions. SQUAT consists of two main components: edge selection and quad attention. The edge selection module selects relevant object pairs, i.e., edges in the scene graph, which helps contextual reasoning, and the quad attention module then updates the edge features using both edge-to-node and edge-to-edge cross-attentions to capture contextual information between objects and object pairs. Experiments demonstrate the strong performance and robustness of SQUAT, achieving the state of the art on the Visual Genome and Open Images v6 benchmarks.
Few-shot Metric Learning: Online Adaptation of Embedding for Retrieval
Nov 14, 2022Abstract:Metric learning aims to build a distance metric typically by learning an effective embedding function that maps similar objects into nearby points in its embedding space. Despite recent advances in deep metric learning, it remains challenging for the learned metric to generalize to unseen classes with a substantial domain gap. To tackle the issue, we explore a new problem of few-shot metric learning that aims to adapt the embedding function to the target domain with only a few annotated data. We introduce three few-shot metric learning baselines and propose the Channel-Rectifier Meta-Learning (CRML), which effectively adapts the metric space online by adjusting channels of intermediate layers. Experimental analyses on miniImageNet, CUB-200-2011, MPII, as well as a new dataset, miniDeepFashion, demonstrate that our method consistently improves the learned metric by adapting it to target classes and achieves a greater gain in image retrieval when the domain gap from the source classes is larger.
Attentive Semantic Alignment with Offset-Aware Correlation Kernels
Oct 26, 2018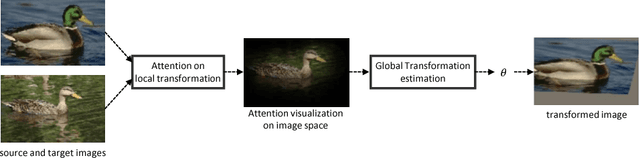
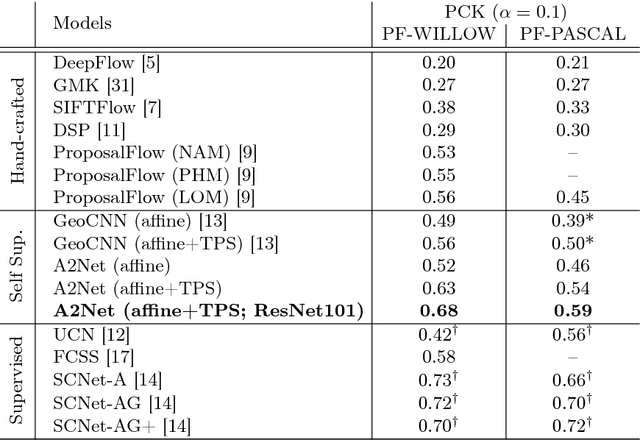
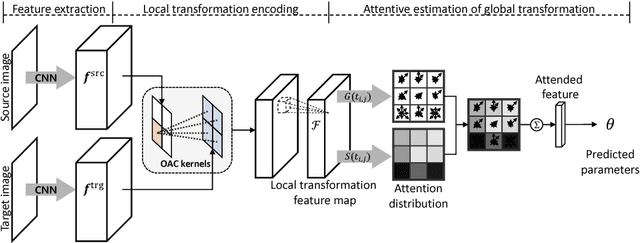
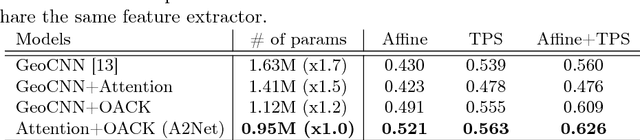
Abstract:Semantic correspondence is the problem of establishing correspondences across images depicting different instances of the same object or scene class. One of recent approaches to this problem is to estimate parameters of a global transformation model that densely aligns one image to the other. Since an entire correlation map between all feature pairs across images is typically used to predict such a global transformation, noisy features from different backgrounds, clutter, and occlusion distract the predictor from correct estimation of the alignment. This is a challenging issue, in particular, in the problem of semantic correspondence where a large degree of image variations is often involved. In this paper, we introduce an attentive semantic alignment method that focuses on reliable correlations, filtering out distractors. For effective attention, we also propose an offset-aware correlation kernel that learns to capture translation-invariant local transformations in computing correlation values over spatial locations. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the attentive model and offset-aware kernel, and the proposed model combining both techniques achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge