Sunghyun Cho
Edge-Aware Image Manipulation via Diffusion Models with a Novel Structure-Preservation Loss
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in image editing leverage latent diffusion models (LDMs) for versatile, text-prompt-driven edits across diverse tasks. Yet, maintaining pixel-level edge structures-crucial for tasks such as photorealistic style transfer or image tone adjustment-remains as a challenge for latent-diffusion-based editing. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel Structure Preservation Loss (SPL) that leverages local linear models to quantify structural differences between input and edited images. Our training-free approach integrates SPL directly into the diffusion model's generative process to ensure structural fidelity. This core mechanism is complemented by a post-processing step to mitigate LDM decoding distortions, a masking strategy for precise edit localization, and a color preservation loss to preserve hues in unedited areas. Experiments confirm SPL enhances structural fidelity, delivering state-of-the-art performance in latent-diffusion-based image editing. Our code will be publicly released at https://github.com/gongms00/SPL.
Efficient Real-World Deblurring using Single Images: AIM 2025 Challenge Report
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:This paper reviews the AIM 2025 Efficient Real-World Deblurring using Single Images Challenge, which aims to advance in efficient real-blur restoration. The challenge is based on a new test set based on the well known RSBlur dataset. Pairs of blur and degraded images in this dataset are captured using a double-camera system. Participant were tasked with developing solutions to effectively deblur these type of images while fulfilling strict efficiency constraints: fewer than 5 million model parameters and a computational budget under 200 GMACs. A total of 71 participants registered, with 4 teams finally submitting valid solutions. The top-performing approach achieved a PSNR of 31.1298 dB, showcasing the potential of efficient methods in this domain. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenge, compares the proposed solutions, and serves as a valuable reference for researchers in efficient real-world image deblurring.
Elevating 3D Models: High-Quality Texture and Geometry Refinement from a Low-Quality Model
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:High-quality 3D assets are essential for various applications in computer graphics and 3D vision but remain scarce due to significant acquisition costs. To address this shortage, we introduce Elevate3D, a novel framework that transforms readily accessible low-quality 3D assets into higher quality. At the core of Elevate3D is HFS-SDEdit, a specialized texture enhancement method that significantly improves texture quality while preserving the appearance and geometry while fixing its degradations. Furthermore, Elevate3D operates in a view-by-view manner, alternating between texture and geometry refinement. Unlike previous methods that have largely overlooked geometry refinement, our framework leverages geometric cues from images refined with HFS-SDEdit by employing state-of-the-art monocular geometry predictors. This approach ensures detailed and accurate geometry that aligns seamlessly with the enhanced texture. Elevate3D outperforms recent competitors by achieving state-of-the-art quality in 3D model refinement, effectively addressing the scarcity of high-quality open-source 3D assets.
Subject-driven Video Generation via Disentangled Identity and Motion
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:We propose to train a subject-driven customized video generation model through decoupling the subject-specific learning from temporal dynamics in zero-shot without additional tuning. A traditional method for video customization that is tuning-free often relies on large, annotated video datasets, which are computationally expensive and require extensive annotation. In contrast to the previous approach, we introduce the use of an image customization dataset directly on training video customization models, factorizing the video customization into two folds: (1) identity injection through image customization dataset and (2) temporal modeling preservation with a small set of unannotated videos through the image-to-video training method. Additionally, we employ random image token dropping with randomized image initialization during image-to-video fine-tuning to mitigate the copy-and-paste issue. To further enhance learning, we introduce stochastic switching during joint optimization of subject-specific and temporal features, mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Our method achieves strong subject consistency and scalability, outperforming existing video customization models in zero-shot settings, demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework.
Exploiting Deblurring Networks for Radiance Fields
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we propose DeepDeblurRF, a novel radiance field deblurring approach that can synthesize high-quality novel views from blurred training views with significantly reduced training time. DeepDeblurRF leverages deep neural network (DNN)-based deblurring modules to enjoy their deblurring performance and computational efficiency. To effectively combine DNN-based deblurring and radiance field construction, we propose a novel radiance field (RF)-guided deblurring and an iterative framework that performs RF-guided deblurring and radiance field construction in an alternating manner. Moreover, DeepDeblurRF is compatible with various scene representations, such as voxel grids and 3D Gaussians, expanding its applicability. We also present BlurRF-Synth, the first large-scale synthetic dataset for training radiance field deblurring frameworks. We conduct extensive experiments on both camera motion blur and defocus blur, demonstrating that DeepDeblurRF achieves state-of-the-art novel-view synthesis quality with significantly reduced training time.
FloVD: Optical Flow Meets Video Diffusion Model for Enhanced Camera-Controlled Video Synthesis
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:This paper presents FloVD, a novel optical-flow-based video diffusion model for camera-controllable video generation. FloVD leverages optical flow maps to represent motions of the camera and moving objects. This approach offers two key benefits. Since optical flow can be directly estimated from videos, our approach allows for the use of arbitrary training videos without ground-truth camera parameters. Moreover, as background optical flow encodes 3D correlation across different viewpoints, our method enables detailed camera control by leveraging the background motion. To synthesize natural object motion while supporting detailed camera control, our framework adopts a two-stage video synthesis pipeline consisting of optical flow generation and flow-conditioned video synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method over previous approaches in terms of accurate camera control and natural object motion synthesis.
DC-VSR: Spatially and Temporally Consistent Video Super-Resolution with Video Diffusion Prior
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Video super-resolution (VSR) aims to reconstruct a high-resolution (HR) video from a low-resolution (LR) counterpart. Achieving successful VSR requires producing realistic HR details and ensuring both spatial and temporal consistency. To restore realistic details, diffusion-based VSR approaches have recently been proposed. However, the inherent randomness of diffusion, combined with their tile-based approach, often leads to spatio-temporal inconsistencies. In this paper, we propose DC-VSR, a novel VSR approach to produce spatially and temporally consistent VSR results with realistic textures. To achieve spatial and temporal consistency, DC-VSR adopts a novel Spatial Attention Propagation (SAP) scheme and a Temporal Attention Propagation (TAP) scheme that propagate information across spatio-temporal tiles based on the self-attention mechanism. To enhance high-frequency details, we also introduce Detail-Suppression Self-Attention Guidance (DSSAG), a novel diffusion guidance scheme. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that DC-VSR achieves spatially and temporally consistent, high-quality VSR results, outperforming previous approaches.
Locality-aware Gaussian Compression for Fast and High-quality Rendering
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:We present LocoGS, a locality-aware 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework that exploits the spatial coherence of 3D Gaussians for compact modeling of volumetric scenes. To this end, we first analyze the local coherence of 3D Gaussian attributes, and propose a novel locality-aware 3D Gaussian representation that effectively encodes locally-coherent Gaussian attributes using a neural field representation with a minimal storage requirement. On top of the novel representation, LocoGS is carefully designed with additional components such as dense initialization, an adaptive spherical harmonics bandwidth scheme and different encoding schemes for different Gaussian attributes to maximize compression performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms the rendering quality of existing compact Gaussian representations for representative real-world 3D datasets while achieving from 54.6$\times$ to 96.6$\times$ compressed storage size and from 2.1$\times$ to 2.4$\times$ rendering speed than 3DGS. Even our approach also demonstrates an averaged 2.4$\times$ higher rendering speed than the state-of-the-art compression method with comparable compression performance.
LayeringDiff: Layered Image Synthesis via Generation, then Disassembly with Generative Knowledge
Jan 02, 2025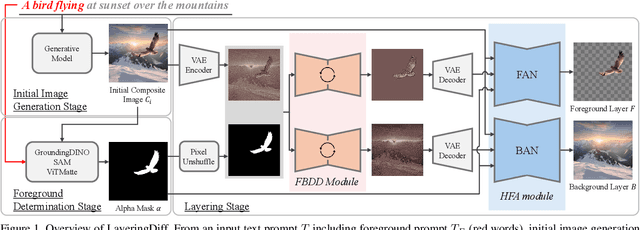
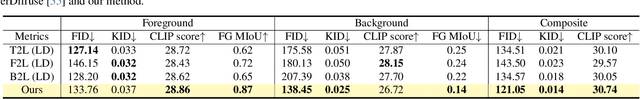
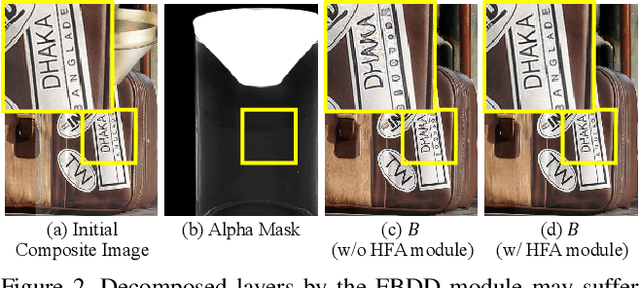
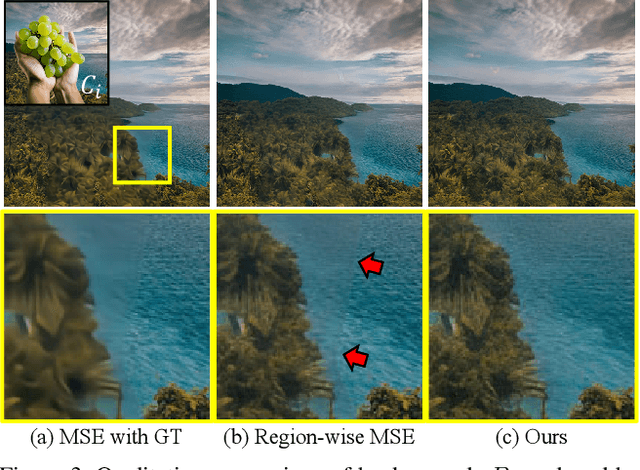
Abstract:Layers have become indispensable tools for professional artists, allowing them to build a hierarchical structure that enables independent control over individual visual elements. In this paper, we propose LayeringDiff, a novel pipeline for the synthesis of layered images, which begins by generating a composite image using an off-the-shelf image generative model, followed by disassembling the image into its constituent foreground and background layers. By extracting layers from a composite image, rather than generating them from scratch, LayeringDiff bypasses the need for large-scale training to develop generative capabilities for individual layers. Furthermore, by utilizing a pretrained off-the-shelf generative model, our method can produce diverse contents and object scales in synthesized layers. For effective layer decomposition, we adapt a large-scale pretrained generative prior to estimate foreground and background layers. We also propose high-frequency alignment modules to refine the fine-details of the estimated layers. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively synthesizes layered images and supports various practical applications.
Addressing Attribute Leakages in Diffusion-based Image Editing without Training
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have become a cornerstone in image editing, offering flexibility with language prompts and source images. However, a key challenge is attribute leakage, where unintended modifications occur in non-target regions or within target regions due to attribute interference. Existing methods often suffer from leakage due to naive text embeddings and inadequate handling of End-of-Sequence (EOS) token embeddings. To address this, we propose ALE-Edit (Attribute-leakage-free editing), a novel framework to minimize attribute leakage with three components: (1) Object-Restricted Embeddings (ORE) to localize object-specific attributes in text embeddings, (2) Region-Guided Blending for Cross-Attention Masking (RGB-CAM) to align attention with target regions, and (3) Background Blending (BB) to preserve non-edited regions. Additionally, we introduce ALE-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating attribute leakage with new metrics for target-external and target-internal leakage. Experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly reduces attribute leakage while maintaining high editing quality, providing an efficient and tuning-free solution for multi-object image editing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge