Donguk Kim
Exploring the Capabilities of LLM Encoders for Image-Text Retrieval in Chest X-rays
Sep 17, 2025



Abstract:Vision-language pretraining has advanced image-text alignment, yet progress in radiology remains constrained by the heterogeneity of clinical reports, including abbreviations, impression-only notes, and stylistic variability. Unlike general-domain settings where more data often leads to better performance, naively scaling to large collections of noisy reports can plateau or even degrade model learning. We ask whether large language model (LLM) encoders can provide robust clinical representations that transfer across diverse styles and better guide image-text alignment. We introduce LLM2VEC4CXR, a domain-adapted LLM encoder for chest X-ray reports, and LLM2CLIP4CXR, a dual-tower framework that couples this encoder with a vision backbone. LLM2VEC4CXR improves clinical text understanding over BERT-based baselines, handles abbreviations and style variation, and achieves strong clinical alignment on report-level metrics. LLM2CLIP4CXR leverages these embeddings to boost retrieval accuracy and clinically oriented scores, with stronger cross-dataset generalization than prior medical CLIP variants. Trained on 1.6M CXR studies from public and private sources with heterogeneous and noisy reports, our models demonstrate that robustness -- not scale alone -- is the key to effective multimodal learning. We release models to support further research in medical image-text representation learning.
LayeringDiff: Layered Image Synthesis via Generation, then Disassembly with Generative Knowledge
Jan 02, 2025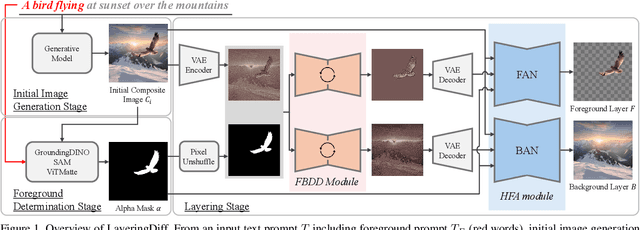
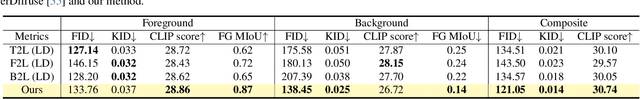
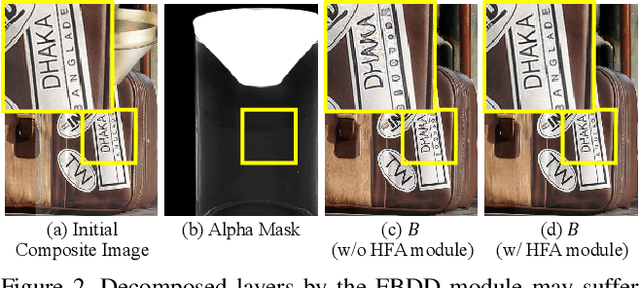
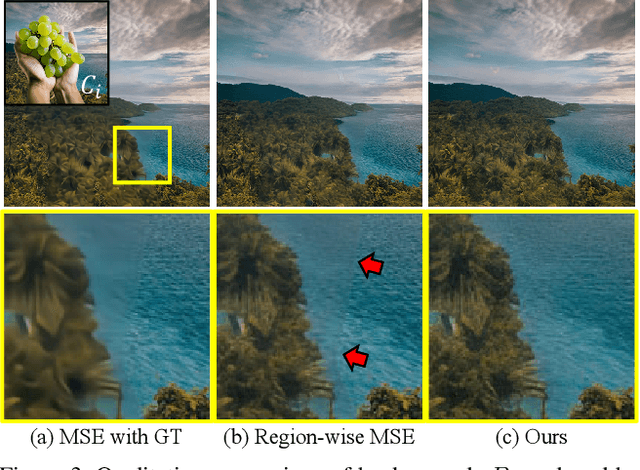
Abstract:Layers have become indispensable tools for professional artists, allowing them to build a hierarchical structure that enables independent control over individual visual elements. In this paper, we propose LayeringDiff, a novel pipeline for the synthesis of layered images, which begins by generating a composite image using an off-the-shelf image generative model, followed by disassembling the image into its constituent foreground and background layers. By extracting layers from a composite image, rather than generating them from scratch, LayeringDiff bypasses the need for large-scale training to develop generative capabilities for individual layers. Furthermore, by utilizing a pretrained off-the-shelf generative model, our method can produce diverse contents and object scales in synthesized layers. For effective layer decomposition, we adapt a large-scale pretrained generative prior to estimate foreground and background layers. We also propose high-frequency alignment modules to refine the fine-details of the estimated layers. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively synthesizes layered images and supports various practical applications.
RITUAL: Random Image Transformations as a Universal Anti-hallucination Lever in LVLMs
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have revolutionized how machines understand and generate textual responses based on visual inputs. Despite their impressive capabilities, they often produce "hallucinatory" outputs that do not accurately reflect the visual information, posing challenges in reliability and trustworthiness. Current methods such as contrastive decoding have made strides in addressing these issues by contrasting the original probability distribution of generated tokens with distorted counterparts; yet, generating visually-faithful outputs remains a challenge. In this work, we shift our focus to the opposite: What could serve as a complementary enhancement to the original probability distribution? We propose a simple, training-free method termed RITUAL to enhance robustness against hallucinations in LVLMs. Our approach employs random image transformations as complements to the original probability distribution, aiming to mitigate the likelihood of hallucinatory visual explanations by enriching the model's exposure to varied visual scenarios. Our empirical results show that while the isolated use of transformed images initially degrades performance, strategic implementation of these transformations can indeed serve as effective complements. Notably, our method is compatible with current contrastive decoding methods and does not require external models or costly self-feedback mechanisms, making it a practical addition. In experiments, RITUAL significantly outperforms existing contrastive decoding methods across several object hallucination benchmarks, including POPE, CHAIR, and MME.
Don't Miss the Forest for the Trees: Attentional Vision Calibration for Large Vision Language Models
May 28, 2024Abstract:This study addresses the issue observed in Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs), where excessive attention on a few image tokens, referred to as blind tokens, leads to hallucinatory responses in tasks requiring fine-grained understanding of visual objects. We found that tokens receiving lower attention weights often hold essential information for identifying nuanced object details -- ranging from merely recognizing object existence to identifying their attributes (color, position, etc.) and understanding their relationships. To counteract the over-emphasis on blind tokens and to accurately respond to user queries, we introduce a technique called Attentional Vision Calibration (AVC). During the decoding phase, AVC identifies blind tokens by analyzing the image-related attention distribution. It then dynamically adjusts the logits for the next token prediction by contrasting the logits conditioned on the original visual tokens with those conditioned on the blind tokens. This effectively lowers the dependency on blind tokens and promotes a more balanced consideration of all tokens. We validate AVC on benchmarks such as POPE, MME, and AMBER, where it consistently outperforms existing decoding techniques in mitigating object hallucinations in LVLMs.
Flow-Assisted Motion Learning Network for Weakly-Supervised Group Activity Recognition
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Group Activity Recognition (WSGAR) aims to understand the activity performed together by a group of individuals with the video-level label and without actor-level labels. We propose Flow-Assisted Motion Learning Network (Flaming-Net) for WSGAR, which consists of the motion-aware actor encoder to extract actor features and the two-pathways relation module to infer the interaction among actors and their activity. Flaming-Net leverages an additional optical flow modality in the training stage to enhance its motion awareness when finding locally active actors. The first pathway of the relation module, the actor-centric path, initially captures the temporal dynamics of individual actors and then constructs inter-actor relationships. In parallel, the group-centric path starts by building spatial connections between actors within the same timeframe and then captures simultaneous spatio-temporal dynamics among them. We demonstrate that Flaming-Net achieves new state-of-the-art WSGAR results on two benchmarks, including a 2.8%p higher MPCA score on the NBA dataset. Importantly, we use the optical flow modality only for training and not for inference.
HOReeNet: 3D-aware Hand-Object Grasping Reenactment
Nov 11, 2022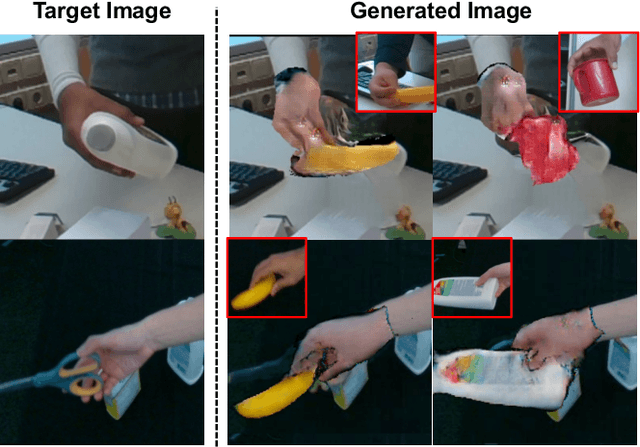
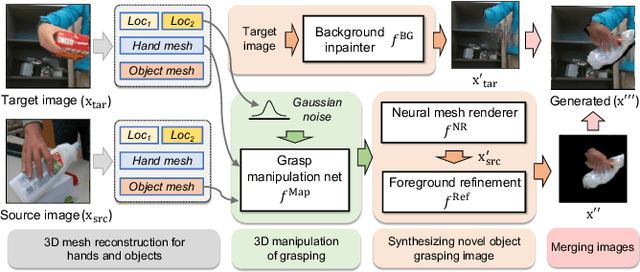

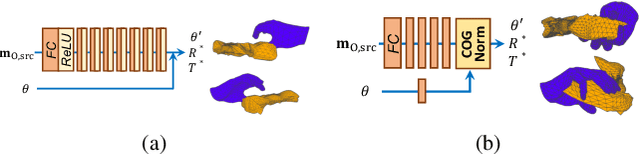
Abstract:We present HOReeNet, which tackles the novel task of manipulating images involving hands, objects, and their interactions. Especially, we are interested in transferring objects of source images to target images and manipulating 3D hand postures to tightly grasp the transferred objects. Furthermore, the manipulation needs to be reflected in the 2D image space. In our reenactment scenario involving hand-object interactions, 3D reconstruction becomes essential as 3D contact reasoning between hands and objects is required to achieve a tight grasp. At the same time, to obtain high-quality 2D images from 3D space, well-designed 3D-to-2D projection and image refinement are required. Our HOReeNet is the first fully differentiable framework proposed for such a task. On hand-object interaction datasets, we compared our HOReeNet to the conventional image translation algorithms and reenactment algorithm. We demonstrated that our approach could achieved the state-of-the-art on the proposed task.
Transformer-based Global 3D Hand Pose Estimation in Two Hands Manipulating Objects Scenarios
Oct 20, 2022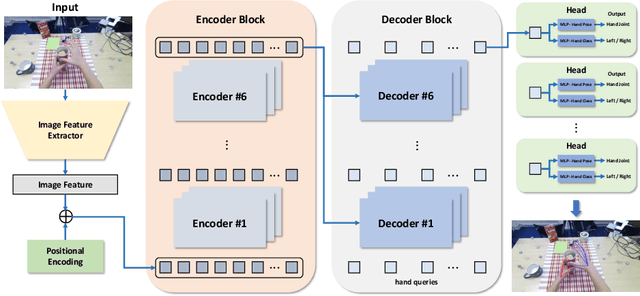
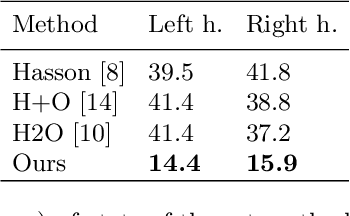
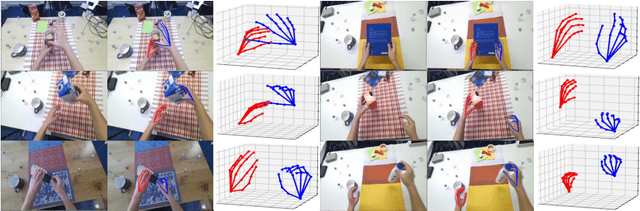

Abstract:This report describes our 1st place solution to ECCV 2022 challenge on Human Body, Hands, and Activities (HBHA) from Egocentric and Multi-view Cameras (hand pose estimation). In this challenge, we aim to estimate global 3D hand poses from the input image where two hands and an object are interacting on the egocentric viewpoint. Our proposed method performs end-to-end multi-hand pose estimation via transformer architecture. In particular, our method robustly estimates hand poses in a scenario where two hands interact. Additionally, we propose an algorithm that considers hand scales to robustly estimate the absolute depth. The proposed algorithm works well even when the hand sizes are various for each person. Our method attains 14.4 mm (left) and 15.9 mm (right) errors for each hand in the test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge