Honggyu An
Repurposing Video Diffusion Transformers for Robust Point Tracking
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Point tracking aims to localize corresponding points across video frames, serving as a fundamental task for 4D reconstruction, robotics, and video editing. Existing methods commonly rely on shallow convolutional backbones such as ResNet that process frames independently, lacking temporal coherence and producing unreliable matching costs under challenging conditions. Through systematic analysis, we find that video Diffusion Transformers (DiTs), pre-trained on large-scale real-world videos with spatio-temporal attention, inherently exhibit strong point tracking capability and robustly handle dynamic motions and frequent occlusions. We propose DiTracker, which adapts video DiTs through: (1) query-key attention matching, (2) lightweight LoRA tuning, and (3) cost fusion with a ResNet backbone. Despite training with 8 times smaller batch size, DiTracker achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging ITTO benchmark and matches or outperforms state-of-the-art models on TAP-Vid benchmarks. Our work validates video DiT features as an effective and efficient foundation for point tracking.
Visual Representation Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Models
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) trained with visual instruction tuning have achieved strong performance across diverse tasks, yet they remain limited in vision-centric tasks such as object counting or spatial reasoning. We attribute this gap to the prevailing text-only supervision paradigm, which provides only indirect guidance for the visual pathway and often leads MLLMs to discard fine-grained visual details during training. In this paper, we present VIsual Representation ALignment (VIRAL), a simple yet effective regularization strategy that aligns the internal visual representations of MLLMs with those of pre-trained vision foundation models (VFMs). By explicitly enforcing this alignment, VIRAL enables the model not only to retain critical visual details from the input vision encoder but also to complement additional visual knowledge from VFMs, thereby enhancing its ability to reason over complex visual inputs. Our experiments demonstrate consistent improvements across all tasks on widely adopted multimodal benchmarks. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to validate the key design choices underlying our framework. We believe this simple finding opens up an important direction for the effective integration of visual information in training MLLMs.
D^2USt3R: Enhancing 3D Reconstruction with 4D Pointmaps for Dynamic Scenes
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:We address the task of 3D reconstruction in dynamic scenes, where object motions degrade the quality of previous 3D pointmap regression methods, such as DUSt3R, originally designed for static 3D scene reconstruction. Although these methods provide an elegant and powerful solution in static settings, they struggle in the presence of dynamic motions that disrupt alignment based solely on camera poses. To overcome this, we propose D^2USt3R that regresses 4D pointmaps that simultaneiously capture both static and dynamic 3D scene geometry in a feed-forward manner. By explicitly incorporating both spatial and temporal aspects, our approach successfully encapsulates spatio-temporal dense correspondence to the proposed 4D pointmaps, enhancing downstream tasks. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our proposed approach consistently achieves superior reconstruction performance across various datasets featuring complex motions.
Cross-View Completion Models are Zero-shot Correspondence Estimators
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:In this work, we explore new perspectives on cross-view completion learning by drawing an analogy to self-supervised correspondence learning. Through our analysis, we demonstrate that the cross-attention map within cross-view completion models captures correspondence more effectively than other correlations derived from encoder or decoder features. We verify the effectiveness of the cross-attention map by evaluating on both zero-shot matching and learning-based geometric matching and multi-frame depth estimation. Project page is available at https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/ZeroCo/.
Local All-Pair Correspondence for Point Tracking
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:We introduce LocoTrack, a highly accurate and efficient model designed for the task of tracking any point (TAP) across video sequences. Previous approaches in this task often rely on local 2D correlation maps to establish correspondences from a point in the query image to a local region in the target image, which often struggle with homogeneous regions or repetitive features, leading to matching ambiguities. LocoTrack overcomes this challenge with a novel approach that utilizes all-pair correspondences across regions, i.e., local 4D correlation, to establish precise correspondences, with bidirectional correspondence and matching smoothness significantly enhancing robustness against ambiguities. We also incorporate a lightweight correlation encoder to enhance computational efficiency, and a compact Transformer architecture to integrate long-term temporal information. LocoTrack achieves unmatched accuracy on all TAP-Vid benchmarks and operates at a speed almost 6 times faster than the current state-of-the-art.
Relaxing Accurate Initialization Constraint for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has recently demonstrated impressive capabilities in real-time novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction. However, 3DGS heavily depends on the accurate initialization derived from Structure-from-Motion (SfM) methods. When trained with randomly initialized point clouds, 3DGS fails to maintain its ability to produce high-quality images, undergoing large performance drops of 4-5 dB in PSNR. Through extensive analysis of SfM initialization in the frequency domain and analysis of a 1D regression task with multiple 1D Gaussians, we propose a novel optimization strategy dubbed RAIN-GS (Relaxing Accurate Initialization Constraint for 3D Gaussian Splatting), that successfully trains 3D Gaussians from random point clouds. We show the effectiveness of our strategy through quantitative and qualitative comparisons on multiple datasets, largely improving the performance in all settings. Our project page and code can be found at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/RAIN-GS.
DäRF: Boosting Radiance Fields from Sparse Inputs with Monocular Depth Adaptation
May 30, 2023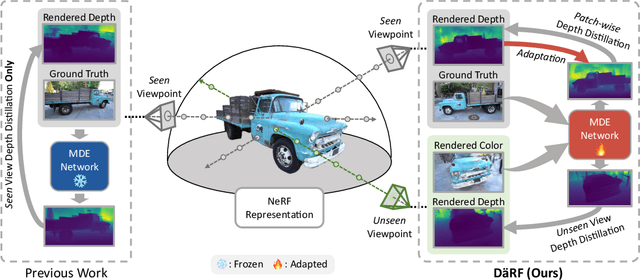
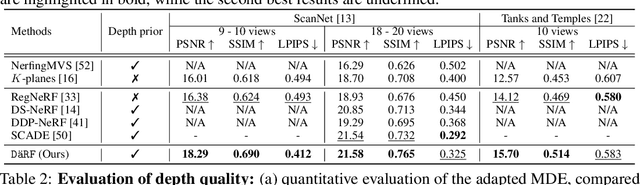
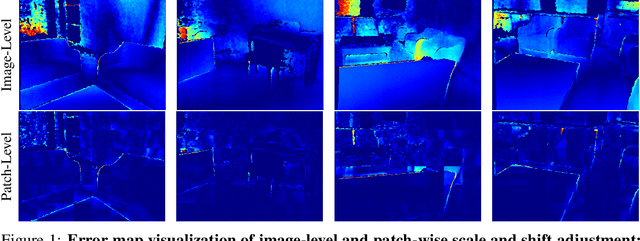
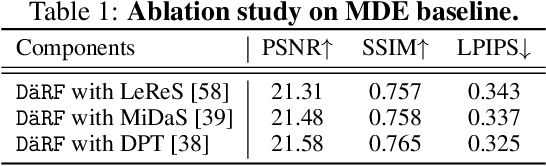
Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) shows powerful performance in novel view synthesis and 3D geometry reconstruction, but it suffers from critical performance degradation when the number of known viewpoints is drastically reduced. Existing works attempt to overcome this problem by employing external priors, but their success is limited to certain types of scenes or datasets. Employing monocular depth estimation (MDE) networks, pretrained on large-scale RGB-D datasets, with powerful generalization capability would be a key to solving this problem: however, using MDE in conjunction with NeRF comes with a new set of challenges due to various ambiguity problems exhibited by monocular depths. In this light, we propose a novel framework, dubbed D\"aRF, that achieves robust NeRF reconstruction with a handful of real-world images by combining the strengths of NeRF and monocular depth estimation through online complementary training. Our framework imposes the MDE network's powerful geometry prior to NeRF representation at both seen and unseen viewpoints to enhance its robustness and coherence. In addition, we overcome the ambiguity problems of monocular depths through patch-wise scale-shift fitting and geometry distillation, which adapts the MDE network to produce depths aligned accurately with NeRF geometry. Experiments show our framework achieves state-of-the-art results both quantitatively and qualitatively, demonstrating consistent and reliable performance in both indoor and outdoor real-world datasets. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/DaRF/.
Semi-Supervised Learning of Monocular Depth Estimation via Consistency Regularization with K-way Disjoint Masking
Dec 22, 2022
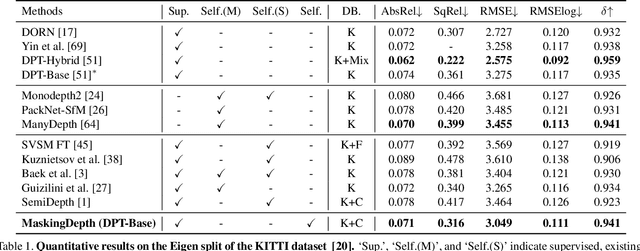
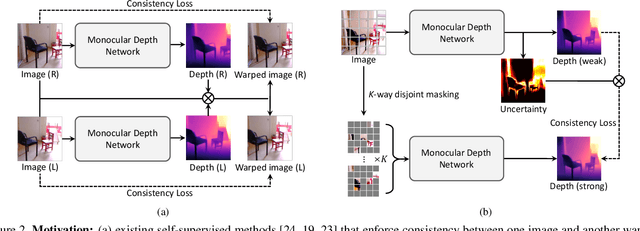
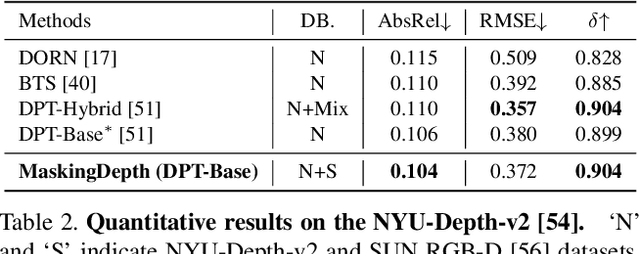
Abstract:Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) has recently accomplished successful achievements in various fields such as image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation, which typically require a lot of labour to construct ground-truth. Especially in the depth estimation task, annotating training data is very costly and time-consuming, and thus recent SSL regime seems an attractive solution. In this paper, for the first time, we introduce a novel framework for semi-supervised learning of monocular depth estimation networks, using consistency regularization to mitigate the reliance on large ground-truth depth data. We propose a novel data augmentation approach, called K-way disjoint masking, which allows the network for learning how to reconstruct invisible regions so that the model not only becomes robust to perturbations but also generates globally consistent output depth maps. Experiments on the KITTI and NYU-Depth-v2 datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of each component in our pipeline, robustness to the use of fewer and fewer annotated images, and superior results compared to other state-of-the-art, semi-supervised methods for monocular depth estimation. Our code is available at https://github.com/KU-CVLAB/MaskingDepth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge