Seonghoon Park
Cross-View Completion Models are Zero-shot Correspondence Estimators
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:In this work, we explore new perspectives on cross-view completion learning by drawing an analogy to self-supervised correspondence learning. Through our analysis, we demonstrate that the cross-attention map within cross-view completion models captures correspondence more effectively than other correlations derived from encoder or decoder features. We verify the effectiveness of the cross-attention map by evaluating on both zero-shot matching and learning-based geometric matching and multi-frame depth estimation. Project page is available at https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/ZeroCo/.
Relaxing Accurate Initialization Constraint for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has recently demonstrated impressive capabilities in real-time novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction. However, 3DGS heavily depends on the accurate initialization derived from Structure-from-Motion (SfM) methods. When trained with randomly initialized point clouds, 3DGS fails to maintain its ability to produce high-quality images, undergoing large performance drops of 4-5 dB in PSNR. Through extensive analysis of SfM initialization in the frequency domain and analysis of a 1D regression task with multiple 1D Gaussians, we propose a novel optimization strategy dubbed RAIN-GS (Relaxing Accurate Initialization Constraint for 3D Gaussian Splatting), that successfully trains 3D Gaussians from random point clouds. We show the effectiveness of our strategy through quantitative and qualitative comparisons on multiple datasets, largely improving the performance in all settings. Our project page and code can be found at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/RAIN-GS.
Context Enhanced Transformer for Single Image Object Detection
Dec 26, 2023



Abstract:With the increasing importance of video data in real-world applications, there is a rising need for efficient object detection methods that utilize temporal information. While existing video object detection (VOD) techniques employ various strategies to address this challenge, they typically depend on locally adjacent frames or randomly sampled images within a clip. Although recent Transformer-based VOD methods have shown promising results, their reliance on multiple inputs and additional network complexity to incorporate temporal information limits their practical applicability. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to single image object detection, called Context Enhanced TRansformer (CETR), by incorporating temporal context into DETR using a newly designed memory module. To efficiently store temporal information, we construct a class-wise memory that collects contextual information across data. Additionally, we present a classification-based sampling technique to selectively utilize the relevant memory for the current image. In the testing, We introduce a test-time memory adaptation method that updates individual memory functions by considering the test distribution. Experiments with CityCam and ImageNet VID datasets exhibit the efficiency of the framework on various video systems. The project page and code will be made available at: https://ku-cvlab.github.io/CETR.
DäRF: Boosting Radiance Fields from Sparse Inputs with Monocular Depth Adaptation
May 30, 2023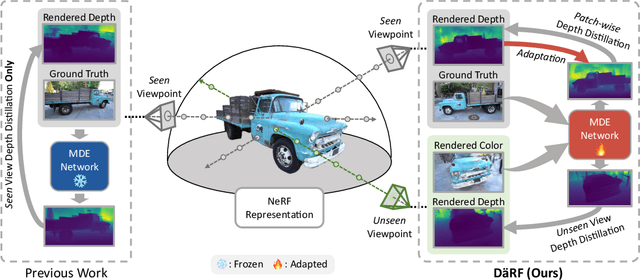
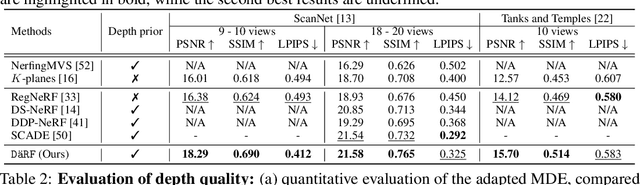
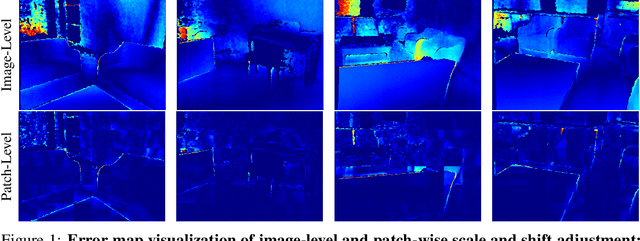
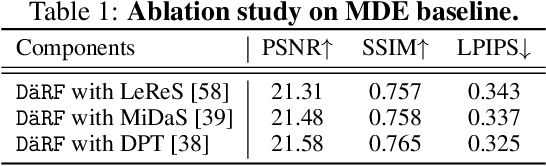
Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) shows powerful performance in novel view synthesis and 3D geometry reconstruction, but it suffers from critical performance degradation when the number of known viewpoints is drastically reduced. Existing works attempt to overcome this problem by employing external priors, but their success is limited to certain types of scenes or datasets. Employing monocular depth estimation (MDE) networks, pretrained on large-scale RGB-D datasets, with powerful generalization capability would be a key to solving this problem: however, using MDE in conjunction with NeRF comes with a new set of challenges due to various ambiguity problems exhibited by monocular depths. In this light, we propose a novel framework, dubbed D\"aRF, that achieves robust NeRF reconstruction with a handful of real-world images by combining the strengths of NeRF and monocular depth estimation through online complementary training. Our framework imposes the MDE network's powerful geometry prior to NeRF representation at both seen and unseen viewpoints to enhance its robustness and coherence. In addition, we overcome the ambiguity problems of monocular depths through patch-wise scale-shift fitting and geometry distillation, which adapts the MDE network to produce depths aligned accurately with NeRF geometry. Experiments show our framework achieves state-of-the-art results both quantitatively and qualitatively, demonstrating consistent and reliable performance in both indoor and outdoor real-world datasets. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/DaRF/.
Semi-Supervised Learning of Monocular Depth Estimation via Consistency Regularization with K-way Disjoint Masking
Dec 22, 2022
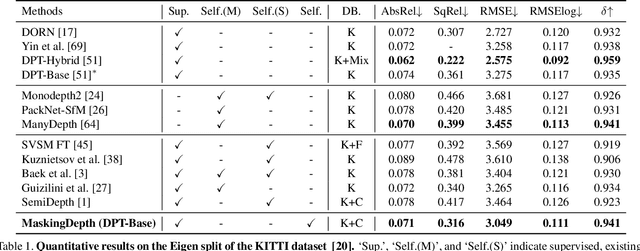
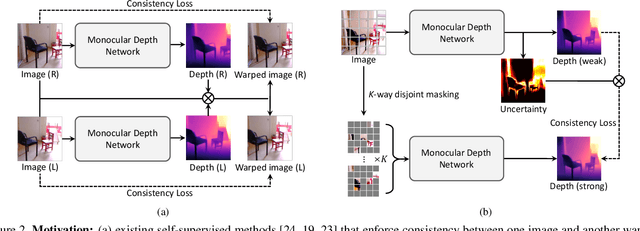
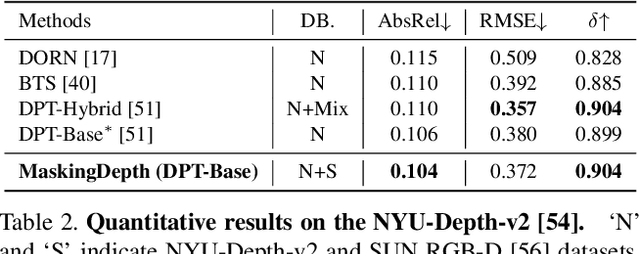
Abstract:Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) has recently accomplished successful achievements in various fields such as image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation, which typically require a lot of labour to construct ground-truth. Especially in the depth estimation task, annotating training data is very costly and time-consuming, and thus recent SSL regime seems an attractive solution. In this paper, for the first time, we introduce a novel framework for semi-supervised learning of monocular depth estimation networks, using consistency regularization to mitigate the reliance on large ground-truth depth data. We propose a novel data augmentation approach, called K-way disjoint masking, which allows the network for learning how to reconstruct invisible regions so that the model not only becomes robust to perturbations but also generates globally consistent output depth maps. Experiments on the KITTI and NYU-Depth-v2 datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of each component in our pipeline, robustness to the use of fewer and fewer annotated images, and superior results compared to other state-of-the-art, semi-supervised methods for monocular depth estimation. Our code is available at https://github.com/KU-CVLAB/MaskingDepth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge