Jiahui Huang
VideoMaMa: Mask-Guided Video Matting via Generative Prior
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Generalizing video matting models to real-world videos remains a significant challenge due to the scarcity of labeled data. To address this, we present Video Mask-to-Matte Model (VideoMaMa) that converts coarse segmentation masks into pixel accurate alpha mattes, by leveraging pretrained video diffusion models. VideoMaMa demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization to real-world footage, even though it is trained solely on synthetic data. Building on this capability, we develop a scalable pseudo-labeling pipeline for large-scale video matting and construct the Matting Anything in Video (MA-V) dataset, which offers high-quality matting annotations for more than 50K real-world videos spanning diverse scenes and motions. To validate the effectiveness of this dataset, we fine-tune the SAM2 model on MA-V to obtain SAM2-Matte, which outperforms the same model trained on existing matting datasets in terms of robustness on in-the-wild videos. These findings emphasize the importance of large-scale pseudo-labeled video matting and showcase how generative priors and accessible segmentation cues can drive scalable progress in video matting research.
TimeGMM: Single-Pass Probabilistic Forecasting via Adaptive Gaussian Mixture Models with Reversible Normalization
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Probabilistic time series forecasting is crucial for quantifying future uncertainty, with significant applications in fields such as energy and finance. However, existing methods often rely on computationally expensive sampling or restrictive parametric assumptions to characterize future distributions, which limits predictive performance and introduces distributional mismatch. To address these challenges, this paper presents TimeGMM, a novel probabilistic forecasting framework based on Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) that captures complex future distributions in a single forward pass. A key component is GMM-adapted Reversible Instance Normalization (GRIN), a novel module designed to dynamically adapt to temporal-probabilistic distribution shifts. The framework integrates a dedicated Temporal Encoder (TE-Module) with a Conditional Temporal-Probabilistic Decoder (CTPD-Module) to jointly capture temporal dependencies and mixture distribution parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TimeGMM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving maximum improvements of 22.48\% in CRPS and 21.23\% in NMAE.
NeuralSSD: A Neural Solver for Signed Distance Surface Reconstruction
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We proposed a generalized method, NeuralSSD, for reconstructing a 3D implicit surface from the widely-available point cloud data. NeuralSSD is a solver-based on the neural Galerkin method, aimed at reconstructing higher-quality and accurate surfaces from input point clouds. Implicit method is preferred due to its ability to accurately represent shapes and its robustness in handling topological changes. However, existing parameterizations of implicit fields lack explicit mechanisms to ensure a tight fit between the surface and input data. To address this, we propose a novel energy equation that balances the reliability of point cloud information. Additionally, we introduce a new convolutional network that learns three-dimensional information to achieve superior optimization results. This approach ensures that the reconstructed surface closely adheres to the raw input points and infers valuable inductive biases from point clouds, resulting in a highly accurate and stable surface reconstruction. NeuralSSD is evaluated on a variety of challenging datasets, including the ShapeNet and Matterport datasets, and achieves state-of-the-art results in terms of both surface reconstruction accuracy and generalizability.
Learning to Track Any Points from Human Motion
Jul 08, 2025



Abstract:Human motion, with its inherent complexities, such as non-rigid deformations, articulated movements, clothing distortions, and frequent occlusions caused by limbs or other individuals, provides a rich and challenging source of supervision that is crucial for training robust and generalizable point trackers. Despite the suitability of human motion, acquiring extensive training data for point tracking remains difficult due to laborious manual annotation. Our proposed pipeline, AnthroTAP, addresses this by proposing an automated pipeline to generate pseudo-labeled training data, leveraging the Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) model. We first fit the SMPL model to detected humans in video frames, project the resulting 3D mesh vertices onto 2D image planes to generate pseudo-trajectories, handle occlusions using ray-casting, and filter out unreliable tracks based on optical flow consistency. A point tracking model trained on AnthroTAP annotated dataset achieves state-of-the-art performance on the TAP-Vid benchmark, surpassing other models trained on real videos while using 10,000 times less data and only 1 day in 4 GPUs, compared to 256 GPUs used in recent state-of-the-art.
FRAME: Pre-Training Video Feature Representations via Anticipation and Memory
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Dense video prediction tasks, such as object tracking and semantic segmentation, require video encoders that generate temporally consistent, spatially dense features for every frame. However, existing approaches fall short: image encoders like DINO or CLIP lack temporal awareness, while video models such as VideoMAE underperform compared to image encoders on dense prediction tasks. We address this gap with FRAME, a self-supervised video frame encoder tailored for dense video understanding. FRAME learns to predict current and future DINO patch features from past and present RGB frames, leading to spatially precise and temporally coherent representations. To our knowledge, FRAME is the first video encoder to leverage image-based models for dense prediction while outperforming them on tasks requiring fine-grained visual correspondence. As an auxiliary capability, FRAME aligns its class token with CLIP's semantic space, supporting language-driven tasks such as video classification. We evaluate FRAME across six dense prediction tasks on seven datasets, where it consistently outperforms image encoders and existing self-supervised video models. Despite its versatility, FRAME maintains a compact architecture suitable for a range of downstream applications.
Seurat: From Moving Points to Depth
Apr 20, 2025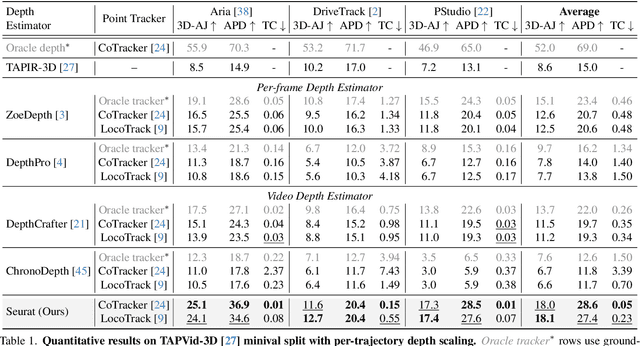
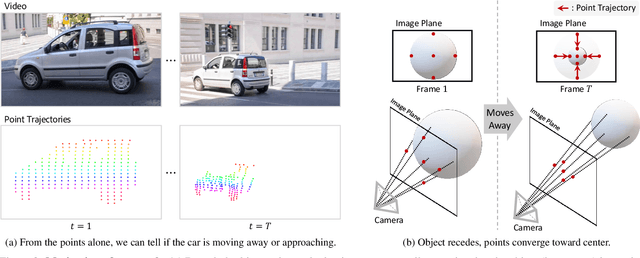
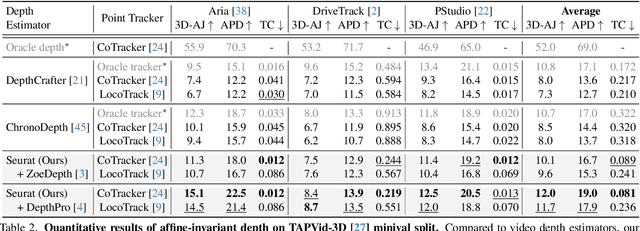
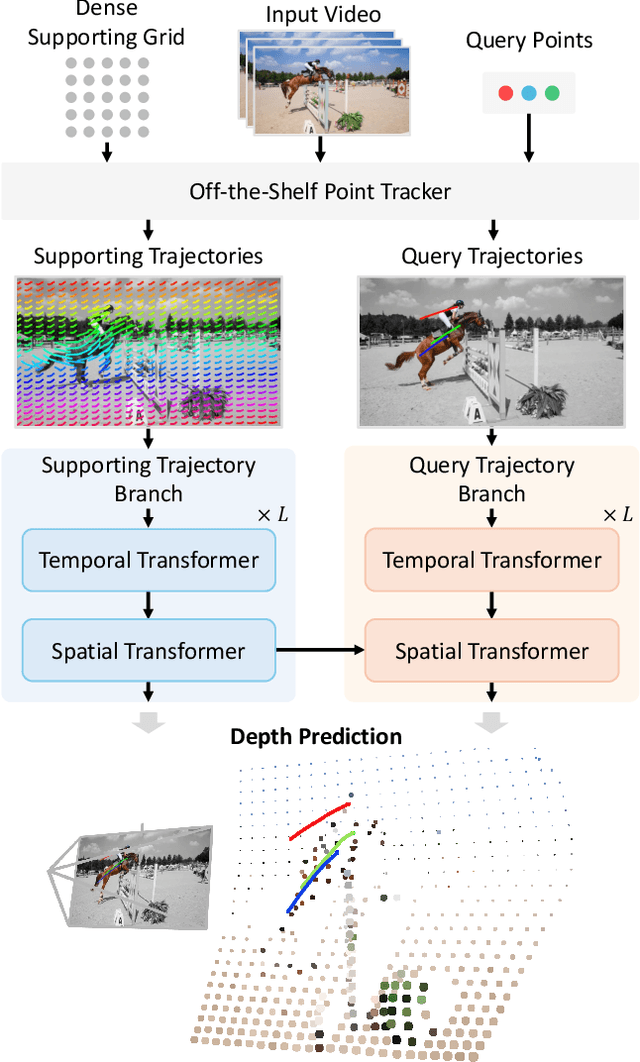
Abstract:Accurate depth estimation from monocular videos remains challenging due to ambiguities inherent in single-view geometry, as crucial depth cues like stereopsis are absent. However, humans often perceive relative depth intuitively by observing variations in the size and spacing of objects as they move. Inspired by this, we propose a novel method that infers relative depth by examining the spatial relationships and temporal evolution of a set of tracked 2D trajectories. Specifically, we use off-the-shelf point tracking models to capture 2D trajectories. Then, our approach employs spatial and temporal transformers to process these trajectories and directly infer depth changes over time. Evaluated on the TAPVid-3D benchmark, our method demonstrates robust zero-shot performance, generalizing effectively from synthetic to real-world datasets. Results indicate that our approach achieves temporally smooth, high-accuracy depth predictions across diverse domains.
VideoPanda: Video Panoramic Diffusion with Multi-view Attention
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:High resolution panoramic video content is paramount for immersive experiences in Virtual Reality, but is non-trivial to collect as it requires specialized equipment and intricate camera setups. In this work, we introduce VideoPanda, a novel approach for synthesizing 360$^\circ$ videos conditioned on text or single-view video data. VideoPanda leverages multi-view attention layers to augment a video diffusion model, enabling it to generate consistent multi-view videos that can be combined into immersive panoramic content. VideoPanda is trained jointly using two conditions: text-only and single-view video, and supports autoregressive generation of long-videos. To overcome the computational burden of multi-view video generation, we randomly subsample the duration and camera views used during training and show that the model is able to gracefully generalize to generating more frames during inference. Extensive evaluations on both real-world and synthetic video datasets demonstrate that VideoPanda generates more realistic and coherent 360$^\circ$ panoramas across all input conditions compared to existing methods. Visit the project website at https://research-staging.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/VideoPanda/ for results.
GEN3C: 3D-Informed World-Consistent Video Generation with Precise Camera Control
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:We present GEN3C, a generative video model with precise Camera Control and temporal 3D Consistency. Prior video models already generate realistic videos, but they tend to leverage little 3D information, leading to inconsistencies, such as objects popping in and out of existence. Camera control, if implemented at all, is imprecise, because camera parameters are mere inputs to the neural network which must then infer how the video depends on the camera. In contrast, GEN3C is guided by a 3D cache: point clouds obtained by predicting the pixel-wise depth of seed images or previously generated frames. When generating the next frames, GEN3C is conditioned on the 2D renderings of the 3D cache with the new camera trajectory provided by the user. Crucially, this means that GEN3C neither has to remember what it previously generated nor does it have to infer the image structure from the camera pose. The model, instead, can focus all its generative power on previously unobserved regions, as well as advancing the scene state to the next frame. Our results demonstrate more precise camera control than prior work, as well as state-of-the-art results in sparse-view novel view synthesis, even in challenging settings such as driving scenes and monocular dynamic video. Results are best viewed in videos. Check out our webpage! https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/GEN3C/
MotionCanvas: Cinematic Shot Design with Controllable Image-to-Video Generation
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a method that allows users to design cinematic video shots in the context of image-to-video generation. Shot design, a critical aspect of filmmaking, involves meticulously planning both camera movements and object motions in a scene. However, enabling intuitive shot design in modern image-to-video generation systems presents two main challenges: first, effectively capturing user intentions on the motion design, where both camera movements and scene-space object motions must be specified jointly; and second, representing motion information that can be effectively utilized by a video diffusion model to synthesize the image animations. To address these challenges, we introduce MotionCanvas, a method that integrates user-driven controls into image-to-video (I2V) generation models, allowing users to control both object and camera motions in a scene-aware manner. By connecting insights from classical computer graphics and contemporary video generation techniques, we demonstrate the ability to achieve 3D-aware motion control in I2V synthesis without requiring costly 3D-related training data. MotionCanvas enables users to intuitively depict scene-space motion intentions, and translates them into spatiotemporal motion-conditioning signals for video diffusion models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on a wide range of real-world image content and shot-design scenarios, highlighting its potential to enhance the creative workflows in digital content creation and adapt to various image and video editing applications.
Exploring Temporally-Aware Features for Point Tracking
Jan 21, 2025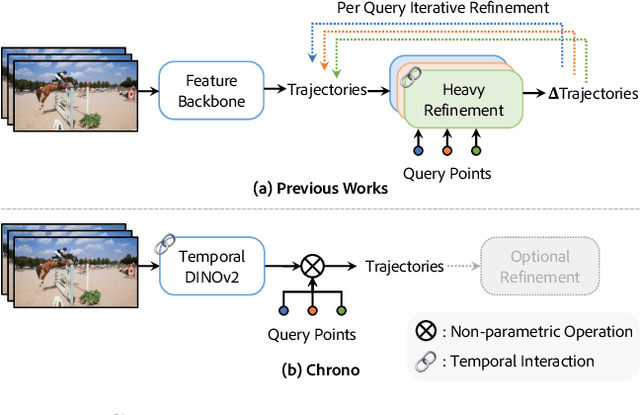
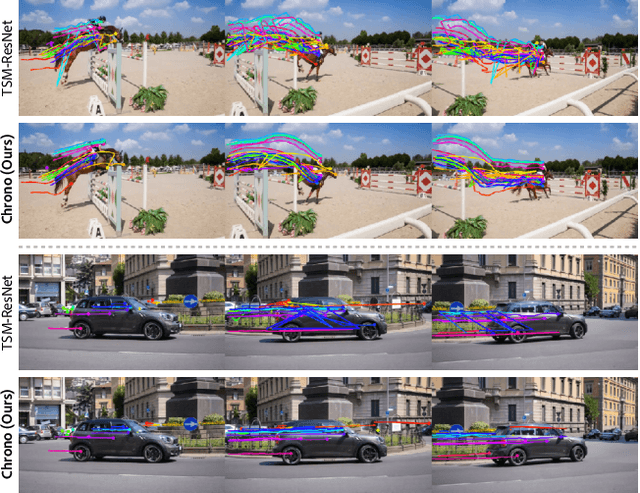
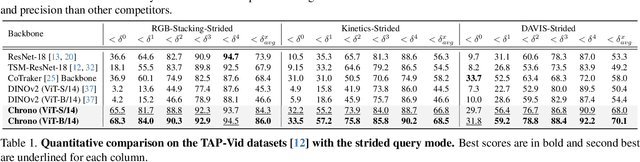

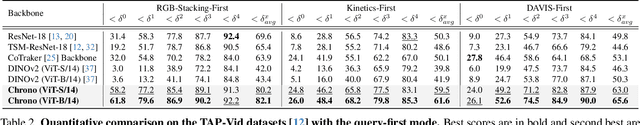
Abstract:Point tracking in videos is a fundamental task with applications in robotics, video editing, and more. While many vision tasks benefit from pre-trained feature backbones to improve generalizability, point tracking has primarily relied on simpler backbones trained from scratch on synthetic data, which may limit robustness in real-world scenarios. Additionally, point tracking requires temporal awareness to ensure coherence across frames, but using temporally-aware features is still underexplored. Most current methods often employ a two-stage process: an initial coarse prediction followed by a refinement stage to inject temporal information and correct errors from the coarse stage. These approach, however, is computationally expensive and potentially redundant if the feature backbone itself captures sufficient temporal information. In this work, we introduce Chrono, a feature backbone specifically designed for point tracking with built-in temporal awareness. Leveraging pre-trained representations from self-supervised learner DINOv2 and enhanced with a temporal adapter, Chrono effectively captures long-term temporal context, enabling precise prediction even without the refinement stage. Experimental results demonstrate that Chrono achieves state-of-the-art performance in a refiner-free setting on the TAP-Vid-DAVIS and TAP-Vid-Kinetics datasets, among common feature backbones used in point tracking as well as DINOv2, with exceptional efficiency. Project page: https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/Chrono/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge