Yogesh Balaji
DuoGen: Towards General Purpose Interleaved Multimodal Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Interleaved multimodal generation enables capabilities beyond unimodal generation models, such as step-by-step instructional guides, visual planning, and generating visual drafts for reasoning. However, the quality of existing interleaved generation models under general instructions remains limited by insufficient training data and base model capacity. We present DuoGen, a general-purpose interleaved generation framework that systematically addresses data curation, architecture design, and evaluation. On the data side, we build a large-scale, high-quality instruction-tuning dataset by combining multimodal conversations rewritten from curated raw websites, and diverse synthetic examples covering everyday scenarios. Architecturally, DuoGen leverages the strong visual understanding of a pretrained multimodal LLM and the visual generation capabilities of a diffusion transformer (DiT) pretrained on video generation, avoiding costly unimodal pretraining and enabling flexible base model selection. A two-stage decoupled strategy first instruction-tunes the MLLM, then aligns DiT with it using curated interleaved image-text sequences. Across public and newly proposed benchmarks, DuoGen outperforms prior open-source models in text quality, image fidelity, and image-context alignment, and also achieves state-of-the-art performance on text-to-image and image editing among unified generation models. Data and code will be released at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/duogen/.
InfoTok: Adaptive Discrete Video Tokenizer via Information-Theoretic Compression
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate and efficient discrete video tokenization is essential for long video sequences processing. Yet, the inherent complexity and variable information density of videos present a significant bottleneck for current tokenizers, which rigidly compress all content at a fixed rate, leading to redundancy or information loss. Drawing inspiration from Shannon's information theory, this paper introduces InfoTok, a principled framework for adaptive video tokenization. We rigorously prove that existing data-agnostic training methods are suboptimal in representation length, and present a novel evidence lower bound (ELBO)-based algorithm that approaches theoretical optimality. Leveraging this framework, we develop a transformer-based adaptive compressor that enables adaptive tokenization. Empirical results demonstrate state-of-the-art compression performance, saving 20% tokens without influence on performance, and achieving 2.3x compression rates while still outperforming prior heuristic adaptive approaches. By allocating tokens according to informational richness, InfoTok enables a more compressed yet accurate tokenization for video representation, offering valuable insights for future research.
A Comprehensive Study of Decoder-Only LLMs for Text-to-Image Generation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Both text-to-image generation and large language models (LLMs) have made significant advancements. However, many text-to-image models still employ the somewhat outdated T5 and CLIP as their text encoders. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of using modern decoder-only LLMs as text encoders for text-to-image diffusion models. We build a standardized training and evaluation pipeline that allows us to isolate and evaluate the effect of different text embeddings. We train a total of 27 text-to-image models with 12 different text encoders to analyze the critical aspects of LLMs that could impact text-to-image generation, including the approaches to extract embeddings, different LLMs variants, and model sizes. Our experiments reveal that the de facto way of using last-layer embeddings as conditioning leads to inferior performance. Instead, we explore embeddings from various layers and find that using layer-normalized averaging across all layers significantly improves alignment with complex prompts. Most LLMs with this conditioning outperform the baseline T5 model, showing enhanced performance in advanced visio-linguistic reasoning skills.
Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform for Physical AI
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Physical AI needs to be trained digitally first. It needs a digital twin of itself, the policy model, and a digital twin of the world, the world model. In this paper, we present the Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform to help developers build customized world models for their Physical AI setups. We position a world foundation model as a general-purpose world model that can be fine-tuned into customized world models for downstream applications. Our platform covers a video curation pipeline, pre-trained world foundation models, examples of post-training of pre-trained world foundation models, and video tokenizers. To help Physical AI builders solve the most critical problems of our society, we make our platform open-source and our models open-weight with permissive licenses available via https://github.com/NVIDIA/Cosmos.
Edify Image: High-Quality Image Generation with Pixel Space Laplacian Diffusion Models
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:We introduce Edify Image, a family of diffusion models capable of generating photorealistic image content with pixel-perfect accuracy. Edify Image utilizes cascaded pixel-space diffusion models trained using a novel Laplacian diffusion process, in which image signals at different frequency bands are attenuated at varying rates. Edify Image supports a wide range of applications, including text-to-image synthesis, 4K upsampling, ControlNets, 360 HDR panorama generation, and finetuning for image customization.
One-Step Diffusion Policy: Fast Visuomotor Policies via Diffusion Distillation
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models, praised for their success in generative tasks, are increasingly being applied to robotics, demonstrating exceptional performance in behavior cloning. However, their slow generation process stemming from iterative denoising steps poses a challenge for real-time applications in resource-constrained robotics setups and dynamically changing environments. In this paper, we introduce the One-Step Diffusion Policy (OneDP), a novel approach that distills knowledge from pre-trained diffusion policies into a single-step action generator, significantly accelerating response times for robotic control tasks. We ensure the distilled generator closely aligns with the original policy distribution by minimizing the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence along the diffusion chain, requiring only $2\%$-$10\%$ additional pre-training cost for convergence. We evaluated OneDP on 6 challenging simulation tasks as well as 4 self-designed real-world tasks using the Franka robot. The results demonstrate that OneDP not only achieves state-of-the-art success rates but also delivers an order-of-magnitude improvement in inference speed, boosting action prediction frequency from 1.5 Hz to 62 Hz, establishing its potential for dynamic and computationally constrained robotic applications. We share the project page at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/onedp/.
JeDi: Joint-Image Diffusion Models for Finetuning-Free Personalized Text-to-Image Generation
Jul 08, 2024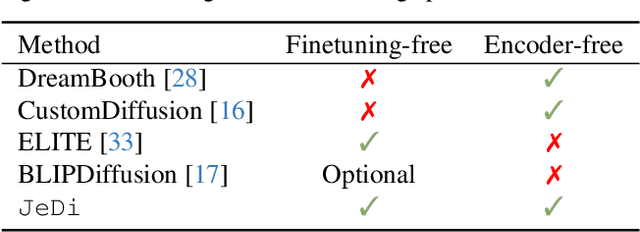
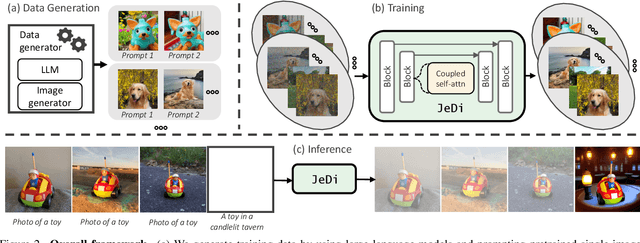
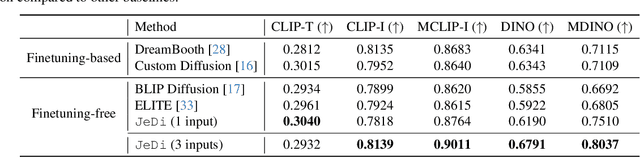
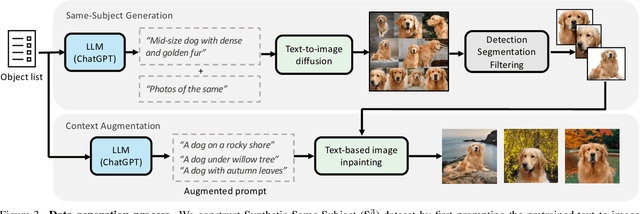
Abstract:Personalized text-to-image generation models enable users to create images that depict their individual possessions in diverse scenes, finding applications in various domains. To achieve the personalization capability, existing methods rely on finetuning a text-to-image foundation model on a user's custom dataset, which can be non-trivial for general users, resource-intensive, and time-consuming. Despite attempts to develop finetuning-free methods, their generation quality is much lower compared to their finetuning counterparts. In this paper, we propose Joint-Image Diffusion (\jedi), an effective technique for learning a finetuning-free personalization model. Our key idea is to learn the joint distribution of multiple related text-image pairs that share a common subject. To facilitate learning, we propose a scalable synthetic dataset generation technique. Once trained, our model enables fast and easy personalization at test time by simply using reference images as input during the sampling process. Our approach does not require any expensive optimization process or additional modules and can faithfully preserve the identity represented by any number of reference images. Experimental results show that our model achieves state-of-the-art generation quality, both quantitatively and qualitatively, significantly outperforming both the prior finetuning-based and finetuning-free personalization baselines.
Preserve Your Own Correlation: A Noise Prior for Video Diffusion Models
May 17, 2023Abstract:Despite tremendous progress in generating high-quality images using diffusion models, synthesizing a sequence of animated frames that are both photorealistic and temporally coherent is still in its infancy. While off-the-shelf billion-scale datasets for image generation are available, collecting similar video data of the same scale is still challenging. Also, training a video diffusion model is computationally much more expensive than its image counterpart. In this work, we explore finetuning a pretrained image diffusion model with video data as a practical solution for the video synthesis task. We find that naively extending the image noise prior to video noise prior in video diffusion leads to sub-optimal performance. Our carefully designed video noise prior leads to substantially better performance. Extensive experimental validation shows that our model, Preserve Your Own Correlation (PYoCo), attains SOTA zero-shot text-to-video results on the UCF-101 and MSR-VTT benchmarks. It also achieves SOTA video generation quality on the small-scale UCF-101 benchmark with a $10\times$ smaller model using significantly less computation than the prior art.
eDiff-I: Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with an Ensemble of Expert Denoisers
Nov 17, 2022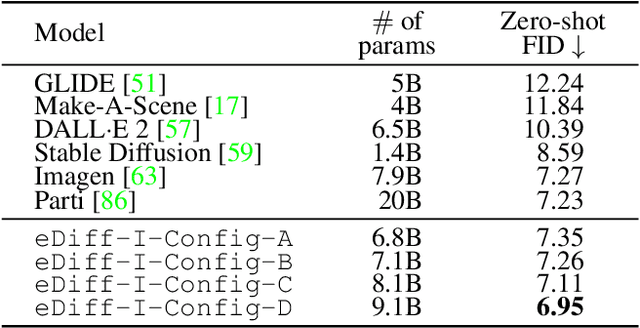


Abstract:Large-scale diffusion-based generative models have led to breakthroughs in text-conditioned high-resolution image synthesis. Starting from random noise, such text-to-image diffusion models gradually synthesize images in an iterative fashion while conditioning on text prompts. We find that their synthesis behavior qualitatively changes throughout this process: Early in sampling, generation strongly relies on the text prompt to generate text-aligned content, while later, the text conditioning is almost entirely ignored. This suggests that sharing model parameters throughout the entire generation process may not be ideal. Therefore, in contrast to existing works, we propose to train an ensemble of text-to-image diffusion models specialized for different synthesis stages. To maintain training efficiency, we initially train a single model, which is then split into specialized models that are trained for the specific stages of the iterative generation process. Our ensemble of diffusion models, called eDiff-I, results in improved text alignment while maintaining the same inference computation cost and preserving high visual quality, outperforming previous large-scale text-to-image diffusion models on the standard benchmark. In addition, we train our model to exploit a variety of embeddings for conditioning, including the T5 text, CLIP text, and CLIP image embeddings. We show that these different embeddings lead to different behaviors. Notably, the CLIP image embedding allows an intuitive way of transferring the style of a reference image to the target text-to-image output. Lastly, we show a technique that enables eDiff-I's "paint-with-words" capability. A user can select the word in the input text and paint it in a canvas to control the output, which is very handy for crafting the desired image in mind. The project page is available at https://deepimagination.cc/eDiff-I/
A Comprehensive Study of Image Classification Model Sensitivity to Foregrounds, Backgrounds, and Visual Attributes
Jan 26, 2022
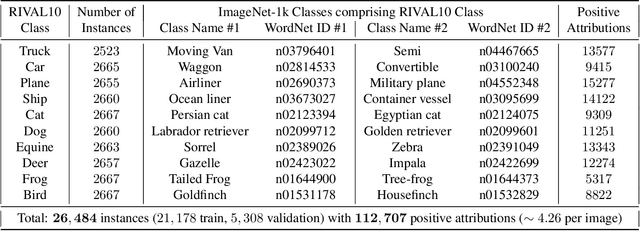
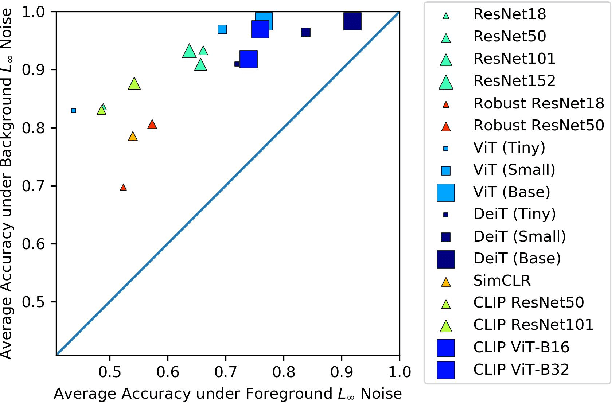

Abstract:While datasets with single-label supervision have propelled rapid advances in image classification, additional annotations are necessary in order to quantitatively assess how models make predictions. To this end, for a subset of ImageNet samples, we collect segmentation masks for the entire object and $18$ informative attributes. We call this dataset RIVAL10 (RIch Visual Attributes with Localization), consisting of roughly $26k$ instances over $10$ classes. Using RIVAL10, we evaluate the sensitivity of a broad set of models to noise corruptions in foregrounds, backgrounds and attributes. In our analysis, we consider diverse state-of-the-art architectures (ResNets, Transformers) and training procedures (CLIP, SimCLR, DeiT, Adversarial Training). We find that, somewhat surprisingly, in ResNets, adversarial training makes models more sensitive to the background compared to foreground than standard training. Similarly, contrastively-trained models also have lower relative foreground sensitivity in both transformers and ResNets. Lastly, we observe intriguing adaptive abilities of transformers to increase relative foreground sensitivity as corruption level increases. Using saliency methods, we automatically discover spurious features that drive the background sensitivity of models and assess alignment of saliency maps with foregrounds. Finally, we quantitatively study the attribution problem for neural features by comparing feature saliency with ground-truth localization of semantic attributes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge