Lu Ling
I-Scene: 3D Instance Models are Implicit Generalizable Spatial Learners
Dec 15, 2025



Abstract:Generalization remains the central challenge for interactive 3D scene generation. Existing learning-based approaches ground spatial understanding in limited scene dataset, restricting generalization to new layouts. We instead reprogram a pre-trained 3D instance generator to act as a scene level learner, replacing dataset-bounded supervision with model-centric spatial supervision. This reprogramming unlocks the generator transferable spatial knowledge, enabling generalization to unseen layouts and novel object compositions. Remarkably, spatial reasoning still emerges even when the training scenes are randomly composed objects. This demonstrates that the generator's transferable scene prior provides a rich learning signal for inferring proximity, support, and symmetry from purely geometric cues. Replacing widely used canonical space, we instantiate this insight with a view-centric formulation of the scene space, yielding a fully feed-forward, generalizable scene generator that learns spatial relations directly from the instance model. Quantitative and qualitative results show that a 3D instance generator is an implicit spatial learner and reasoner, pointing toward foundation models for interactive 3D scene understanding and generation. Project page: https://luling06.github.io/I-Scene-project/
Scenethesis: A Language and Vision Agentic Framework for 3D Scene Generation
May 05, 2025Abstract:Synthesizing interactive 3D scenes from text is essential for gaming, virtual reality, and embodied AI. However, existing methods face several challenges. Learning-based approaches depend on small-scale indoor datasets, limiting the scene diversity and layout complexity. While large language models (LLMs) can leverage diverse text-domain knowledge, they struggle with spatial realism, often producing unnatural object placements that fail to respect common sense. Our key insight is that vision perception can bridge this gap by providing realistic spatial guidance that LLMs lack. To this end, we introduce Scenethesis, a training-free agentic framework that integrates LLM-based scene planning with vision-guided layout refinement. Given a text prompt, Scenethesis first employs an LLM to draft a coarse layout. A vision module then refines it by generating an image guidance and extracting scene structure to capture inter-object relations. Next, an optimization module iteratively enforces accurate pose alignment and physical plausibility, preventing artifacts like object penetration and instability. Finally, a judge module verifies spatial coherence. Comprehensive experiments show that Scenethesis generates diverse, realistic, and physically plausible 3D interactive scenes, making it valuable for virtual content creation, simulation environments, and embodied AI research.
DL3DV-10K: A Large-Scale Scene Dataset for Deep Learning-based 3D Vision
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:We have witnessed significant progress in deep learning-based 3D vision, ranging from neural radiance field (NeRF) based 3D representation learning to applications in novel view synthesis (NVS). However, existing scene-level datasets for deep learning-based 3D vision, limited to either synthetic environments or a narrow selection of real-world scenes, are quite insufficient. This insufficiency not only hinders a comprehensive benchmark of existing methods but also caps what could be explored in deep learning-based 3D analysis. To address this critical gap, we present DL3DV-10K, a large-scale scene dataset, featuring 51.2 million frames from 10,510 videos captured from 65 types of point-of-interest (POI) locations, covering both bounded and unbounded scenes, with different levels of reflection, transparency, and lighting. We conducted a comprehensive benchmark of recent NVS methods on DL3DV-10K, which revealed valuable insights for future research in NVS. In addition, we have obtained encouraging results in a pilot study to learn generalizable NeRF from DL3DV-10K, which manifests the necessity of a large-scale scene-level dataset to forge a path toward a foundation model for learning 3D representation. Our DL3DV-10K dataset, benchmark results, and models will be publicly accessible at https://dl3dv-10k.github.io/DL3DV-10K/.
Cooperating Graph Neural Networks with Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vaccine Prioritization
May 09, 2023



Abstract:This study explores the vaccine prioritization strategy to reduce the overall burden of the pandemic when the supply is limited. Existing methods conduct macro-level or simplified micro-level vaccine distribution by assuming the homogeneous behavior within subgroup populations and lacking mobility dynamics integration. Directly applying these models for micro-level vaccine allocation leads to sub-optimal solutions due to the lack of behavioral-related details. To address the issue, we first incorporate the mobility heterogeneity in disease dynamics modeling and mimic the disease evolution process using a Trans-vaccine-SEIR model. Then we develop a novel deep reinforcement learning to seek the optimal vaccine allocation strategy for the high-degree spatial-temporal disease evolution system. The graph neural network is used to effectively capture the structural properties of the mobility contact network and extract the dynamic disease features. In our evaluation, the proposed framework reduces 7% - 10% of infections and deaths than the baseline strategies. Extensive evaluation shows that the proposed framework is robust to seek the optimal vaccine allocation with diverse mobility patterns in the micro-level disease evolution system. In particular, we find the optimal vaccine allocation strategy in the transit usage restriction scenario is significantly more effective than restricting cross-zone mobility for the top 10% age-based and income-based zones. These results provide valuable insights for areas with limited vaccines and low logistic efficacy.
PixHt-Lab: Pixel Height Based Light Effect Generation for Image Compositing
Feb 28, 2023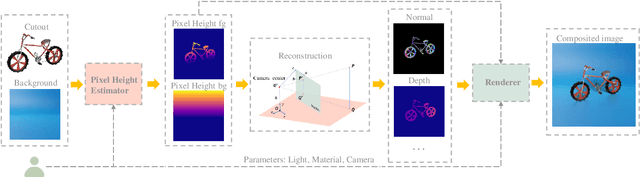
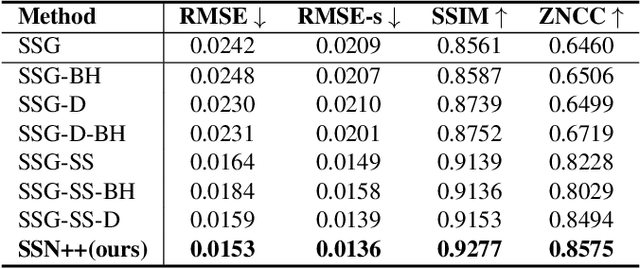

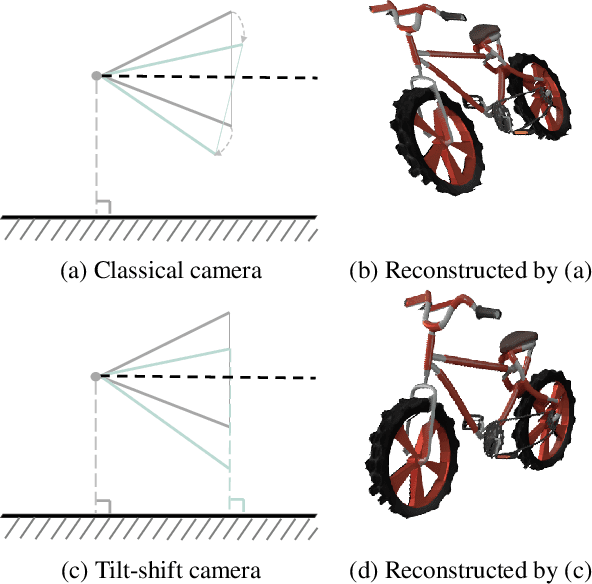
Abstract:Lighting effects such as shadows or reflections are key in making synthetic images realistic and visually appealing. To generate such effects, traditional computer graphics uses a physically-based renderer along with 3D geometry. To compensate for the lack of geometry in 2D Image compositing, recent deep learning-based approaches introduced a pixel height representation to generate soft shadows and reflections. However, the lack of geometry limits the quality of the generated soft shadows and constrain reflections to pure specular ones. We introduce PixHt-Lab, a system leveraging an explicit mapping from pixel height representation to 3D space. Using this mapping, PixHt-Lab reconstructs both the cutout and background geometry and renders realistic, diverse, lighting effects for image compositing. Given a surface with physically-based materials, we can render reflections with varying glossiness. To generate more realistic soft shadows, we further propose to use 3D-aware buffer channels to guide a neural renderer. Both quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that PixHt-Lab significantly improves soft shadow generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge