Anshumali Shrivastava
Rice University
Scout Before You Attend: Sketch-and-Walk Sparse Attention for Efficient LLM Inference
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Self-attention dominates the computational and memory cost of long-context LLM inference across both prefill and decode phases. To address this challenge, we introduce Sketch&Walk Attention, a training-free sparse attention method that determines sparsity with lightweight sketches and deterministic walk. Sketch&Walk applies Hadamard sketching to get inexpensive approximations of attention scores, then aggregates these estimates across layers via a walk mechanism that captures attention influence beyond direct interactions between tokens. The accumulated walk scores are used to select top-k attention blocks, enabling dynamic sparsity with a single training-free algorithm that applies uniformly to both the prefill and decode phases, together with custom sparse attention kernels. Across a wide range of models and tasks, Sketch&Walk maintains near-lossless accuracy at 20% attention density and can slightly outperform dense attention in some settings, while achieving up to 6x inference speedup.
SOCKET: SOft Collison Kernel EsTimator for Sparse Attention
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Exploiting sparsity during long-context inference is central to scaling large language models, as attention dominates the cost of autoregressive decoding. Sparse attention reduces this cost by restricting computation to a subset of tokens, but its effectiveness depends critically on efficient scoring and selection of relevant tokens at inference time. We revisit Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) as a sparsification primitive and introduce SOCKET, a SOft Collision Kernel EsTimator that replaces hard bucket matches with probabilistic, similarity-aware aggregation. Our key insight is that hard LSH produces discrete collision signals and is therefore poorly suited for ranking. In contrast, soft LSH aggregates graded collision evidence across hash tables, preserving the stability of relative ordering among the true top-$k$ tokens. This transformation elevates LSH from a candidate-generation heuristic to a principled and mathematically grounded scoring kernel for sparse attention. Leveraging this property, SOCKET enables efficient token selection without ad-hoc voting mechanism, and matches or surpasses established sparse attention baselines across multiple long-context benchmarks using diverse set of models. With a custom CUDA kernel for scoring keys and a Flash Decode Triton backend for sparse attention, SOCKET achieves up to 1.5$\times$ higher throughput than FlashAttention, making it an effective tool for long-context inference. Code is open-sourced at https://github.com/amarka8/SOCKET.
70% Size, 100% Accuracy: Lossless LLM Compression for Efficient GPU Inference via Dynamic-Length Float
Apr 15, 2025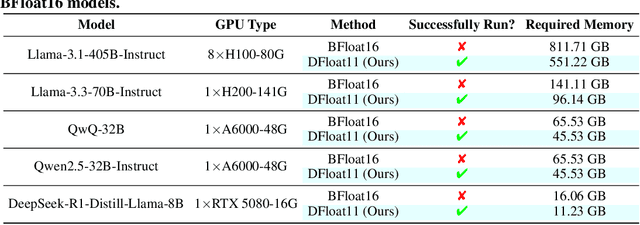
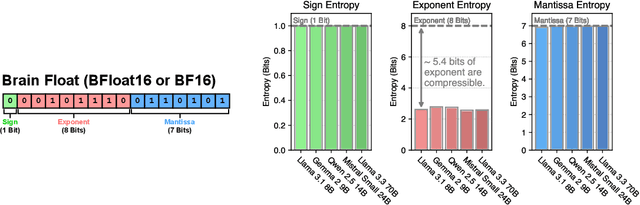
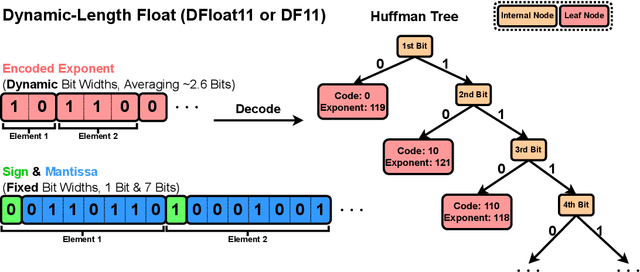
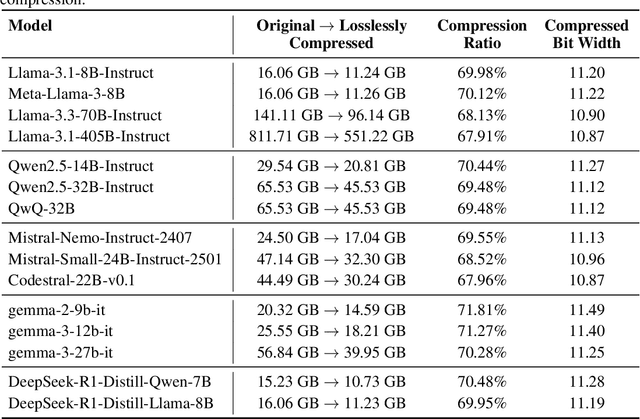
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have grown rapidly in size, creating significant challenges for efficient deployment on resource-constrained hardware. In this paper, we introduce Dynamic-Length Float (DFloat11), a lossless compression framework that reduces LLM size by 30% while preserving outputs that are bit-for-bit identical to the original model. DFloat11 is motivated by the low entropy in the BFloat16 weight representation of LLMs, which reveals significant inefficiency in existing storage format. By applying entropy coding, DFloat11 assigns dynamic-length encodings to weights based on frequency, achieving near information-optimal compression without any loss of precision. To facilitate efficient inference with dynamic-length encodings, we develop a custom GPU kernel for fast online decompression. Our design incorporates the following: (i) decomposition of memory-intensive lookup tables (LUTs) into compact LUTs that fit in GPU SRAM, (ii) a two-phase kernel for coordinating thread read/write positions using lightweight auxiliary variables, and (iii) transformer-block-level decompression to minimize latency. Experiments on recent models, including Llama-3.1, Qwen-2.5, and Gemma-3, validates our hypothesis that DFloat11 achieves around 30% model size reduction while preserving bit-for-bit exact outputs. Compared to a potential alternative of offloading parts of an uncompressed model to the CPU to meet memory constraints, DFloat11 achieves 1.9-38.8x higher throughput in token generation. With a fixed GPU memory budget, DFloat11 enables 5.3-13.17x longer context lengths than uncompressed models. Notably, our method enables lossless inference of Llama-3.1-405B, an 810GB model, on a single node equipped with 8x80GB GPUs. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/LeanModels/DFloat11.
I3S: Importance Sampling Subspace Selection for Low-Rank Optimization in LLM Pretraining
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Low-rank optimization has emerged as a promising approach to enabling memory-efficient training of large language models (LLMs). Existing low-rank optimization methods typically project gradients onto a low-rank subspace, reducing the memory cost of storing optimizer states. A key challenge in these methods is identifying suitable subspaces to ensure an effective optimization trajectory. Most existing approaches select the dominant subspace to preserve gradient information, as this intuitively provides the best approximation. However, we find that in practice, the dominant subspace stops changing during pretraining, thereby constraining weight updates to similar subspaces. In this paper, we propose importance sampling subspace selection (I3S) for low-rank optimization, which theoretically offers a comparable convergence rate to the dominant subspace approach. Empirically, we demonstrate that I3S significantly outperforms previous methods in LLM pretraining tasks.
SpaLLM: Unified Compressive Adaptation of Large Language Models with Sketching
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Compressive adaptation approaches, such as QLoRA, are widely popular alternatives for reducing memory requirements during fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) while producing models capable of handling various downstream tasks. The key idea is to employ a "two-tower" architecture: compressing pre-trained LLM parameters into compact representations and fine-tuning the additive full-precision adapter, which typically has few tunable parameters in low-rank format. However, the strict algebraic assumptions, such as low-rank assumption, and the complexity of composing two-tower architectures are some of the known shortcomings, resulting in a poor accuracy-efficiency trade-off. In response to these known limitations, we propose SpaLLM (Sketched Parameter Adaptation of LLMs), a novel compressive adaptation approach for LLMs. This method is also the first to illustrate parameter-sharing compression methods for LLM fine-tuning, which, unlike QLoRA, are free from strict low-rank algebraic assumptions on adapters. Furthermore, our proposal unifies model compression and adaptation into a single, streamlined process, eliminating the need for two-tower architectures. SpaLLM sketches pre-trained LLM weights into lookup tables and directly fine-tunes the values in these tables. This approach simplifies LLMs' compressive adaptation workflow, potentially improves multi-user serving efficiency, and delivers significantly better accuracy for both natural language understanding and generation tasks. Moreover, by avoiding the "two-tower" architecture, our framework only requires one compressed matrix multiplication per layer during inference, demonstrating superior inference efficiency compared to previous methods.
LeanQuant: Accurate Large Language Model Quantization with Loss-Error-Aware Grid
Jul 14, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have numerous applications across various domains, but their high computational and memory demands pose significant deployment challenges. Weight quantization is an effective technique for reducing the decoding latency and memory requirements of LLMs. Existing approaches primarily aim to maintain the quality of quantized models by preserving outliers in input features, but they still suffer significant quality loss at lower bit widths. Our approach builds on Optimal Brain Quantization (OBQ), an iterative weight-update-based quantization framework. We identify a key limitation of OBQ, specifically that its uniform quantization grid is suboptimal for maintaining model quality, as it introduces large errors to the task loss. To address this, we propose LeanQuant, which learns a loss-error-aware quantization grid by leveraging the inverse diagonal Hessian. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that LeanQuant is both efficient and accurate; it can quantize a 70-billion-parameter model in 6 hours using a single 32GB GPU and performs favorably compared to competitive baselines in the 4-bit, 3-bit, and 2-bit regions.
IDentity with Locality: An ideal hash for gene sequence search
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:Gene sequence search is a fundamental operation in computational genomics. Due to the petabyte scale of genome archives, most gene search systems now use hashing-based data structures such as Bloom Filters (BF). The state-of-the-art systems such as Compact bit-slicing signature index (COBS) and Repeated And Merged Bloom filters (RAMBO) use BF with Random Hash (RH) functions for gene representation and identification. The standard recipe is to cast the gene search problem as a sequence of membership problems testing if each subsequent gene substring (called kmer) of Q is present in the set of kmers of the entire gene database D. We observe that RH functions, which are crucial to the memory and the computational advantage of BF, are also detrimental to the system performance of gene-search systems. While subsequent kmers being queried are likely very similar, RH, oblivious to any similarity, uniformly distributes the kmers to different parts of potentially large BF, thus triggering excessive cache misses and causing system slowdown. We propose a novel hash function called the Identity with Locality (IDL) hash family, which co-locates the keys close in input space without causing collisions. This approach ensures both cache locality and key preservation. IDL functions can be a drop-in replacement for RH functions and help improve the performance of information retrieval systems. We give a simple but practical construction of IDL function families and show that replacing the RH with IDL functions reduces cache misses by a factor of 5x, thus improving query and indexing times of SOTA methods such as COBS and RAMBO by factors up to 2x without compromising their quality. We also provide a theoretical analysis of the false positive rate of BF with IDL functions. Our hash function is the first study that bridges Locality Sensitive Hash (LSH) and RH to obtain cache efficiency.
KV Cache is 1 Bit Per Channel: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with Coupled Quantization
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Efficient deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) requires batching multiple requests together to improve throughput. As the batch size, context length, or model size increases, the size of the key and value (KV) cache can quickly become the main contributor to GPU memory usage and the bottleneck of inference latency. Quantization has emerged as an effective technique for KV cache compression, but existing methods still fail at very low bit widths. We observe that distinct channels of a key/value activation embedding are highly inter-dependent, and the joint entropy of multiple channels grows at a slower rate than the sum of their marginal entropies. Based on this insight, we propose Coupled Quantization (CQ), which couples multiple key/value channels together to exploit their inter-dependency and encode the activations in a more information-efficient manner. Extensive experiments reveal that CQ outperforms or is competitive with existing baselines in preserving model quality. Furthermore, we demonstrate that CQ can preserve model quality with KV cache quantized down to 1-bit.
NoMAD-Attention: Efficient LLM Inference on CPUs Through Multiply-add-free Attention
Mar 02, 2024



Abstract:Large language model inference on Central Processing Units (CPU) is challenging due to the vast quantities of expensive Multiply-Add (MAD) matrix operations in the attention computations. In this paper, we argue that there is a rare gem in modern CPUs, Single-Instruction-Multiple-Data (SIMD) registers, which allow for ultra-low-latency lookups in batch. We leverage this unique capability of CPUs to propose NoMAD-Attention, an efficient attention algorithm that replaces MAD operations with in-register lookups. Through hardware-aware algorithmic designs, NoMAD-Attention achieves the computation of attention scores using repeated fast accesses to SIMD registers despite their highly limited sizes. Moreover, NoMAD-Attention works with pre-trained attention-based LLMs without model finetuning. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that NoMAD-Attention maintains the quality of the original LLMs well, and speeds up the 4-bit quantized LLaMA-7B-based model by up to 2$\times$ at 16k context length. Our results are reproducible at https://github.com/tonyzhang617/nomad-dist.
Wisdom of Committee: Distilling from Foundation Model to Specialized Application Model
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in foundation models have yielded impressive performance across a wide range of tasks. Meanwhile, for specific applications, practitioners have been developing specialized application models. To enjoy the benefits of both kinds of models, one natural path is to transfer the knowledge in foundation models into specialized application models, which are generally more efficient for serving. Techniques from knowledge distillation may be applied here, where the application model learns to mimic the foundation model. However, specialized application models and foundation models have substantial gaps in capacity, employing distinct architectures, using different input features from different modalities, and being optimized on different distributions. These differences in model characteristics lead to significant challenges for distillation methods. In this work, we propose creating a teaching committee comprising both foundation model teachers and complementary teachers. Complementary teachers possess model characteristics akin to the student's, aiming to bridge the gap between the foundation model and specialized application models for a smoother knowledge transfer. Further, to accommodate the dissimilarity among the teachers in the committee, we introduce DiverseDistill, which allows the student to understand the expertise of each teacher and extract task knowledge. Our evaluations demonstrate that adding complementary teachers enhances student performance. Finally, DiverseDistill consistently outperforms baseline distillation methods, regardless of the teacher choices, resulting in significantly improved student performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge