Yan Zhuang
Community-Level Modeling of Gyral Folding Patterns for Robust and Anatomically Informed Individualized Brain Mapping
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Cortical folding exhibits substantial inter-individual variability while preserving stable anatomical landmarks that enable fine-scale characterization of cortical organization. Among these, the three-hinge gyrus (3HG) serves as a key folding primitive, showing consistent topology yet meaningful variations in morphology, connectivity, and function. Existing landmark-based methods typically model each 3HG independently, ignoring that 3HGs form higher-order folding communities that capture mesoscale structure. This simplification weakens anatomical representation and makes one-to-one matching sensitive to positional variability and noise. We propose a spectral graph representation learning framework that models community-level folding units rather than isolated landmarks. Each 3HG is encoded using a dual-profile representation combining surface topology and structural connectivity. Subject-specific spectral clustering identifies coherent folding communities, followed by topological refinement to preserve anatomical continuity. For cross-subject correspondence, we introduce Joint Morphological-Geometric Matching, jointly optimizing geometric and morphometric similarity. Across over 1000 Human Connectome Project subjects, the resulting communities show reduced morphometric variance, stronger modular organization, improved hemispheric consistency, and superior alignment compared with atlas-based and landmark-based or embedding-based baselines. These findings demonstrate that community-level modeling provides a robust and anatomically grounded framework for individualized cortical characterization and reliable cross-subject correspondence.
Attention Distance: A Novel Metric for Directed Fuzzing with Large Language Models
Dec 19, 2025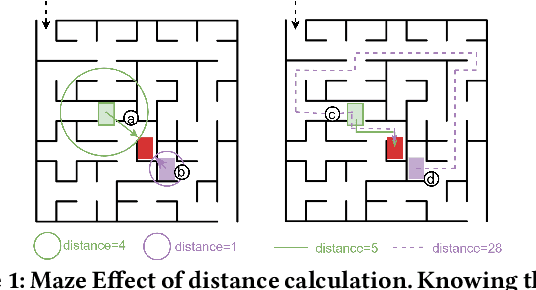
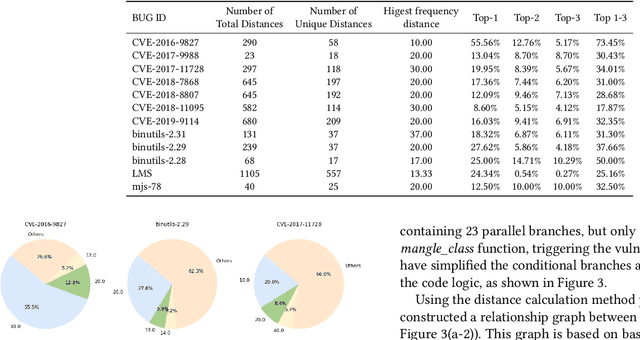
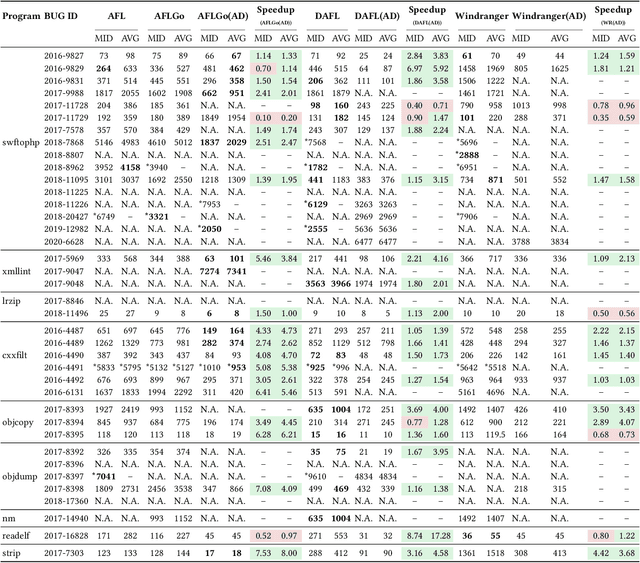
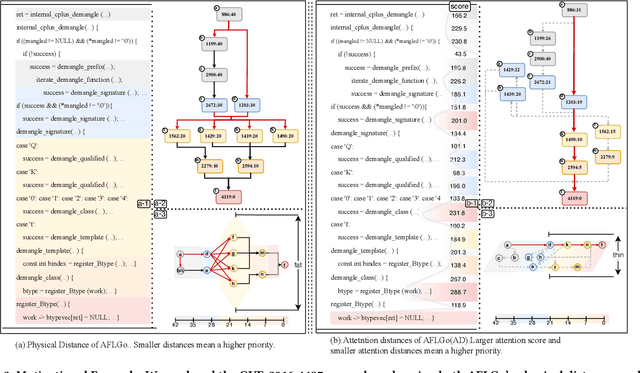
Abstract:In the domain of software security testing, Directed Grey-Box Fuzzing (DGF) has garnered widespread attention for its efficient target localization and excellent detection performance. However, existing approaches measure only the physical distance between seed execution paths and target locations, overlooking logical relationships among code segments. This omission can yield redundant or misleading guidance in complex binaries, weakening DGF's real-world effectiveness. To address this, we introduce \textbf{attention distance}, a novel metric that leverages a large language model's contextual analysis to compute attention scores between code elements and reveal their intrinsic connections. Under the same AFLGo configuration -- without altering any fuzzing components other than the distance metric -- replacing physical distances with attention distances across 38 real vulnerability reproduction experiments delivers a \textbf{3.43$\times$} average increase in testing efficiency over the traditional method. Compared to state-of-the-art directed fuzzers DAFL and WindRanger, our approach achieves \textbf{2.89$\times$} and \textbf{7.13$\times$} improvements, respectively. To further validate the generalizability of attention distance, we integrate it into DAFL and WindRanger, where it also consistently enhances their original performance. All related code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/TheBinKing/Attention\_Distance.git.
SimWorld-Robotics: Synthesizing Photorealistic and Dynamic Urban Environments for Multimodal Robot Navigation and Collaboration
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in foundation models have shown promising results in developing generalist robotics that can perform diverse tasks in open-ended scenarios given multimodal inputs. However, current work has been mainly focused on indoor, household scenarios. In this work, we present SimWorld-Robotics~(SWR), a simulation platform for embodied AI in large-scale, photorealistic urban environments. Built on Unreal Engine 5, SWR procedurally generates unlimited photorealistic urban scenes populated with dynamic elements such as pedestrians and traffic systems, surpassing prior urban simulations in realism, complexity, and scalability. It also supports multi-robot control and communication. With these key features, we build two challenging robot benchmarks: (1) a multimodal instruction-following task, where a robot must follow vision-language navigation instructions to reach a destination in the presence of pedestrians and traffic; and (2) a multi-agent search task, where two robots must communicate to cooperatively locate and meet each other. Unlike existing benchmarks, these two new benchmarks comprehensively evaluate a wide range of critical robot capacities in realistic scenarios, including (1) multimodal instructions grounding, (2) 3D spatial reasoning in large environments, (3) safe, long-range navigation with people and traffic, (4) multi-robot collaboration, and (5) grounded communication. Our experimental results demonstrate that state-of-the-art models, including vision-language models (VLMs), struggle with our tasks, lacking robust perception, reasoning, and planning abilities necessary for urban environments.
Utility of Pancreas Surface Lobularity as a CT Biomarker for Opportunistic Screening of Type 2 Diabetes
Nov 13, 2025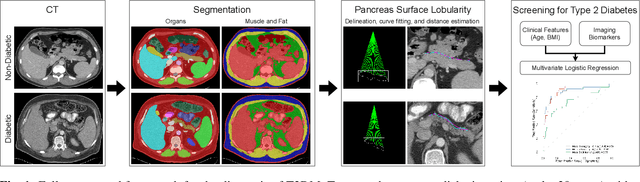
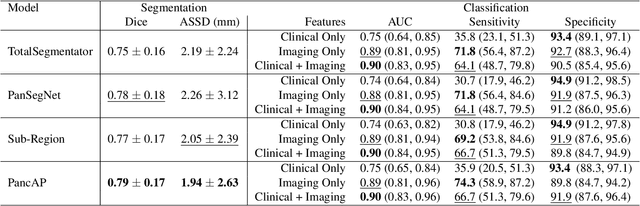
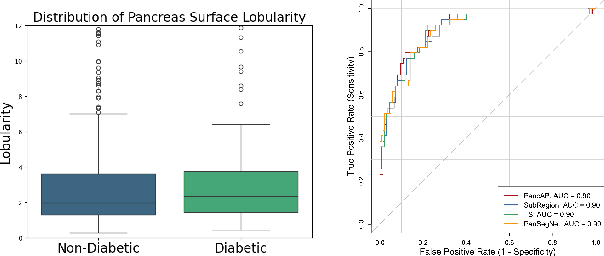
Abstract:Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Early detection is crucial as it can alter pancreas function through morphological changes and increased deposition of ectopic fat, eventually leading to organ damage. While studies have shown an association between T2DM and pancreas volume and fat content, the role of increased pancreatic surface lobularity (PSL) in patients with T2DM has not been fully investigated. In this pilot work, we propose a fully automated approach to delineate the pancreas and other abdominal structures, derive CT imaging biomarkers, and opportunistically screen for T2DM. Four deep learning-based models were used to segment the pancreas in an internal dataset of 584 patients (297 males, 437 non-diabetic, age: 45$\pm$15 years). PSL was automatically detected and it was higher for diabetic patients (p=0.01) at 4.26 $\pm$ 8.32 compared to 3.19 $\pm$ 3.62 for non-diabetic patients. The PancAP model achieved the highest Dice score of 0.79 $\pm$ 0.17 and lowest ASSD error of 1.94 $\pm$ 2.63 mm (p$<$0.05). For predicting T2DM, a multivariate model trained with CT biomarkers attained 0.90 AUC, 66.7\% sensitivity, and 91.9\% specificity. Our results suggest that PSL is useful for T2DM screening and could potentially help predict the early onset of T2DM.
am-ELO: A Stable Framework for Arena-based LLM Evaluation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Arena-based evaluation is a fundamental yet significant evaluation paradigm for modern AI models, especially large language models (LLMs). Existing framework based on ELO rating system suffers from the inevitable instability problem due to ranking inconsistency and the lack of attention to the varying abilities of annotators. In this paper, we introduce a novel stable arena framework to address these issues by enhancing the ELO Rating System. Specifically, we replace the iterative update method with a Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) approach, m-ELO, and provide theoretical proof of the consistency and stability of the MLE approach for model ranking. Additionally, we proposed the am-ELO, which modify the Elo Rating's probability function to incorporate annotator abilities, enabling the simultaneous estimation of model scores and annotator reliability. Experiments demonstrate that this method ensures stability, proving that this framework offers a more robust, accurate, and stable evaluation method for LLMs.
Benchmarking Multi-Organ Segmentation Tools for Multi-Parametric T1-weighted Abdominal MRI
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:The segmentation of multiple organs in multi-parametric MRI studies is critical for many applications in radiology, such as correlating imaging biomarkers with disease status (e.g., cirrhosis, diabetes). Recently, three publicly available tools, such as MRSegmentator (MRSeg), TotalSegmentator MRI (TS), and TotalVibeSegmentator (VIBE), have been proposed for multi-organ segmentation in MRI. However, the performance of these tools on specific MRI sequence types has not yet been quantified. In this work, a subset of 40 volumes from the public Duke Liver Dataset was curated. The curated dataset contained 10 volumes each from the pre-contrast fat saturated T1, arterial T1w, venous T1w, and delayed T1w phases, respectively. Ten abdominal structures were manually annotated in these volumes. Next, the performance of the three public tools was benchmarked on this curated dataset. The results indicated that MRSeg obtained a Dice score of 80.7 $\pm$ 18.6 and Hausdorff Distance (HD) error of 8.9 $\pm$ 10.4 mm. It fared the best ($p < .05$) across the different sequence types in contrast to TS and VIBE.
GyralNet Subnetwork Partitioning via Differentiable Spectral Modularity Optimization
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Understanding the structural and functional organization of the human brain requires a detailed examination of cortical folding patterns, among which the three-hinge gyrus (3HG) has been identified as a key structural landmark. GyralNet, a network representation of cortical folding, models 3HGs as nodes and gyral crests as edges, highlighting their role as critical hubs in cortico-cortical connectivity. However, existing methods for analyzing 3HGs face significant challenges, including the sub-voxel scale of 3HGs at typical neuroimaging resolutions, the computational complexity of establishing cross-subject correspondences, and the oversimplification of treating 3HGs as independent nodes without considering their community-level relationships. To address these limitations, we propose a fully differentiable subnetwork partitioning framework that employs a spectral modularity maximization optimization strategy to modularize the organization of 3HGs within GyralNet. By incorporating topological structural similarity and DTI-derived connectivity patterns as attribute features, our approach provides a biologically meaningful representation of cortical organization. Extensive experiments on the Human Connectome Project (HCP) dataset demonstrate that our method effectively partitions GyralNet at the individual level while preserving the community-level consistency of 3HGs across subjects, offering a robust foundation for understanding brain connectivity.
Core-Periphery Principle Guided State Space Model for Functional Connectome Classification
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Understanding the organization of human brain networks has become a central focus in neuroscience, particularly in the study of functional connectivity, which plays a crucial role in diagnosing neurological disorders. Advances in functional magnetic resonance imaging and machine learning techniques have significantly improved brain network analysis. However, traditional machine learning approaches struggle to capture the complex relationships between brain regions, while deep learning methods, particularly Transformer-based models, face computational challenges due to their quadratic complexity in long-sequence modeling. To address these limitations, we propose a Core-Periphery State-Space Model (CP-SSM), an innovative framework for functional connectome classification. Specifically, we introduce Mamba, a selective state-space model with linear complexity, to effectively capture long-range dependencies in functional brain networks. Furthermore, inspired by the core-periphery (CP) organization, a fundamental characteristic of brain networks that enhances efficient information transmission, we design CP-MoE, a CP-guided Mixture-of-Experts that improves the representation learning of brain connectivity patterns. We evaluate CP-SSM on two benchmark fMRI datasets: ABIDE and ADNI. Experimental results demonstrate that CP-SSM surpasses Transformer-based models in classification performance while significantly reducing computational complexity. These findings highlight the effectiveness and efficiency of CP-SSM in modeling brain functional connectivity, offering a promising direction for neuroimaging-based neurological disease diagnosis.
LEAVS: An LLM-based Labeler for Abdominal CT Supervision
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Extracting structured labels from radiology reports has been employed to create vision models to simultaneously detect several types of abnormalities. However, existing works focus mainly on the chest region. Few works have been investigated on abdominal radiology reports due to more complex anatomy and a wider range of pathologies in the abdomen. We propose LEAVS (Large language model Extractor for Abdominal Vision Supervision). This labeler can annotate the certainty of presence and the urgency of seven types of abnormalities for nine abdominal organs on CT radiology reports. To ensure broad coverage, we chose abnormalities that encompass most of the finding types from CT reports. Our approach employs a specialized chain-of-thought prompting strategy for a locally-run LLM using sentence extraction and multiple-choice questions in a tree-based decision system. We demonstrate that the LLM can extract several abnormality types across abdominal organs with an average F1 score of 0.89, significantly outperforming competing labelers and humans. Additionally, we show that extraction of urgency labels achieved performance comparable to human annotations. Finally, we demonstrate that the abnormality labels contain valuable information for training a single vision model that classifies several organs as normal or abnormal. We release our code and structured annotations for a public CT dataset containing over 1,000 CT volumes.
Brain-Adapter: Enhancing Neurological Disorder Analysis with Adapter-Tuning Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 27, 2025


Abstract:Understanding brain disorders is crucial for accurate clinical diagnosis and treatment. Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offer a promising approach to interpreting medical images with the support of text descriptions. However, previous research has primarily focused on 2D medical images, leaving richer spatial information of 3D images under-explored, and single-modality-based methods are limited by overlooking the critical clinical information contained in other modalities. To address this issue, this paper proposes Brain-Adapter, a novel approach that incorporates an extra bottleneck layer to learn new knowledge and instill it into the original pre-trained knowledge. The major idea is to incorporate a lightweight bottleneck layer to train fewer parameters while capturing essential information and utilize a Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) strategy to align multimodal data within a unified representation space. Extensive experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of our approach in integrating multimodal data to significantly improve the diagnosis accuracy without high computational costs, highlighting the potential to enhance real-world diagnostic workflows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge