Jianquan Li
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM's visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
K-Sort Arena: Efficient and Reliable Benchmarking for Generative Models via K-wise Human Preferences
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of visual generative models necessitates efficient and reliable evaluation methods. Arena platform, which gathers user votes on model comparisons, can rank models with human preferences. However, traditional Arena methods, while established, require an excessive number of comparisons for ranking to converge and are vulnerable to preference noise in voting, suggesting the need for better approaches tailored to contemporary evaluation challenges. In this paper, we introduce K-Sort Arena, an efficient and reliable platform based on a key insight: images and videos possess higher perceptual intuitiveness than texts, enabling rapid evaluation of multiple samples simultaneously. Consequently, K-Sort Arena employs K-wise comparisons, allowing K models to engage in free-for-all competitions, which yield much richer information than pairwise comparisons. To enhance the robustness of the system, we leverage probabilistic modeling and Bayesian updating techniques. We propose an exploration-exploitation-based matchmaking strategy to facilitate more informative comparisons. In our experiments, K-Sort Arena exhibits 16.3x faster convergence compared to the widely used ELO algorithm. To further validate the superiority and obtain a comprehensive leaderboard, we collect human feedback via crowdsourced evaluations of numerous cutting-edge text-to-image and text-to-video models. Thanks to its high efficiency, K-Sort Arena can continuously incorporate emerging models and update the leaderboard with minimal votes. Our project has undergone several months of internal testing and is now available at https://huggingface.co/spaces/ksort/K-Sort-Arena
Incorporating Lexical and Syntactic Knowledge for Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Transfer
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised cross-lingual transfer involves transferring knowledge between languages without explicit supervision. Although numerous studies have been conducted to improve performance in such tasks by focusing on cross-lingual knowledge, particularly lexical and syntactic knowledge, current approaches are limited as they only incorporate syntactic or lexical information. Since each type of information offers unique advantages and no previous attempts have combined both, we attempt to explore the potential of this approach. In this paper, we present a novel framework called "Lexicon-Syntax Enhanced Multilingual BERT" that combines both lexical and syntactic knowledge. Specifically, we use Multilingual BERT (mBERT) as the base model and employ two techniques to enhance its learning capabilities. The code-switching technique is used to implicitly teach the model lexical alignment information, while a syntactic-based graph attention network is designed to help the model encode syntactic structure. To integrate both types of knowledge, we input code-switched sequences into both the syntactic module and the mBERT base model simultaneously. Our extensive experimental results demonstrate this framework can consistently outperform all baselines of zero-shot cross-lingual transfer, with the gains of 1.0~3.7 points on text classification, named entity recognition (ner), and semantic parsing tasks. Keywords:cross-lingual transfer, lexicon, syntax, code-switching, graph attention network
Online Training of Large Language Models: Learn while chatting
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models(LLMs) have dramatically revolutionized the field of Natural Language Processing(NLP), offering remarkable capabilities that have garnered widespread usage. However, existing interaction paradigms between LLMs and users are constrained by either inflexibility, limitations in customization, or a lack of persistent learning. This inflexibility is particularly evident as users, especially those without programming skills, have restricted avenues to enhance or personalize the model. Existing frameworks further complicate the model training and deployment process due to their computational inefficiencies and lack of user-friendly interfaces. To overcome these challenges, this paper introduces a novel interaction paradigm-'Online Training using External Interactions'-that merges the benefits of persistent, real-time model updates with the flexibility for individual customization through external interactions such as AI agents or online/offline knowledge bases.
ALLaVA: Harnessing GPT4V-synthesized Data for A Lite Vision-Language Model
Feb 18, 2024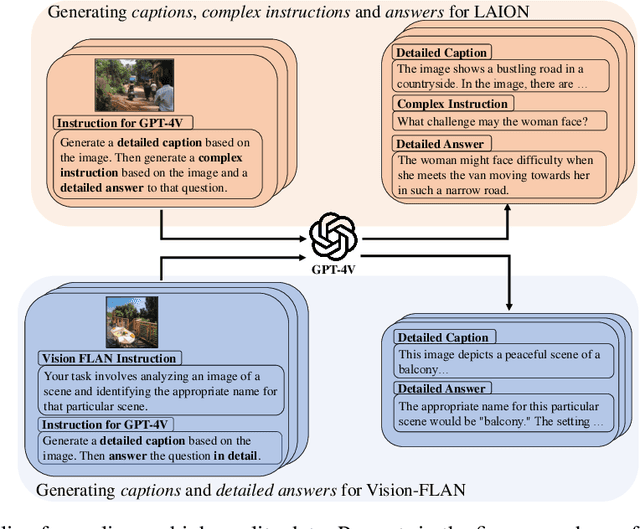
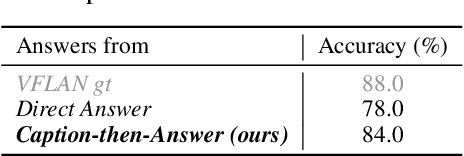
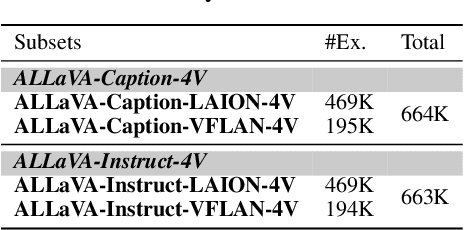
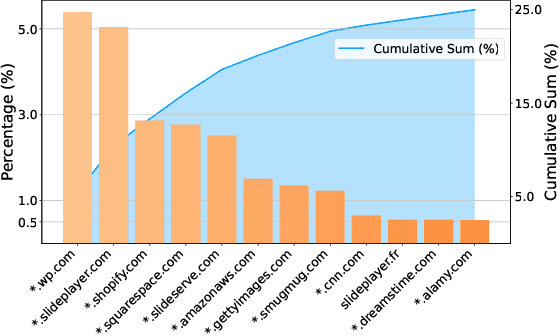
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have enabled processing of multimodal inputs in language models but require significant computational resources for deployment, especially in edge devices. This study aims to bridge the performance gap between traditional-scale LVLMs and resource-friendly lite versions by adopting high-quality training data. To do this, a synthetic dataset is created by leveraging GPT-4V's ability to generate detailed captions, complex reasoning instructions and detailed answers from images. The resulted model trained with our data, ALLaVA, achieves competitive performance on 12 benchmarks up to 3B LVLMs. This work highlights the feasibility of adopting high-quality data in crafting more efficient LVLMs. Our online demo is available at \url{https://allava.freedomai.cn}.
MLLM-Bench, Evaluating Multi-modal LLMs using GPT-4V
Nov 23, 2023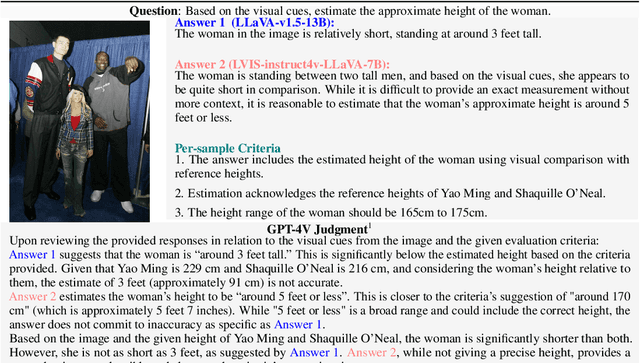
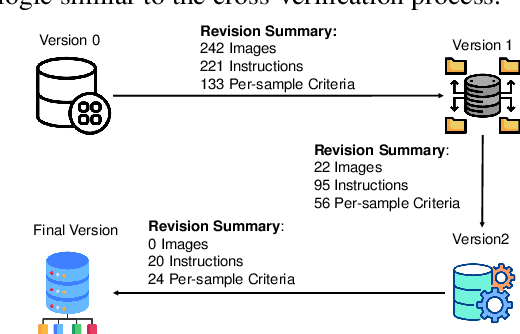

Abstract:In the pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the integration of vision in language models has marked a significant milestone. The advent of vision-language models (MLLMs) like GPT-4V have expanded AI applications, aligning with the multi-modal capabilities of the human brain. However, evaluating the efficacy of MLLMs poses a substantial challenge due to the subjective nature of tasks that lack definitive answers. Existing automatic evaluation methodologies on multi-modal large language models rely on objective queries that have standard answers, inadequately addressing the nuances of creative and associative multi-modal tasks. To address this, we introduce MLLM-Bench, an innovative benchmark inspired by Vicuna, spanning a diverse array of scenarios, including Perception, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creation along with the ethical consideration. MLLM-Bench is designed to reflect user experience more accurately and provide a more holistic assessment of model performance. Comparative evaluations indicate a significant performance gap between existing open-source models and GPT-4V. We posit that MLLM-Bench will catalyze progress in the open-source community towards developing user-centric vision-language models that meet a broad spectrum of real-world applications. See online leaderboard in \url{https://mllm-bench.llmzoo.com}.
HuatuoGPT-II, One-stage Training for Medical Adaption of LLMs
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Adapting a language model into a specific domain, a.k.a `domain adaption', is a common practice when specialized knowledge, e.g. medicine, is not encapsulated in a general language model like Llama2. The challenge lies in the heterogeneity of data across the two training stages, as it varies in languages, genres, or formats. To tackle this and simplify the learning protocol, we propose to transform heterogeneous data, from the both pre-training and supervised stages, into a unified, simple input-output pair format. We validate the new protocol in the domains where proprietary LLMs like ChatGPT perform relatively poorly, such as Traditional Chinese Medicine. The developed model, HuatuoGPT-II, has shown state-of-the-art performance in Chinese medicine domain on a number of benchmarks, e.g. medical licensing exams. It even outperforms proprietary models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 in some aspects, especially in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Expert manual evaluations further validate HuatuoGPT-II's advantages over existing LLMs. Notably, HuatuoGPT-II was benchmarked in a fresh Chinese National Medical Licensing Examination where it achieved the best performance, showcasing not only its effectiveness but also its generalization capabilities.
AceGPT, Localizing Large Language Models in Arabic
Sep 22, 2023



Abstract:This paper explores the imperative need and methodology for developing a localized Large Language Model (LLM) tailored for Arabic, a language with unique cultural characteristics that are not adequately addressed by current mainstream models like ChatGPT. Key concerns additionally arise when considering cultural sensitivity and local values. To this end, the paper outlines a packaged solution, including further pre-training with Arabic texts, supervised fine-tuning (SFT) using native Arabic instructions and GPT-4 responses in Arabic, and reinforcement learning with AI feedback (RLAIF) using a reward model that is sensitive to local culture and values. The objective is to train culturally aware and value-aligned Arabic LLMs that can serve the diverse application-specific needs of Arabic-speaking communities. Extensive evaluations demonstrated that the resulting LLM called `AceGPT' is the SOTA open Arabic LLM in various benchmarks, including instruction-following benchmark (i.e., Arabic Vicuna-80 and Arabic AlpacaEval), knowledge benchmark (i.e., Arabic MMLU and EXAMs), as well as the newly-proposed Arabic cultural \& value alignment benchmark. Notably, AceGPT outperforms ChatGPT in the popular Vicuna-80 benchmark when evaluated with GPT-4, despite the benchmark's limited scale. % Natural Language Understanding (NLU) benchmark (i.e., ALUE) Codes, data, and models are in https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/AceGPT.
CMB: A Comprehensive Medical Benchmark in Chinese
Aug 17, 2023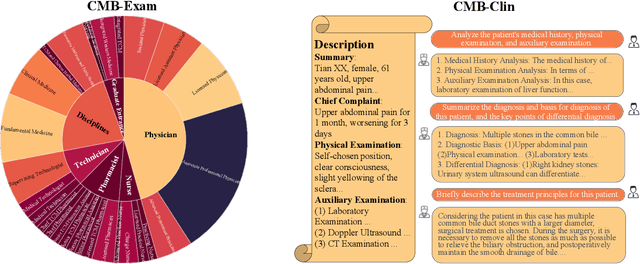
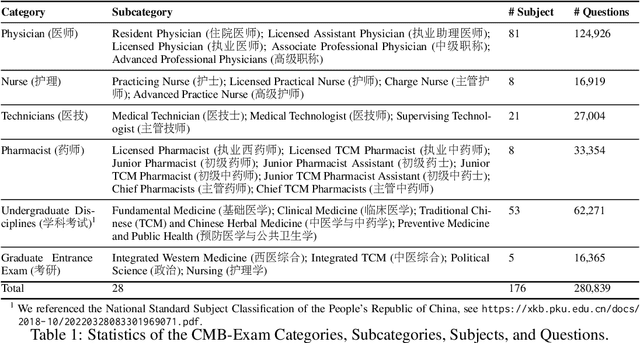
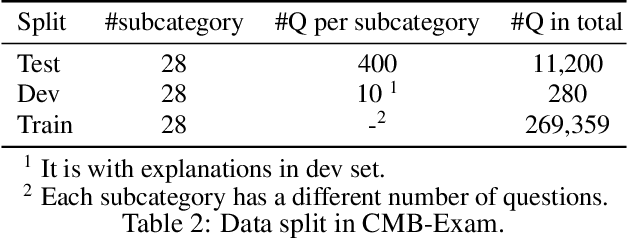
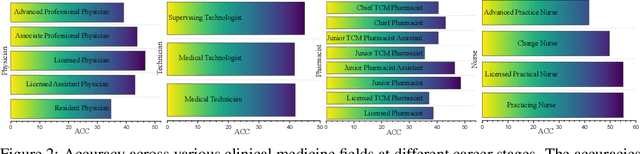
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) provide a possibility to make a great breakthrough in medicine. The establishment of a standardized medical benchmark becomes a fundamental cornerstone to measure progression. However, medical environments in different regions have their local characteristics, e.g., the ubiquity and significance of traditional Chinese medicine within China. Therefore, merely translating English-based medical evaluation may result in \textit{contextual incongruities} to a local region. To solve the issue, we propose a localized medical benchmark called CMB, a Comprehensive Medical Benchmark in Chinese, designed and rooted entirely within the native Chinese linguistic and cultural framework. While traditional Chinese medicine is integral to this evaluation, it does not constitute its entirety. Using this benchmark, we have evaluated several prominent large-scale LLMs, including ChatGPT, GPT-4, dedicated Chinese LLMs, and LLMs specialized in the medical domain. It is worth noting that our benchmark is not devised as a leaderboard competition but as an instrument for self-assessment of model advancements. We hope this benchmark could facilitate the widespread adoption and enhancement of medical LLMs within China. Check details in \url{https://cmedbenchmark.llmzoo.com/}.
HuatuoGPT, towards Taming Language Model to Be a Doctor
May 24, 2023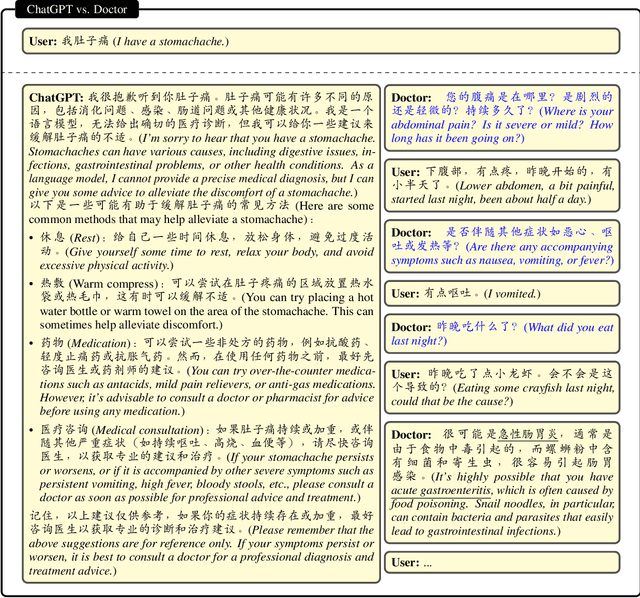
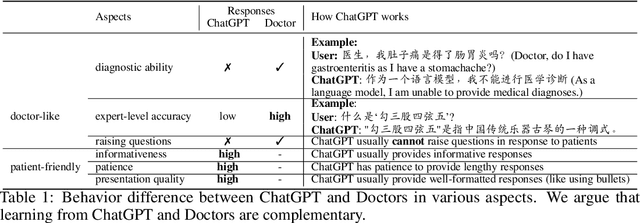
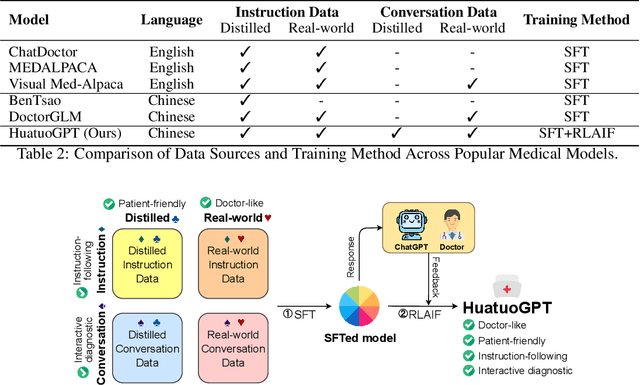
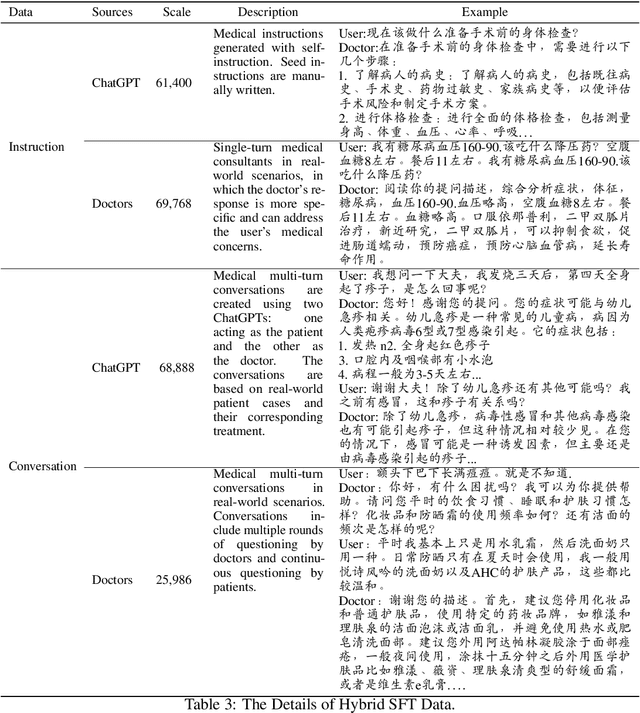
Abstract:In this paper, we present HuatuoGPT, a large language model (LLM) for medical consultation. The core recipe of HuatuoGPT is to leverage both \textit{distilled data from ChatGPT} and \textit{real-world data from doctors} in the supervised fine-tuned stage. The responses of ChatGPT are usually detailed, well-presented and informative while it cannot perform like a doctor in many aspects, e.g. for integrative diagnosis. We argue that real-world data from doctors would be complementary to distilled data in the sense the former could tame a distilled language model to perform like doctors. To better leverage the strengths of both data, we train a reward model to align the language model with the merits that both data bring, following an RLAIF (reinforced learning from AI feedback) fashion. To evaluate and benchmark the models, we propose a comprehensive evaluation scheme (including automatic and manual metrics). Experimental results demonstrate that HuatuoGPT achieves state-of-the-art results in performing medical consultation among open-source LLMs in GPT-4 evaluation, human evaluation, and medical benchmark datasets. It is worth noting that by using additional real-world data and RLAIF, the distilled language model (i.e., HuatuoGPT) outperforms its teacher model ChatGPT in most cases. Our code, data, and models are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/HuatuoGPT}. The online demo is available at \url{https://www.HuatuoGPT.cn/}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge