Kurt Keutzer
Quant VideoGen: Auto-Regressive Long Video Generation via 2-Bit KV-Cache Quantization
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Despite rapid progress in autoregressive video diffusion, an emerging system algorithm bottleneck limits both deployability and generation capability: KV cache memory. In autoregressive video generation models, the KV cache grows with generation history and quickly dominates GPU memory, often exceeding 30 GB, preventing deployment on widely available hardware. More critically, constrained KV cache budgets restrict the effective working memory, directly degrading long horizon consistency in identity, layout, and motion. To address this challenge, we present Quant VideoGen (QVG), a training free KV cache quantization framework for autoregressive video diffusion models. QVG leverages video spatiotemporal redundancy through Semantic Aware Smoothing, producing low magnitude, quantization friendly residuals. It further introduces Progressive Residual Quantization, a coarse to fine multi stage scheme that reduces quantization error while enabling a smooth quality memory trade off. Across LongCat Video, HY WorldPlay, and Self Forcing benchmarks, QVG establishes a new Pareto frontier between quality and memory efficiency, reducing KV cache memory by up to 7.0 times with less than 4% end to end latency overhead while consistently outperforming existing baselines in generation quality.
Residual Context Diffusion Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) have emerged as a promising alternative to purely autoregressive language models because they can decode multiple tokens in parallel. However, state-of-the-art block-wise dLLMs rely on a "remasking" mechanism that decodes only the most confident tokens and discards the rest, effectively wasting computation. We demonstrate that recycling computation from the discarded tokens is beneficial, as these tokens retain contextual information useful for subsequent decoding iterations. In light of this, we propose Residual Context Diffusion (RCD), a module that converts these discarded token representations into contextual residuals and injects them back for the next denoising step. RCD uses a decoupled two-stage training pipeline to bypass the memory bottlenecks associated with backpropagation. We validate our method on both long CoT reasoning (SDAR) and short CoT instruction following (LLaDA) models. We demonstrate that a standard dLLM can be efficiently converted to the RCD paradigm with merely ~1 billion tokens. RCD consistently improves frontier dLLMs by 5-10 points in accuracy with minimal extra computation overhead across a wide range of benchmarks. Notably, on the most challenging AIME tasks, RCD nearly doubles baseline accuracy and attains up to 4-5x fewer denoising steps at equivalent accuracy levels.
Jet-RL: Enabling On-Policy FP8 Reinforcement Learning with Unified Training and Rollout Precision Flow
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is essential for enhancing the complex reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, existing RL training pipelines are computationally inefficient and resource-intensive, with the rollout phase accounting for over 70% of total training time. Quantized RL training, particularly using FP8 precision, offers a promising approach to mitigating this bottleneck. A commonly adopted strategy applies FP8 precision during rollout while retaining BF16 precision for training. In this work, we present the first comprehensive study of FP8 RL training and demonstrate that the widely used BF16-training + FP8-rollout strategy suffers from severe training instability and catastrophic accuracy collapse under long-horizon rollouts and challenging tasks. Our analysis shows that these failures stem from the off-policy nature of the approach, which introduces substantial numerical mismatch between training and inference. Motivated by these observations, we propose Jet-RL, an FP8 RL training framework that enables robust and stable RL optimization. The key idea is to adopt a unified FP8 precision flow for both training and rollout, thereby minimizing numerical discrepancies and eliminating the need for inefficient inter-step calibration. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of Jet-RL: our method achieves up to 33% speedup in the rollout phase, up to 41% speedup in the training phase, and a 16% end-to-end speedup over BF16 training, while maintaining stable convergence across all settings and incurring negligible accuracy degradation.
Mitrasamgraha: A Comprehensive Classical Sanskrit Machine Translation Dataset
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:While machine translation is regarded as a "solved problem" for many high-resource languages, close analysis quickly reveals that this is not the case for content that shows challenges such as poetic language, philosophical concepts, multi-layered metaphorical expressions, and more. Sanskrit literature is a prime example of this, as it combines a large number of such challenges in addition to inherent linguistic features like sandhi, compounding, and heavy morphology, which further complicate NLP downstream tasks. It spans multiple millennia of text production time as well as a large breadth of different domains, ranging from ritual formulas via epic narratives, philosophical treatises, poetic verses up to scientific material. As of now, there is a strong lack of publicly available resources that cover these different domains and temporal layers of Sanskrit. We therefore introduce Mitrasamgraha, a high-quality Sanskrit-to-English machine translation dataset consisting of 391,548 bitext pairs, more than four times larger than the largest previously available Sanskrit dataset Itih=asa. It covers a time period of more than three millennia and a broad range of historical Sanskrit domains. In contrast to web-crawled datasets, the temporal and domain annotation of this dataset enables fine-grained study of domain and time period effects on MT performance. We also release a validation set consisting of 5,587 and a test set consisting of 5,552 post-corrected bitext pairs. We conduct experiments benchmarking commercial and open models on this dataset and fine-tune NLLB and Gemma models on the dataset, showing significant improvements, while still recognizing significant challenges in the translation of complex compounds, philosophical concepts, and multi-layered metaphors. We also analyze how in-context learning on this dataset impacts the performance of commercial models
MITRA: A Large-Scale Parallel Corpus and Multilingual Pretrained Language Model for Machine Translation and Semantic Retrieval for Pāli, Sanskrit, Buddhist Chinese, and Tibetan
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Ancient Buddhist literature features frequent, yet often unannotated, textual parallels spread across diverse languages: Sanskrit, Pāli, Buddhist Chinese, Tibetan, and more. The scale of this material makes manual examination prohibitive. We present the MITRA framework, which consists of a novel pipeline for multilingual parallel passage mining, MITRA-parallel, a large-scale corpus of 1.74 million parallel sentence pairs between Sanskrit, Chinese, and Tibetan, and the development of the domain-specific pretrained language model Gemma 2 MITRA. We present Gemma 2 MITRA-MT, a version of this base model fine-tuned on machine translation tasks, reaching state-of-the-art performance for machine translation of these languages into English and outperforming even much larger open-source models. We also present Gemma 2 MITRA-E, a semantic embedding model that shows state-of-the-art performance on a novel, detailed semantic embedding benchmark. We make the parallel dataset, model weights, and semantic similarity benchmark openly available to aid both NLP research and philological studies in Buddhist and classical Asian literature.
StreamDiffusionV2: A Streaming System for Dynamic and Interactive Video Generation
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Generative models are reshaping the live-streaming industry by redefining how content is created, styled, and delivered. Previous image-based streaming diffusion models have powered efficient and creative live streaming products but have hit limits on temporal consistency due to the foundation of image-based designs. Recent advances in video diffusion have markedly improved temporal consistency and sampling efficiency for offline generation. However, offline generation systems primarily optimize throughput by batching large workloads. In contrast, live online streaming operates under strict service-level objectives (SLOs): time-to-first-frame must be minimal, and every frame must meet a per-frame deadline with low jitter. Besides, scalable multi-GPU serving for real-time streams remains largely unresolved so far. To address this, we present StreamDiffusionV2, a training-free pipeline for interactive live streaming with video diffusion models. StreamDiffusionV2 integrates an SLO-aware batching scheduler and a block scheduler, together with a sink-token--guided rolling KV cache, a motion-aware noise controller, and other system-level optimizations. Moreover, we introduce a scalable pipeline orchestration that parallelizes the diffusion process across denoising steps and network layers, achieving near-linear FPS scaling without violating latency guarantees. The system scales seamlessly across heterogeneous GPU environments and supports flexible denoising steps (e.g., 1--4), enabling both ultra-low-latency and higher-quality modes. Without TensorRT or quantization, StreamDiffusionV2 renders the first frame within 0.5s and attains 58.28 FPS with a 14B-parameter model and 64.52 FPS with a 1.3B-parameter model on four H100 GPUs, making state-of-the-art generative live streaming practical and accessible--from individual creators to enterprise-scale platforms.
XQuant: Breaking the Memory Wall for LLM Inference with KV Cache Rematerialization
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Although LLM inference has emerged as a critical workload for many downstream applications, efficiently inferring LLMs is challenging due to the substantial memory footprint and bandwidth requirements. In parallel, compute capabilities have steadily outpaced both memory capacity and bandwidth over the last few decades, a trend that remains evident in modern GPU hardware and exacerbates the challenge of LLM inference. As such, new algorithms are emerging that trade increased computation for reduced memory operations. To that end, we present XQuant, which takes advantage of this trend, enabling an order-of-magnitude reduction in memory consumption through low-bit quantization with substantial accuracy benefits relative to state-of-the-art KV cache quantization methods. We accomplish this by quantizing and caching the layer input activations X, instead of using standard KV caching, and then rematerializing the Keys and Values on-the-fly during inference. This results in an immediate 2$\times$ memory savings compared to KV caching. By applying XQuant, we achieve up to $\sim 7.7\times$ memory savings with $<0.1$ perplexity degradation compared to the FP16 baseline. Furthermore, our approach leverages the fact that X values are similar across layers. Building on this observation, we introduce XQuant-CL, which exploits the cross-layer similarity in the X embeddings for extreme compression. Across different models, XQuant-CL attains up to 10$\times$ memory savings relative to the FP16 baseline with only 0.01 perplexity degradation, and 12.5$\times$ memory savings with only $0.1$ perplexity degradation. XQuant exploits the rapidly increasing compute capabilities of hardware platforms to eliminate the memory bottleneck, while surpassing state-of-the-art KV cache quantization methods and achieving near-FP16 accuracy across a wide range of models.
Radial Attention: $O(n\log n)$ Sparse Attention with Energy Decay for Long Video Generation
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have enabled high-quality video generation, but the additional temporal dimension significantly increases computational costs, making training and inference on long videos prohibitively expensive. In this paper, we identify a phenomenon we term Spatiotemporal Energy Decay in video diffusion models: post-softmax attention scores diminish as spatial and temporal distance between tokens increase, akin to the physical decay of signal or waves over space and time in nature. Motivated by this, we propose Radial Attention, a scalable sparse attention mechanism with $O(n \log n)$ complexity that translates energy decay into exponentially decaying compute density, which is significantly more efficient than standard $O(n^2)$ dense attention and more expressive than linear attention. Specifically, Radial Attention employs a simple, static attention mask where each token attends to spatially nearby tokens, with the attention window size shrinking with temporal distance. Moreover, it allows pre-trained video diffusion models to extend their generation length with efficient LoRA-based fine-tuning. Extensive experiments show that Radial Attention maintains video quality across Wan2.1-14B, HunyuanVideo, and Mochi 1, achieving up to a 1.9$\times$ speedup over the original dense attention. With minimal tuning, it enables video generation up to 4$\times$ longer while reducing training costs by up to 4.4$\times$ compared to direct fine-tuning and accelerating inference by up to 3.7$\times$ compared to dense attention inference.
Multipole Attention for Efficient Long Context Reasoning
Jun 16, 2025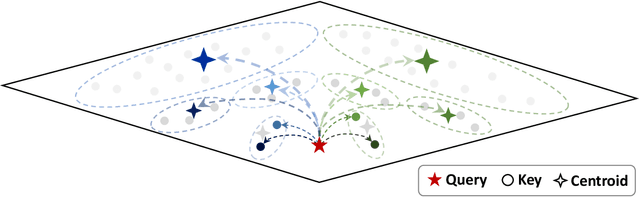

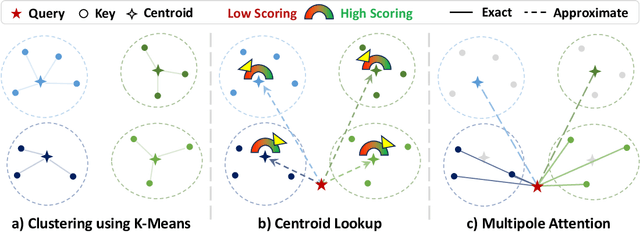
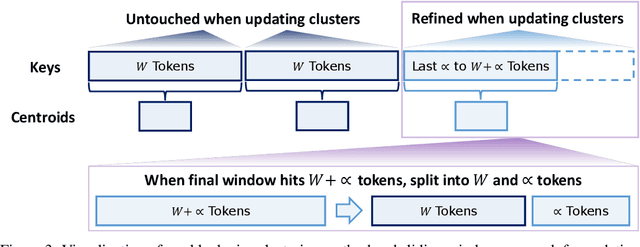
Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have shown promising accuracy improvements on complex problem-solving tasks. While these models have attained high accuracy by leveraging additional computation at test time, they need to generate long chain-of-thought reasoning in order to think before answering, which requires generating thousands of tokens. While sparse attention methods can help reduce the KV cache pressure induced by this long autoregressive reasoning, these methods can introduce errors which disrupt the reasoning process. Additionally, prior methods often pre-process the input to make it easier to identify the important prompt tokens when computing attention during generation, and this pre-processing is challenging to perform online for newly generated reasoning tokens. Our work addresses these challenges by introducing Multipole Attention, which accelerates autoregressive reasoning by only computing exact attention for the most important tokens, while maintaining approximate representations for the remaining tokens. Our method first performs clustering to group together semantically similar key vectors, and then uses the cluster centroids both to identify important key vectors and to approximate the remaining key vectors in order to retain high accuracy. We design a fast cluster update process to quickly re-cluster the input and previously generated tokens, thereby allowing for accelerating attention to the previous output tokens. We evaluate our method using emerging LRMs such as Qwen-8B, demonstrating that our approach can maintain accuracy on complex reasoning tasks even with aggressive attention sparsity settings. We also provide kernel implementations to demonstrate the practical efficiency gains from our method, achieving up to 4.5$\times$ speedup for attention in long-context reasoning applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/SqueezeAILab/MultipoleAttention.
R3D2: Realistic 3D Asset Insertion via Diffusion for Autonomous Driving Simulation
Jun 09, 2025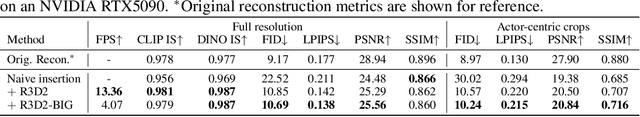


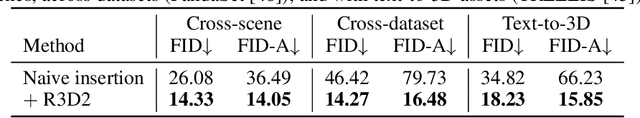
Abstract:Validating autonomous driving (AD) systems requires diverse and safety-critical testing, making photorealistic virtual environments essential. Traditional simulation platforms, while controllable, are resource-intensive to scale and often suffer from a domain gap with real-world data. In contrast, neural reconstruction methods like 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offer a scalable solution for creating photorealistic digital twins of real-world driving scenes. However, they struggle with dynamic object manipulation and reusability as their per-scene optimization-based methodology tends to result in incomplete object models with integrated illumination effects. This paper introduces R3D2, a lightweight, one-step diffusion model designed to overcome these limitations and enable realistic insertion of complete 3D assets into existing scenes by generating plausible rendering effects-such as shadows and consistent lighting-in real time. This is achieved by training R3D2 on a novel dataset: 3DGS object assets are generated from in-the-wild AD data using an image-conditioned 3D generative model, and then synthetically placed into neural rendering-based virtual environments, allowing R3D2 to learn realistic integration. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that R3D2 significantly enhances the realism of inserted assets, enabling use-cases like text-to-3D asset insertion and cross-scene/dataset object transfer, allowing for true scalability in AD validation. To promote further research in scalable and realistic AD simulation, we will release our dataset and code, see https://research.zenseact.com/publications/R3D2/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge