Zhiyu Lin
Decoding the Ear: A Framework for Objectifying Expressiveness from Human Preference Through Efficient Alignment
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Recent speech-to-speech (S2S) models generate intelligible speech but still lack natural expressiveness, largely due to the absence of a reliable evaluation metric. Existing approaches, such as subjective MOS ratings, low-level acoustic features, and emotion recognition are costly, limited, or incomplete. To address this, we present DeEAR (Decoding the Expressive Preference of eAR), a framework that converts human preference for speech expressiveness into an objective score. Grounded in phonetics and psychology, DeEAR evaluates speech across three dimensions: Emotion, Prosody, and Spontaneity, achieving strong alignment with human perception (Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient, SRCC = 0.86) using fewer than 500 annotated samples. Beyond reliable scoring, DeEAR enables fair benchmarking and targeted data curation. It not only distinguishes expressiveness gaps across S2S models but also selects 14K expressive utterances to form ExpressiveSpeech, which improves the expressive score (from 2.0 to 23.4 on a 100-point scale) of S2S models. Demos and codes are available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/ExpressiveSpeech
LLMs Caught in the Crossfire: Malware Requests and Jailbreak Challenges
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) has heightened concerns about their security, particularly their vulnerability to jailbreak attacks that leverage crafted prompts to generate malicious outputs. While prior research has been conducted on general security capabilities of LLMs, their specific susceptibility to jailbreak attacks in code generation remains largely unexplored. To fill this gap, we propose MalwareBench, a benchmark dataset containing 3,520 jailbreaking prompts for malicious code-generation, designed to evaluate LLM robustness against such threats. MalwareBench is based on 320 manually crafted malicious code generation requirements, covering 11 jailbreak methods and 29 code functionality categories. Experiments show that mainstream LLMs exhibit limited ability to reject malicious code-generation requirements, and the combination of multiple jailbreak methods further reduces the model's security capabilities: specifically, the average rejection rate for malicious content is 60.93%, dropping to 39.92% when combined with jailbreak attack algorithms. Our work highlights that the code security capabilities of LLMs still pose significant challenges.
WebUIBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models in WebUI-to-Code
Jun 09, 2025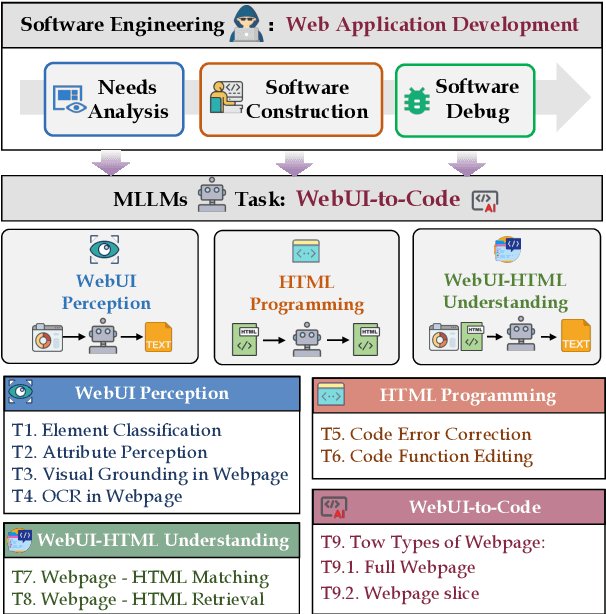
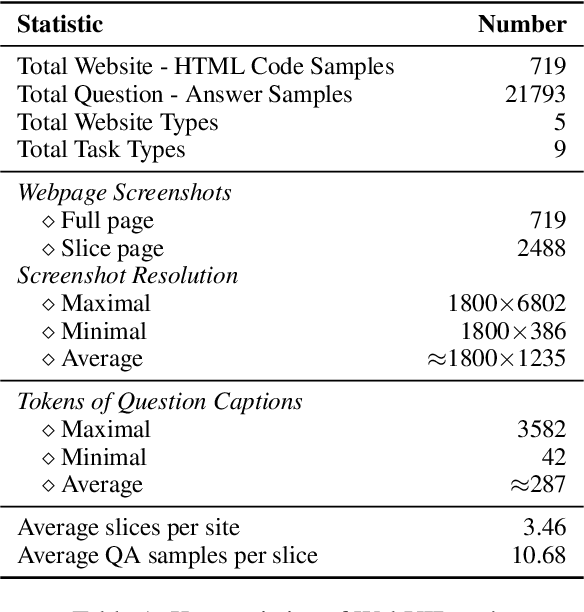

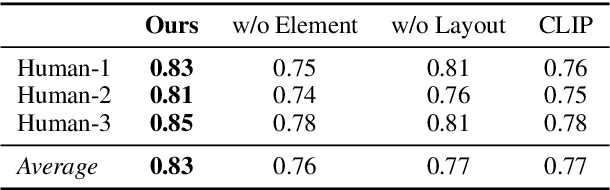
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Generative AI technology, Multimodal Large Language Models(MLLMs) have the potential to act as AI software engineers capable of executing complex web application development. Considering that the model requires a confluence of multidimensional sub-capabilities to address the challenges of various development phases, constructing a multi-view evaluation framework is crucial for accurately guiding the enhancement of development efficiency. However, existing benchmarks usually fail to provide an assessment of sub-capabilities and focus solely on webpage generation outcomes. In this work, we draw inspiration from the principles of software engineering and further propose WebUIBench, a benchmark systematically designed to evaluate MLLMs in four key areas: WebUI Perception, HTML Programming,WebUI-HTML Understanding, and WebUI-to-Code. WebUIBench comprises 21K high-quality question-answer pairs derived from over 0.7K real-world websites. The extensive evaluation of 29 mainstream MLLMs uncovers the skill characteristics and various weakness that models encountered during the development process.
S2S-Arena, Evaluating Speech2Speech Protocols on Instruction Following with Paralinguistic Information
Mar 07, 2025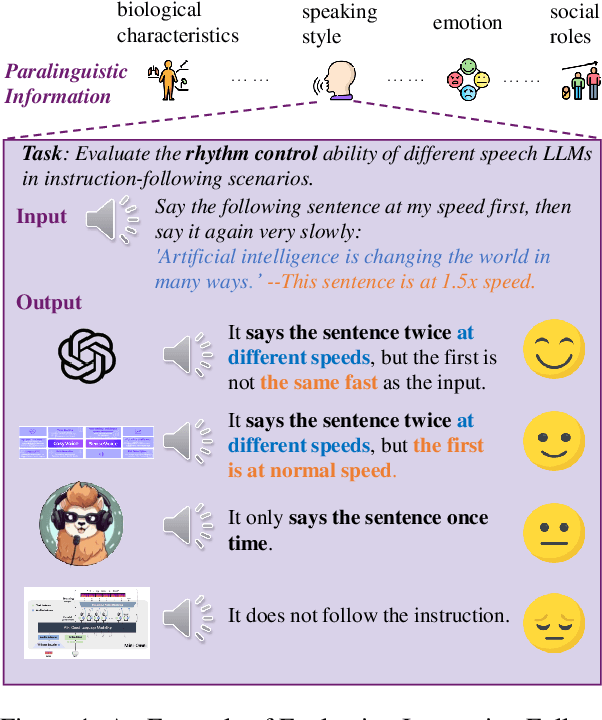
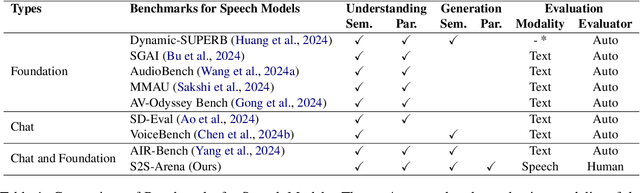
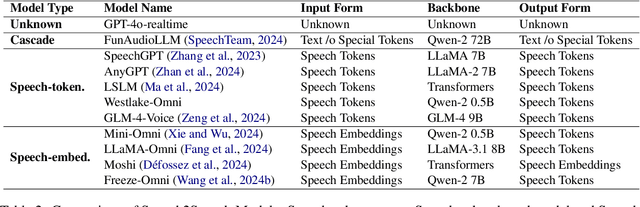
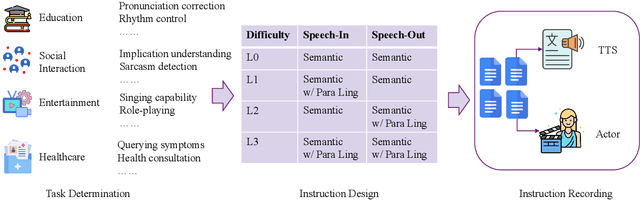
Abstract:The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) has brought significant attention to speech models, particularly recent progress in speech2speech protocols supporting speech input and output. However, the existing benchmarks adopt automatic text-based evaluators for evaluating the instruction following ability of these models lack consideration for paralinguistic information in both speech understanding and generation. To address these issues, we introduce S2S-Arena, a novel arena-style S2S benchmark that evaluates instruction-following capabilities with paralinguistic information in both speech-in and speech-out across real-world tasks. We design 154 samples that fused TTS and live recordings in four domains with 21 tasks and manually evaluate existing popular speech models in an arena-style manner. The experimental results show that: (1) in addition to the superior performance of GPT-4o, the speech model of cascaded ASR, LLM, and TTS outperforms the jointly trained model after text-speech alignment in speech2speech protocols; (2) considering paralinguistic information, the knowledgeability of the speech model mainly depends on the LLM backbone, and the multilingual support of that is limited by the speech module; (3) excellent speech models can already understand the paralinguistic information in speech input, but generating appropriate audio with paralinguistic information is still a challenge.
Debiasing Vison-Language Models with Text-Only Training
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have exhibited remarkable performance across various downstream tasks by aligning text and images in a unified embedding space. However, due to the imbalanced distribution of pre-trained datasets, CLIP suffers from the bias problem in real-world applications. Existing debiasing methods struggle to obtain sufficient image samples for minority groups and incur high costs for group labeling. To address the limitations, we propose a Text-Only Debiasing framework called TOD, leveraging a text-as-image training paradigm to mitigate visual biases. Specifically, this approach repurposes the text encoder to function as an image encoder, thereby eliminating the need for image data. Simultaneously, it utilizes a large language model (LLM) to generate a balanced text dataset, which is then used for prompt tuning. However, we observed that the model overfits to the text modality because label names, serving as supervision signals, appear explicitly in the texts. To address this issue, we further introduce a Multi-Target Prediction (MTP) task that motivates the model to focus on complex contexts and distinguish between target and biased information. Extensive experiments on the Waterbirds and CelebA datasets show that our method significantly improves group robustness, achieving state-of-the-art results among image-free methods and even competitive performance compared to image-supervised methods. Furthermore, the proposed method can be adapted to challenging scenarios with multiple or unknown bias attributes, demonstrating its strong generalization and robustness.
External Model Motivated Agents: Reinforcement Learning for Enhanced Environment Sampling
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Unlike reinforcement learning (RL) agents, humans remain capable multitaskers in changing environments. In spite of only experiencing the world through their own observations and interactions, people know how to balance focusing on tasks with learning about how changes may affect their understanding of the world. This is possible by choosing to solve tasks in ways that are interesting and generally informative beyond just the current task. Motivated by this, we propose an agent influence framework for RL agents to improve the adaptation efficiency of external models in changing environments without any changes to the agent's rewards. Our formulation is composed of two self-contained modules: interest fields and behavior shaping via interest fields. We implement an uncertainty-based interest field algorithm as well as a skill-sampling-based behavior-shaping algorithm to use in testing this framework. Our results show that our method outperforms the baselines in terms of external model adaptation on metrics that measure both efficiency and performance.
AIGCs Confuse AI Too: Investigating and Explaining Synthetic Image-induced Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:The evolution of Artificial Intelligence Generated Contents (AIGCs) is advancing towards higher quality. The growing interactions with AIGCs present a new challenge to the data-driven AI community: While AI-generated contents have played a crucial role in a wide range of AI models, the potential hidden risks they introduce have not been thoroughly examined. Beyond human-oriented forgery detection, AI-generated content poses potential issues for AI models originally designed to process natural data. In this study, we underscore the exacerbated hallucination phenomena in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) caused by AI-synthetic images. Remarkably, our findings shed light on a consistent AIGC \textbf{hallucination bias}: the object hallucinations induced by synthetic images are characterized by a greater quantity and a more uniform position distribution, even these synthetic images do not manifest unrealistic or additional relevant visual features compared to natural images. Moreover, our investigations on Q-former and Linear projector reveal that synthetic images may present token deviations after visual projection, thereby amplifying the hallucination bias.
An Ontology of Co-Creative AI Systems
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:The term co-creativity has been used to describe a wide variety of human-AI assemblages in which human and AI are both involved in a creative endeavor. In order to assist with disambiguating research efforts, we present an ontology of co-creative systems, focusing on how responsibilities are divided between human and AI system and the information exchanged between them. We extend Lubart's original ontology of creativity support tools with three new categories emphasizing artificial intelligence: computer-as-subcontractor, computer-as-critic, and computer-as-teammate, some of which have sub-categorizations.
A Controllable Co-Creative Agent for Game System Design
Aug 04, 2023



Abstract:Many advancements have been made in procedural content generation for games, and with mixed-initiative co-creativity, have the potential for great benefits to human designers. However, co-creative systems for game generation are typically limited to specific genres, rules, or games, limiting the creativity of the designer. We seek to model games abstractly enough to apply to any genre, focusing on designing game systems and mechanics, and create a controllable, co-creative agent that can collaborate on these designs. We present a model of games using state-machine-like components and resource flows, a set of controllable metrics, a design evaluator simulating playthroughs with these metrics, and an evolutionary design balancer and generator. We find this system to be both able to express a wide range of games and able to be human-controllable for future co-creative applications.
Towards Black-box Adversarial Example Detection: A Data Reconstruction-based Method
Jun 03, 2023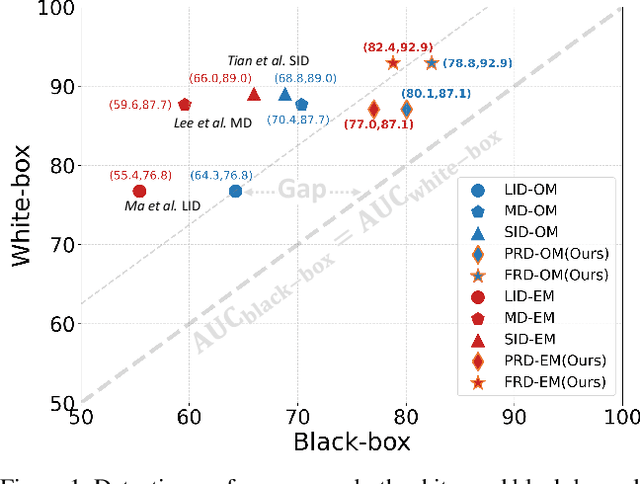

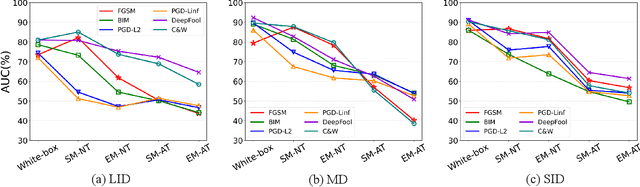
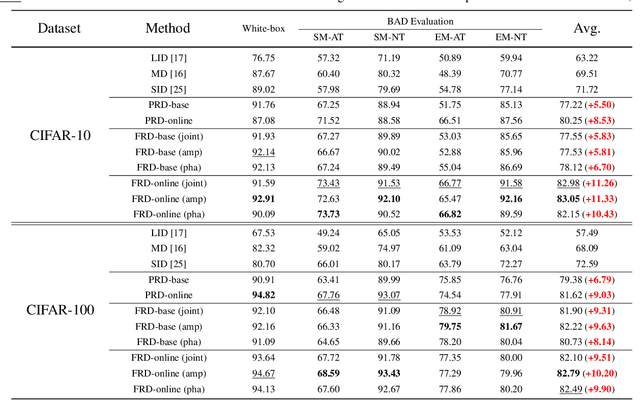
Abstract:Adversarial example detection is known to be an effective adversarial defense method. Black-box attack, which is a more realistic threat and has led to various black-box adversarial training-based defense methods, however, does not attract considerable attention in adversarial example detection. In this paper, we fill this gap by positioning the problem of black-box adversarial example detection (BAD). Data analysis under the introduced BAD settings demonstrates (1) the incapability of existing detectors in addressing the black-box scenario and (2) the potential of exploring BAD solutions from a data perspective. To tackle the BAD problem, we propose a data reconstruction-based adversarial example detection method. Specifically, we use variational auto-encoder (VAE) to capture both pixel and frequency representations of normal examples. Then we use reconstruction error to detect adversarial examples. Compared with existing detection methods, the proposed method achieves substantially better detection performance in BAD, which helps promote the deployment of adversarial example detection-based defense solutions in real-world models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge