Kui Jia
One-Shot Real-World Demonstration Synthesis for Scalable Bimanual Manipulation
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Learning dexterous bimanual manipulation policies critically depends on large-scale, high-quality demonstrations, yet current paradigms face inherent trade-offs: teleoperation provides physically grounded data but is prohibitively labor-intensive, while simulation-based synthesis scales efficiently but suffers from sim-to-real gaps. We present BiDemoSyn, a framework that synthesizes contact-rich, physically feasible bimanual demonstrations from a single real-world example. The key idea is to decompose tasks into invariant coordination blocks and variable, object-dependent adjustments, then adapt them through vision-guided alignment and lightweight trajectory optimization. This enables the generation of thousands of diverse and feasible demonstrations within several hour, without repeated teleoperation or reliance on imperfect simulation. Across six dual-arm tasks, we show that policies trained on BiDemoSyn data generalize robustly to novel object poses and shapes, significantly outperforming recent baselines. By bridging the gap between efficiency and real-world fidelity, BiDemoSyn provides a scalable path toward practical imitation learning for complex bimanual manipulation without compromising physical grounding.
Toward Humanoid Brain-Body Co-design: Joint Optimization of Control and Morphology for Fall Recovery
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots represent a central frontier in embodied intelligence, as their anthropomorphic form enables natural deployment in humans' workspace. Brain-body co-design for humanoids presents a promising approach to realizing this potential by jointly optimizing control policies and physical morphology. Within this context, fall recovery emerges as a critical capability. It not only enhances safety and resilience but also integrates naturally with locomotion systems, thereby advancing the autonomy of humanoids. In this paper, we propose RoboCraft, a scalable humanoid co-design framework for fall recovery that iteratively improves performance through the coupled updates of control policy and morphology. A shared policy pretrained across multiple designs is progressively finetuned on high-performing morphologies, enabling efficient adaptation without retraining from scratch. Concurrently, morphology search is guided by human-inspired priors and optimization algorithms, supported by a priority buffer that balances reevaluation of promising candidates with the exploration of novel designs. Experiments show that \ourmethod{} achieves an average performance gain of 44.55% on seven public humanoid robots, with morphology optimization drives at least 40% of improvements in co-designing four humanoid robots, underscoring the critical role of humanoid co-design.
Nabla-R2D3: Effective and Efficient 3D Diffusion Alignment with 2D Rewards
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Generating high-quality and photorealistic 3D assets remains a longstanding challenge in 3D vision and computer graphics. Although state-of-the-art generative models, such as diffusion models, have made significant progress in 3D generation, they often fall short of human-designed content due to limited ability to follow instructions, align with human preferences, or produce realistic textures, geometries, and physical attributes. In this paper, we introduce Nabla-R2D3, a highly effective and sample-efficient reinforcement learning alignment framework for 3D-native diffusion models using 2D rewards. Built upon the recently proposed Nabla-GFlowNet method, which matches the score function to reward gradients in a principled manner for reward finetuning, our Nabla-R2D3 enables effective adaptation of 3D diffusion models using only 2D reward signals. Extensive experiments show that, unlike vanilla finetuning baselines which either struggle to converge or suffer from reward hacking, Nabla-R2D3 consistently achieves higher rewards and reduced prior forgetting within a few finetuning steps.
SceneLCM: End-to-End Layout-Guided Interactive Indoor Scene Generation with Latent Consistency Model
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Our project page: https://scutyklin.github.io/SceneLCM/. Automated generation of complex, interactive indoor scenes tailored to user prompt remains a formidable challenge. While existing methods achieve indoor scene synthesis, they struggle with rigid editing constraints, physical incoherence, excessive human effort, single-room limitations, and suboptimal material quality. To address these limitations, we propose SceneLCM, an end-to-end framework that synergizes Large Language Model (LLM) for layout design with Latent Consistency Model(LCM) for scene optimization. Our approach decomposes scene generation into four modular pipelines: (1) Layout Generation. We employ LLM-guided 3D spatial reasoning to convert textual descriptions into parametric blueprints(3D layout). And an iterative programmatic validation mechanism iteratively refines layout parameters through LLM-mediated dialogue loops; (2) Furniture Generation. SceneLCM employs Consistency Trajectory Sampling(CTS), a consistency distillation sampling loss guided by LCM, to form fast, semantically rich, and high-quality representations. We also offer two theoretical justification to demonstrate that our CTS loss is equivalent to consistency loss and its distillation error is bounded by the truncation error of the Euler solver; (3) Environment Optimization. We use a multiresolution texture field to encode the appearance of the scene, and optimize via CTS loss. To maintain cross-geometric texture coherence, we introduce a normal-aware cross-attention decoder to predict RGB by cross-attending to the anchors locations in geometrically heterogeneous instance. (4)Physically Editing. SceneLCM supports physically editing by integrating physical simulation, achieved persistent physical realism. Extensive experiments validate SceneLCM's superiority over state-of-the-art techniques, showing its wide-ranging potential for diverse applications.
SignBot: Learning Human-to-Humanoid Sign Language Interaction
May 30, 2025Abstract:Sign language is a natural and visual form of language that uses movements and expressions to convey meaning, serving as a crucial means of communication for individuals who are deaf or hard-of-hearing (DHH). However, the number of people proficient in sign language remains limited, highlighting the need for technological advancements to bridge communication gaps and foster interactions with minorities. Based on recent advancements in embodied humanoid robots, we propose SignBot, a novel framework for human-robot sign language interaction. SignBot integrates a cerebellum-inspired motion control component and a cerebral-oriented module for comprehension and interaction. Specifically, SignBot consists of: 1) Motion Retargeting, which converts human sign language datasets into robot-compatible kinematics; 2) Motion Control, which leverages a learning-based paradigm to develop a robust humanoid control policy for tracking sign language gestures; and 3) Generative Interaction, which incorporates translator, responser, and generator of sign language, thereby enabling natural and effective communication between robots and humans. Simulation and real-world experimental results demonstrate that SignBot can effectively facilitate human-robot interaction and perform sign language motions with diverse robots and datasets. SignBot represents a significant advancement in automatic sign language interaction on embodied humanoid robot platforms, providing a promising solution to improve communication accessibility for the DHH community.
Real-Time Verification of Embodied Reasoning for Generative Skill Acquisition
May 19, 2025Abstract:Generative skill acquisition enables embodied agents to actively learn a scalable and evolving repertoire of control skills, crucial for the advancement of large decision models. While prior approaches often rely on supervision signals from generalist agents (e.g., LLMs), their effectiveness in complex 3D environments remains unclear; exhaustive evaluation incurs substantial computational costs, significantly hindering the efficiency of skill learning. Inspired by recent successes in verification models for mathematical reasoning, we propose VERGSA (Verifying Embodied Reasoning in Generative Skill Acquisition), a framework that systematically integrates real-time verification principles into embodied skill learning. VERGSA establishes 1) a seamless extension from verification of mathematical reasoning into embodied learning by dynamically incorporating contextually relevant tasks into prompts and defining success metrics for both subtasks and overall tasks, and 2) an automated, scalable reward labeling scheme that synthesizes dense reward signals by iteratively finalizing the contribution of scene configuration and subtask learning to overall skill acquisition. To the best of our knowledge, this approach constitutes the first comprehensive training dataset for verification-driven generative skill acquisition, eliminating arduous manual reward engineering. Experiments validate the efficacy of our approach: 1) the exemplar task pool improves the average task success rates by 21%, 2) our verification model boosts success rates by 24% for novel tasks and 36% for encountered tasks, and 3) outperforms LLM-as-a-Judge baselines in verification quality.
Understanding Attention Mechanism in Video Diffusion Models
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Text-to-video (T2V) synthesis models, such as OpenAI's Sora, have garnered significant attention due to their ability to generate high-quality videos from a text prompt. In diffusion-based T2V models, the attention mechanism is a critical component. However, it remains unclear what intermediate features are learned and how attention blocks in T2V models affect various aspects of video synthesis, such as image quality and temporal consistency. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth perturbation analysis of the spatial and temporal attention blocks of T2V models using an information-theoretic approach. Our results indicate that temporal and spatial attention maps affect not only the timing and layout of the videos but also the complexity of spatiotemporal elements and the aesthetic quality of the synthesized videos. Notably, high-entropy attention maps are often key elements linked to superior video quality, whereas low-entropy attention maps are associated with the video's intra-frame structure. Based on our findings, we propose two novel methods to enhance video quality and enable text-guided video editing. These methods rely entirely on lightweight manipulation of the attention matrices in T2V models. The efficacy and effectiveness of our methods are further validated through experimental evaluation across multiple datasets.
PicoPose: Progressive Pixel-to-Pixel Correspondence Learning for Novel Object Pose Estimation
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Novel object pose estimation from RGB images presents a significant challenge for zero-shot generalization, as it involves estimating the relative 6D transformation between an RGB observation and a CAD model of an object that was not seen during training. In this paper, we introduce PicoPose, a novel framework designed to tackle this task using a three-stage pixel-to-pixel correspondence learning process. Firstly, PicoPose matches features from the RGB observation with those from rendered object templates, identifying the best-matched template and establishing coarse correspondences. Secondly, PicoPose smooths the correspondences by globally regressing a 2D affine transformation, including in-plane rotation, scale, and 2D translation, from the coarse correspondence map. Thirdly, PicoPose applies the affine transformation to the feature map of the best-matched template and learns correspondence offsets within local regions to achieve fine-grained correspondences. By progressively refining the correspondences, PicoPose significantly improves the accuracy of object poses computed via PnP/RANSAC. PicoPose achieves state-of-the-art performance on the seven core datasets of the BOP benchmark, demonstrating exceptional generalization to novel objects represented by CAD models or object reference images. Code and models are available at https://github.com/foollh/PicoPose.
Prof. Robot: Differentiable Robot Rendering Without Static and Self-Collisions
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Differentiable rendering has gained significant attention in the field of robotics, with differentiable robot rendering emerging as an effective paradigm for learning robotic actions from image-space supervision. However, the lack of physical world perception in this approach may lead to potential collisions during action optimization. In this work, we introduce a novel improvement on previous efforts by incorporating physical awareness of collisions through the learning of a neural robotic collision classifier. This enables the optimization of actions that avoid collisions with static, non-interactable environments as well as the robot itself. To facilitate effective gradient optimization with the classifier, we identify the underlying issue and propose leveraging Eikonal regularization to ensure consistent gradients for optimization. Our solution can be seamlessly integrated into existing differentiable robot rendering frameworks, utilizing gradients for optimization and providing a foundation for future applications of differentiable rendering in robotics with improved reliability of interactions with the physical world. Both qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the necessity and effectiveness of our method compared to previous solutions.
GAT-Grasp: Gesture-Driven Affordance Transfer for Task-Aware Robotic Grasping
Mar 08, 2025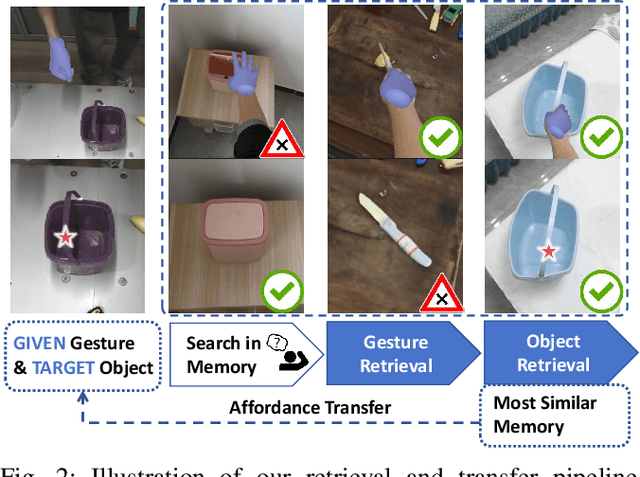
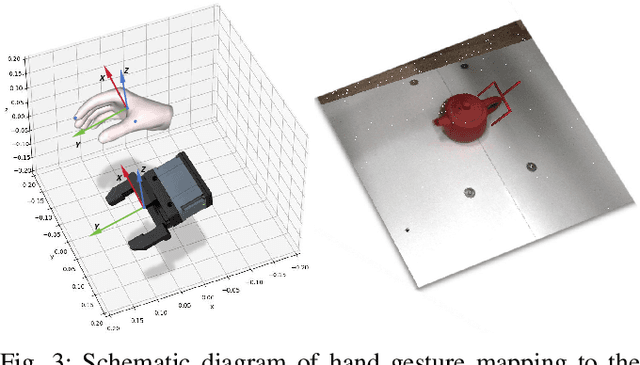
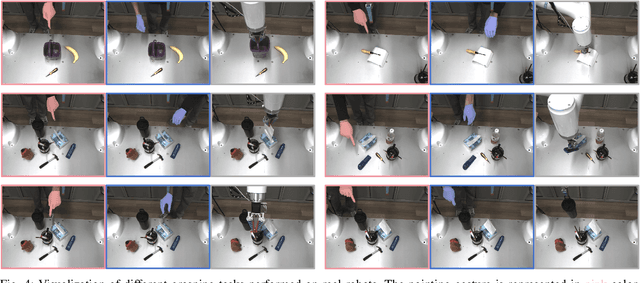
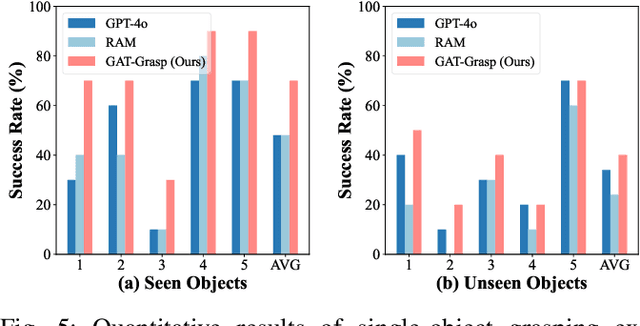
Abstract:Achieving precise and generalizable grasping across diverse objects and environments is essential for intelligent and collaborative robotic systems. However, existing approaches often struggle with ambiguous affordance reasoning and limited adaptability to unseen objects, leading to suboptimal grasp execution. In this work, we propose GAT-Grasp, a gesture-driven grasping framework that directly utilizes human hand gestures to guide the generation of task-specific grasp poses with appropriate positioning and orientation. Specifically, we introduce a retrieval-based affordance transfer paradigm, leveraging the implicit correlation between hand gestures and object affordances to extract grasping knowledge from large-scale human-object interaction videos. By eliminating the reliance on pre-given object priors, GAT-Grasp enables zero-shot generalization to novel objects and cluttered environments. Real-world evaluations confirm its robustness across diverse and unseen scenarios, demonstrating reliable grasp execution in complex task settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge