Zhihao Liang
HY3D-Bench: Generation of 3D Assets
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While recent advances in neural representations and generative models have revolutionized 3D content creation, the field remains constrained by significant data processing bottlenecks. To address this, we introduce HY3D-Bench, an open-source ecosystem designed to establish a unified, high-quality foundation for 3D generation. Our contributions are threefold: (1) We curate a library of 250k high-fidelity 3D objects distilled from large-scale repositories, employing a rigorous pipeline to deliver training-ready artifacts, including watertight meshes and multi-view renderings; (2) We introduce structured part-level decomposition, providing the granularity essential for fine-grained perception and controllable editing; and (3) We bridge real-world distribution gaps via a scalable AIGC synthesis pipeline, contributing 125k synthetic assets to enhance diversity in long-tail categories. Validated empirically through the training of Hunyuan3D-2.1-Small, HY3D-Bench democratizes access to robust data resources, aiming to catalyze innovation across 3D perception, robotics, and digital content creation.
MVD-HuGaS: Human Gaussians from a Single Image via 3D Human Multi-view Diffusion Prior
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:3D human reconstruction from a single image is a challenging problem and has been exclusively studied in the literature. Recently, some methods have resorted to diffusion models for guidance, optimizing a 3D representation via Score Distillation Sampling(SDS) or generating one back-view image for facilitating reconstruction. However, these methods tend to produce unsatisfactory artifacts (\textit{e.g.} flattened human structure or over-smoothing results caused by inconsistent priors from multiple views) and struggle with real-world generalization in the wild. In this work, we present \emph{MVD-HuGaS}, enabling free-view 3D human rendering from a single image via a multi-view human diffusion model. We first generate multi-view images from the single reference image with an enhanced multi-view diffusion model, which is well fine-tuned on high-quality 3D human datasets to incorporate 3D geometry priors and human structure priors. To infer accurate camera poses from the sparse generated multi-view images for reconstruction, an alignment module is introduced to facilitate joint optimization of 3D Gaussians and camera poses. Furthermore, we propose a depth-based Facial Distortion Mitigation module to refine the generated facial regions, thereby improving the overall fidelity of the reconstruction.Finally, leveraging the refined multi-view images, along with their accurate camera poses, MVD-HuGaS optimizes the 3D Gaussians of the target human for high-fidelity free-view renderings. Extensive experiments on Thuman2.0 and 2K2K datasets show that the proposed MVD-HuGaS achieves state-of-the-art performance on single-view 3D human rendering.
LetsTalk: Latent Diffusion Transformer for Talking Video Synthesis
Nov 24, 2024



Abstract:Portrait image animation using audio has rapidly advanced, enabling the creation of increasingly realistic and expressive animated faces. The challenges of this multimodality-guided video generation task involve fusing various modalities while ensuring consistency in timing and portrait. We further seek to produce vivid talking heads. To address these challenges, we present LetsTalk (LatEnt Diffusion TranSformer for Talking Video Synthesis), a diffusion transformer that incorporates modular temporal and spatial attention mechanisms to merge multimodality and enhance spatial-temporal consistency. To handle multimodal conditions, we first summarize three fusion schemes, ranging from shallow to deep fusion compactness, and thoroughly explore their impact and applicability. Then we propose a suitable solution according to the modality differences of image, audio, and video generation. For portrait, we utilize a deep fusion scheme (Symbiotic Fusion) to ensure portrait consistency. For audio, we implement a shallow fusion scheme (Direct Fusion) to achieve audio-animation alignment while preserving diversity. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach generates temporally coherent and realistic videos with enhanced diversity and liveliness.
GUS-IR: Gaussian Splatting with Unified Shading for Inverse Rendering
Nov 12, 2024
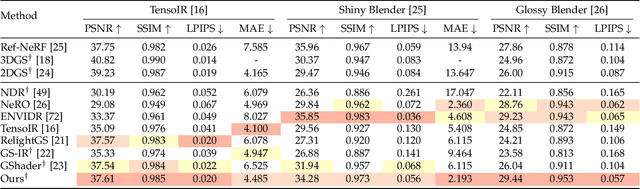

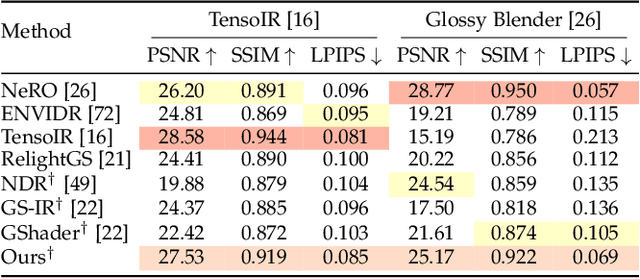
Abstract:Recovering the intrinsic physical attributes of a scene from images, generally termed as the inverse rendering problem, has been a central and challenging task in computer vision and computer graphics. In this paper, we present GUS-IR, a novel framework designed to address the inverse rendering problem for complicated scenes featuring rough and glossy surfaces. This paper starts by analyzing and comparing two prominent shading techniques popularly used for inverse rendering, forward shading and deferred shading, effectiveness in handling complex materials. More importantly, we propose a unified shading solution that combines the advantages of both techniques for better decomposition. In addition, we analyze the normal modeling in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and utilize the shortest axis as normal for each particle in GUS-IR, along with a depth-related regularization, resulting in improved geometric representation and better shape reconstruction. Furthermore, we enhance the probe-based baking scheme proposed by GS-IR to achieve more accurate ambient occlusion modeling to better handle indirect illumination. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the superior performance of GUS-IR in achieving precise intrinsic decomposition and geometric representation, supporting many downstream tasks (such as relighting, retouching) in computer vision, graphics, and extended reality.
GS-ID: Illumination Decomposition on Gaussian Splatting via Diffusion Prior and Parametric Light Source Optimization
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:We present GS-ID, a novel framework for illumination decomposition on Gaussian Splatting, achieving photorealistic novel view synthesis and intuitive light editing. Illumination decomposition is an ill-posed problem facing three main challenges: 1) priors for geometry and material are often lacking; 2) complex illumination conditions involve multiple unknown light sources; and 3) calculating surface shading with numerous light sources is computationally expensive. To address these challenges, we first introduce intrinsic diffusion priors to estimate the attributes for physically based rendering. Then we divide the illumination into environmental and direct components for joint optimization. Last, we employ deferred rendering to reduce the computational load. Our framework uses a learnable environment map and Spherical Gaussians (SGs) to represent light sources parametrically, therefore enabling controllable and photorealistic relighting on Gaussian Splatting. Extensive experiments and applications demonstrate that GS-ID produces state-of-the-art illumination decomposition results while achieving better geometry reconstruction and rendering performance.
Analytic-Splatting: Anti-Aliased 3D Gaussian Splatting via Analytic Integration
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:The 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) gained its popularity recently by combining the advantages of both primitive-based and volumetric 3D representations, resulting in improved quality and efficiency for 3D scene rendering. However, 3DGS is not alias-free, and its rendering at varying resolutions could produce severe blurring or jaggies. This is because 3DGS treats each pixel as an isolated, single point rather than as an area, causing insensitivity to changes in the footprints of pixels. Consequently, this discrete sampling scheme inevitably results in aliasing, owing to the restricted sampling bandwidth. In this paper, we derive an analytical solution to address this issue. More specifically, we use a conditioned logistic function as the analytic approximation of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) in a one-dimensional Gaussian signal and calculate the Gaussian integral by subtracting the CDFs. We then introduce this approximation in the two-dimensional pixel shading, and present Analytic-Splatting, which analytically approximates the Gaussian integral within the 2D-pixel window area to better capture the intensity response of each pixel. Moreover, we use the approximated response of the pixel window integral area to participate in the transmittance calculation of volume rendering, making Analytic-Splatting sensitive to the changes in pixel footprint at different resolutions. Experiments on various datasets validate that our approach has better anti-aliasing capability that gives more details and better fidelity.
Advances in 3D Generation: A Survey
Jan 31, 2024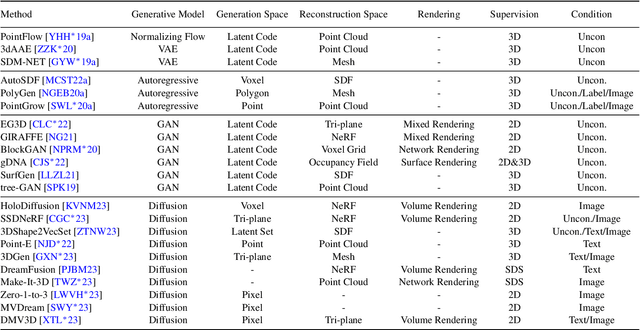
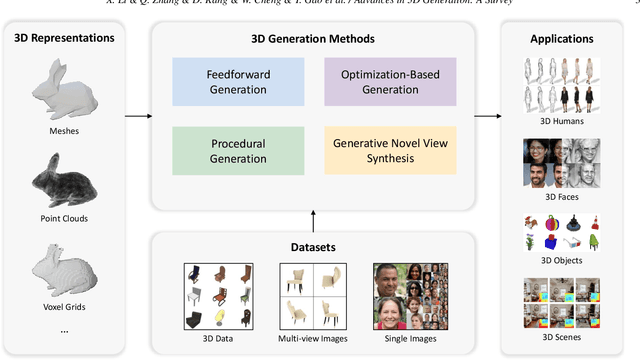
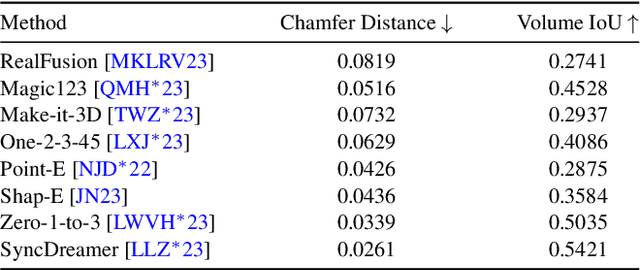
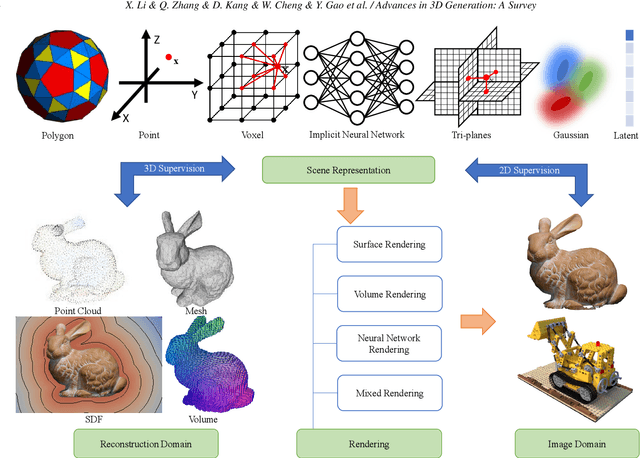
Abstract:Generating 3D models lies at the core of computer graphics and has been the focus of decades of research. With the emergence of advanced neural representations and generative models, the field of 3D content generation is developing rapidly, enabling the creation of increasingly high-quality and diverse 3D models. The rapid growth of this field makes it difficult to stay abreast of all recent developments. In this survey, we aim to introduce the fundamental methodologies of 3D generation methods and establish a structured roadmap, encompassing 3D representation, generation methods, datasets, and corresponding applications. Specifically, we introduce the 3D representations that serve as the backbone for 3D generation. Furthermore, we provide a comprehensive overview of the rapidly growing literature on generation methods, categorized by the type of algorithmic paradigms, including feedforward generation, optimization-based generation, procedural generation, and generative novel view synthesis. Lastly, we discuss available datasets, applications, and open challenges. We hope this survey will help readers explore this exciting topic and foster further advancements in the field of 3D content generation.
Sur2f: A Hybrid Representation for High-Quality and Efficient Surface Reconstruction from Multi-view Images
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:Multi-view surface reconstruction is an ill-posed, inverse problem in 3D vision research. It involves modeling the geometry and appearance with appropriate surface representations. Most of the existing methods rely either on explicit meshes, using surface rendering of meshes for reconstruction, or on implicit field functions, using volume rendering of the fields for reconstruction. The two types of representations in fact have their respective merits. In this work, we propose a new hybrid representation, termed Sur2f, aiming to better benefit from both representations in a complementary manner. Technically, we learn two parallel streams of an implicit signed distance field and an explicit surrogate surface Sur2f mesh, and unify volume rendering of the implicit signed distance function (SDF) and surface rendering of the surrogate mesh with a shared, neural shader; the unified shading promotes their convergence to the same, underlying surface. We synchronize learning of the surrogate mesh by driving its deformation with functions induced from the implicit SDF. In addition, the synchronized surrogate mesh enables surface-guided volume sampling, which greatly improves the sampling efficiency per ray in volume rendering. We conduct thorough experiments showing that Sur$^2$f outperforms existing reconstruction methods and surface representations, including hybrid ones, in terms of both recovery quality and recovery efficiency.
GS-IR: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:We propose GS-IR, a novel inverse rendering approach based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) that leverages forward mapping volume rendering to achieve photorealistic novel view synthesis and relighting results. Unlike previous works that use implicit neural representations and volume rendering (e.g. NeRF), which suffer from low expressive power and high computational complexity, we extend GS, a top-performance representation for novel view synthesis, to estimate scene geometry, surface material, and environment illumination from multi-view images captured under unknown lighting conditions. There are two main problems when introducing GS to inverse rendering: 1) GS does not support producing plausible normal natively; 2) forward mapping (e.g. rasterization and splatting) cannot trace the occlusion like backward mapping (e.g. ray tracing). To address these challenges, our GS-IR proposes an efficient optimization scheme that incorporates a depth-derivation-based regularization for normal estimation and a baking-based occlusion to model indirect lighting. The flexible and expressive GS representation allows us to achieve fast and compact geometry reconstruction, photorealistic novel view synthesis, and effective physically-based rendering. We demonstrate the superiority of our method over baseline methods through qualitative and quantitative evaluations on various challenging scenes.
HelixSurf: A Robust and Efficient Neural Implicit Surface Learning of Indoor Scenes with Iterative Intertwined Regularization
Mar 01, 2023Abstract:Recovery of an underlying scene geometry from multiview images stands as a long-time challenge in computer vision research. The recent promise leverages neural implicit surface learning and differentiable volume rendering, and achieves both the recovery of scene geometry and synthesis of novel views, where deep priors of neural models are used as an inductive smoothness bias. While promising for object-level surfaces, these methods suffer when coping with complex scene surfaces. In the meanwhile, traditional multi-view stereo can recover the geometry of scenes with rich textures, by globally optimizing the local, pixel-wise correspondences across multiple views. We are thus motivated to make use of the complementary benefits from the two strategies, and propose a method termed Helix-shaped neural implicit Surface learning or HelixSurf; HelixSurf uses the intermediate prediction from one strategy as the guidance to regularize the learning of the other one, and conducts such intertwined regularization iteratively during the learning process. We also propose an efficient scheme for differentiable volume rendering in HelixSurf. Experiments on surface reconstruction of indoor scenes show that our method compares favorably with existing methods and is orders of magnitude faster, even when some of existing methods are assisted with auxiliary training data. The source code is available at https://github.com/Gorilla-Lab-SCUT/HelixSurf.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge