Ruixiang Wang
On Path to Multimodal Historical Reasoning: HistBench and HistAgent
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to remarkable progress across domains, yet their capabilities in the humanities, particularly history, remain underexplored. Historical reasoning poses unique challenges for AI, involving multimodal source interpretation, temporal inference, and cross-linguistic analysis. While general-purpose agents perform well on many existing benchmarks, they lack the domain-specific expertise required to engage with historical materials and questions. To address this gap, we introduce HistBench, a new benchmark of 414 high-quality questions designed to evaluate AI's capacity for historical reasoning and authored by more than 40 expert contributors. The tasks span a wide range of historical problems-from factual retrieval based on primary sources to interpretive analysis of manuscripts and images, to interdisciplinary challenges involving archaeology, linguistics, or cultural history. Furthermore, the benchmark dataset spans 29 ancient and modern languages and covers a wide range of historical periods and world regions. Finding the poor performance of LLMs and other agents on HistBench, we further present HistAgent, a history-specific agent equipped with carefully designed tools for OCR, translation, archival search, and image understanding in History. On HistBench, HistAgent based on GPT-4o achieves an accuracy of 27.54% pass@1 and 36.47% pass@2, significantly outperforming LLMs with online search and generalist agents, including GPT-4o (18.60%), DeepSeek-R1(14.49%) and Open Deep Research-smolagents(20.29% pass@1 and 25.12% pass@2). These results highlight the limitations of existing LLMs and generalist agents and demonstrate the advantages of HistAgent for historical reasoning.
GAT-Grasp: Gesture-Driven Affordance Transfer for Task-Aware Robotic Grasping
Mar 08, 2025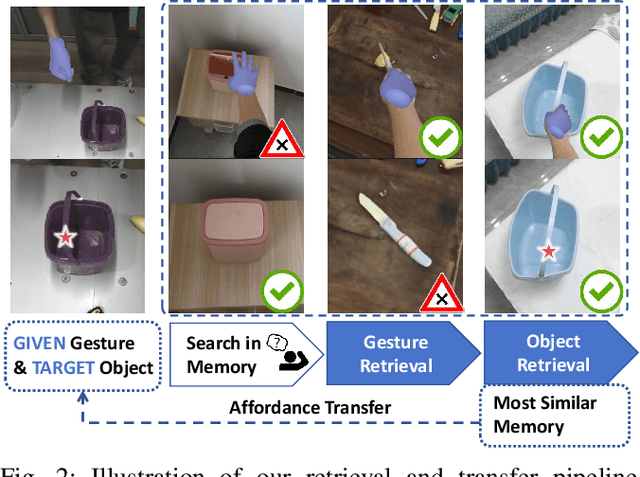
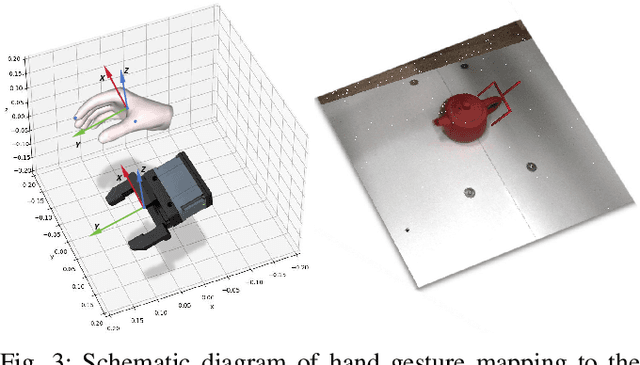
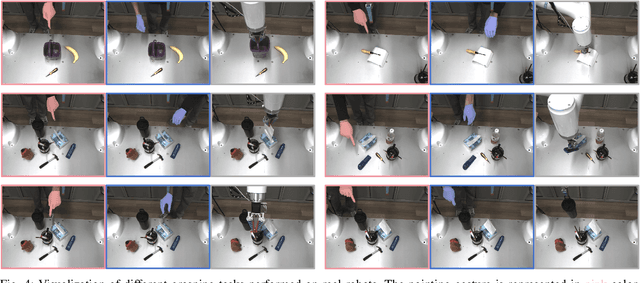
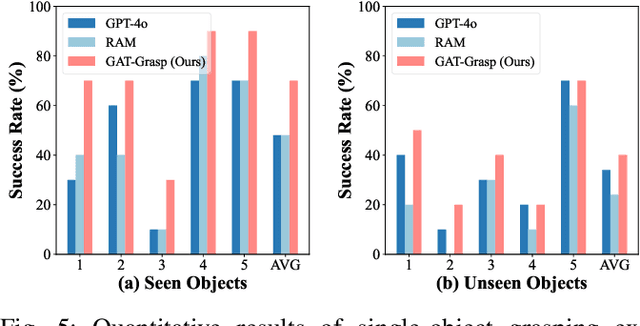
Abstract:Achieving precise and generalizable grasping across diverse objects and environments is essential for intelligent and collaborative robotic systems. However, existing approaches often struggle with ambiguous affordance reasoning and limited adaptability to unseen objects, leading to suboptimal grasp execution. In this work, we propose GAT-Grasp, a gesture-driven grasping framework that directly utilizes human hand gestures to guide the generation of task-specific grasp poses with appropriate positioning and orientation. Specifically, we introduce a retrieval-based affordance transfer paradigm, leveraging the implicit correlation between hand gestures and object affordances to extract grasping knowledge from large-scale human-object interaction videos. By eliminating the reliance on pre-given object priors, GAT-Grasp enables zero-shot generalization to novel objects and cluttered environments. Real-world evaluations confirm its robustness across diverse and unseen scenarios, demonstrating reliable grasp execution in complex task settings.
You Only Teach Once: Learn One-Shot Bimanual Robotic Manipulation from Video Demonstrations
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Bimanual robotic manipulation is a long-standing challenge of embodied intelligence due to its characteristics of dual-arm spatial-temporal coordination and high-dimensional action spaces. Previous studies rely on pre-defined action taxonomies or direct teleoperation to alleviate or circumvent these issues, often making them lack simplicity, versatility and scalability. Differently, we believe that the most effective and efficient way for teaching bimanual manipulation is learning from human demonstrated videos, where rich features such as spatial-temporal positions, dynamic postures, interaction states and dexterous transitions are available almost for free. In this work, we propose the YOTO (You Only Teach Once), which can extract and then inject patterns of bimanual actions from as few as a single binocular observation of hand movements, and teach dual robot arms various complex tasks. Furthermore, based on keyframes-based motion trajectories, we devise a subtle solution for rapidly generating training demonstrations with diverse variations of manipulated objects and their locations. These data can then be used to learn a customized bimanual diffusion policy (BiDP) across diverse scenes. In experiments, YOTO achieves impressive performance in mimicking 5 intricate long-horizon bimanual tasks, possesses strong generalization under different visual and spatial conditions, and outperforms existing visuomotor imitation learning methods in accuracy and efficiency. Our project link is https://hnuzhy.github.io/projects/YOTO.
Bridging the Resource Gap: Deploying Advanced Imitation Learning Models onto Affordable Embedded Platforms
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Advanced imitation learning with structures like the transformer is increasingly demonstrating its advantages in robotics. However, deploying these large-scale models on embedded platforms remains a major challenge. In this paper, we propose a pipeline that facilitates the migration of advanced imitation learning algorithms to edge devices. The process is achieved via an efficient model compression method and a practical asynchronous parallel method Temporal Ensemble with Dropped Actions (TEDA) that enhances the smoothness of operations. To show the efficiency of the proposed pipeline, large-scale imitation learning models are trained on a server and deployed on an edge device to complete various manipulation tasks.
Investigating LLM Applications in E-Commerce
Aug 23, 2024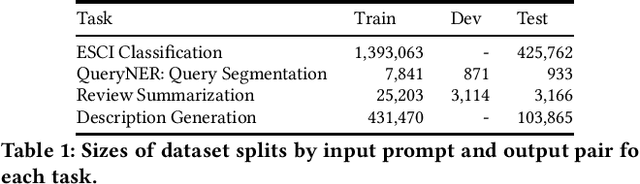
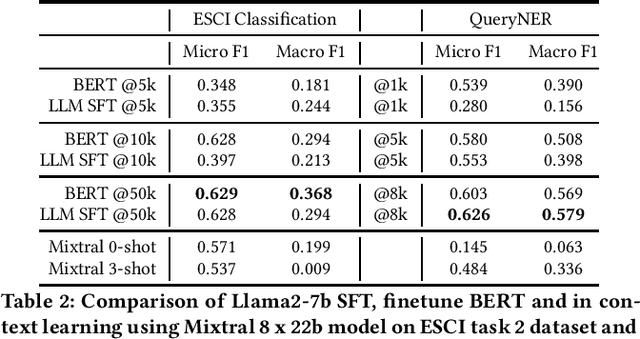
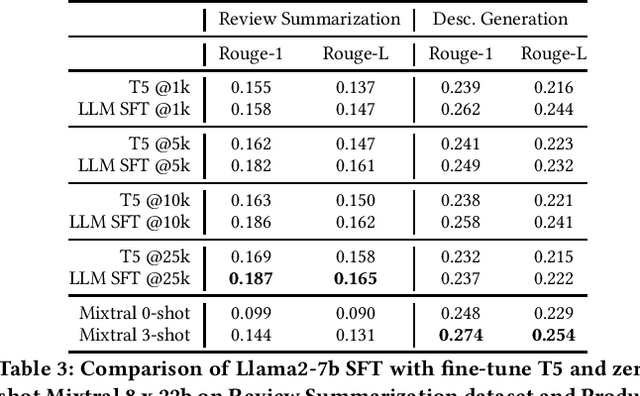

Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized natural language processing in various applications especially in e-commerce. One crucial step before the application of such LLMs in these fields is to understand and compare the performance in different use cases in such tasks. This paper explored the efficacy of LLMs in the e-commerce domain, focusing on instruction-tuning an open source LLM model with public e-commerce datasets of varying sizes and comparing the performance with the conventional models prevalent in industrial applications. We conducted a comprehensive comparison between LLMs and traditional pre-trained language models across specific tasks intrinsic to the e-commerce domain, namely classification, generation, summarization, and named entity recognition (NER). Furthermore, we examined the effectiveness of the current niche industrial application of very large LLM, using in-context learning, in e-commerce specific tasks. Our findings indicate that few-shot inference with very large LLMs often does not outperform fine-tuning smaller pre-trained models, underscoring the importance of task-specific model optimization.Additionally, we investigated different training methodologies such as single-task training, mixed-task training, and LoRA merging both within domain/tasks and between different tasks. Through rigorous experimentation and analysis, this paper offers valuable insights into the potential effectiveness of LLMs to advance natural language processing capabilities within the e-commerce industry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge