Zhe Wu
Boosting Instance Awareness via Cross-View Correlation with 4D Radar and Camera for 3D Object Detection
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:4D millimeter-wave radar has emerged as a promising sensing modality for autonomous driving due to its robustness and affordability. However, its sparse and weak geometric cues make reliable instance activation difficult, limiting the effectiveness of existing radar-camera fusion paradigms. BEV-level fusion offers global scene understanding but suffers from weak instance focus, while perspective-level fusion captures instance details but lacks holistic context. To address these limitations, we propose SIFormer, a scene-instance aware transformer for 3D object detection using 4D radar and camera. SIFormer first suppresses background noise during view transformation through segmentation- and depth-guided localization. It then introduces a cross-view activation mechanism that injects 2D instance cues into BEV space, enabling reliable instance awareness under weak radar geometry. Finally, a transformer-based fusion module aggregates complementary image semantics and radar geometry for robust perception. As a result, with the aim of enhancing instance awareness, SIFormer bridges the gap between the two paradigms, combining their complementary strengths to address inherent sparse nature of radar and improve detection accuracy. Experiments demonstrate that SIFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on View-of-Delft, TJ4DRadSet and NuScenes datasets. Source code is available at github.com/shawnnnkb/SIFormer.
Towards Scalable Meta-Learning of near-optimal Interpretable Models via Synthetic Model Generations
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Decision trees are widely used in high-stakes fields like finance and healthcare due to their interpretability. This work introduces an efficient, scalable method for generating synthetic pre-training data to enable meta-learning of decision trees. Our approach samples near-optimal decision trees synthetically, creating large-scale, realistic datasets. Using the MetaTree transformer architecture, we demonstrate that this method achieves performance comparable to pre-training on real-world data or with computationally expensive optimal decision trees. This strategy significantly reduces computational costs, enhances data generation flexibility, and paves the way for scalable and efficient meta-learning of interpretable decision tree models.
Hi-Agent: Hierarchical Vision-Language Agents for Mobile Device Control
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Building agents that autonomously operate mobile devices has attracted increasing attention. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) show promise, most existing approaches rely on direct state-to-action mappings, which lack structured reasoning and planning, and thus generalize poorly to novel tasks or unseen UI layouts. We introduce Hi-Agent, a trainable hierarchical vision-language agent for mobile control, featuring a high-level reasoning model and a low-level action model that are jointly optimized. For efficient training, we reformulate multi-step decision-making as a sequence of single-step subgoals and propose a foresight advantage function, which leverages execution feedback from the low-level model to guide high-level optimization. This design alleviates the path explosion issue encountered by Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) in long-horizon tasks and enables stable, critic-free joint training. Hi-Agent achieves a new State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) 87.9% task success rate on the Android-in-the-Wild (AitW) benchmark, significantly outperforming prior methods across three paradigms: prompt-based (AppAgent: 17.7%), supervised (Filtered BC: 54.5%), and reinforcement learning-based (DigiRL: 71.9%). It also demonstrates competitive zero-shot generalization on the ScreenSpot-v2 benchmark. On the more challenging AndroidWorld benchmark, Hi-Agent also scales effectively with larger backbones, showing strong adaptability in high-complexity mobile control scenarios.
Recurrent Cross-View Object Geo-Localization
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Cross-view object geo-localization (CVOGL) aims to determine the location of a specific object in high-resolution satellite imagery given a query image with a point prompt. Existing approaches treat CVOGL as a one-shot detection task, directly regressing object locations from cross-view information aggregation, but they are vulnerable to feature noise and lack mechanisms for error correction. In this paper, we propose ReCOT, a Recurrent Cross-view Object geo-localization Transformer, which reformulates CVOGL as a recurrent localization task. ReCOT introduces a set of learnable tokens that encode task-specific intent from the query image and prompt embeddings, and iteratively attend to the reference features to refine the predicted location. To enhance this recurrent process, we incorporate two complementary modules: (1) a SAM-based knowledge distillation strategy that transfers segmentation priors from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to provide clearer semantic guidance without additional inference cost, and (2) a Reference Feature Enhancement Module (RFEM) that introduces a hierarchical attention to emphasize object-relevant regions in the reference features. Extensive experiments on standard CVOGL benchmarks demonstrate that ReCOT achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance while reducing parameters by 60% compared to previous SOTA approaches.
Bridging Modality Gaps in e-Commerce Products via Vision-Language Alignment
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Item information, such as titles and attributes, is essential for effective user engagement in e-commerce. However, manual or semi-manual entry of structured item specifics often produces inconsistent quality, errors, and slow turnaround, especially for Customer-to-Customer sellers. Generating accurate descriptions directly from item images offers a promising alternative. Existing retrieval-based solutions address some of these issues but often miss fine-grained visual details and struggle with niche or specialized categories. We propose Optimized Preference-Based AI for Listings (OPAL), a framework for generating schema-compliant, high-quality item descriptions from images using a fine-tuned multimodal large language model (MLLM). OPAL addresses key challenges in multimodal e-commerce applications, including bridging modality gaps and capturing detailed contextual information. It introduces two data refinement methods: MLLM-Assisted Conformity Enhancement, which ensures alignment with structured schema requirements, and LLM-Assisted Contextual Understanding, which improves the capture of nuanced and fine-grained information from visual inputs. OPAL uses visual instruction tuning combined with direct preference optimization to fine-tune the MLLM, reducing hallucinations and improving robustness across different backbone architectures. We evaluate OPAL on real-world e-commerce datasets, showing that it consistently outperforms baseline methods in both description quality and schema completion rates. These results demonstrate that OPAL effectively bridges the gap between visual and textual modalities, delivering richer, more accurate, and more consistent item descriptions. This work advances automated listing optimization and supports scalable, high-quality content generation in e-commerce platforms.
NEAR$^2$: A Nested Embedding Approach to Efficient Product Retrieval and Ranking
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:E-commerce information retrieval (IR) systems struggle to simultaneously achieve high accuracy in interpreting complex user queries and maintain efficient processing of vast product catalogs. The dual challenge lies in precisely matching user intent with relevant products while managing the computational demands of real-time search across massive inventories. In this paper, we propose a Nested Embedding Approach to product Retrieval and Ranking, called NEAR$^2$, which can achieve up to $12$ times efficiency in embedding size at inference time while introducing no extra cost in training and improving performance in accuracy for various encoder-based Transformer models. We validate our approach using different loss functions for the retrieval and ranking task, including multiple negative ranking loss and online contrastive loss, on four different test sets with various IR challenges such as short and implicit queries. Our approach achieves an improved performance over a smaller embedding dimension, compared to any existing models.
CDFormer: Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection Transformer Against Feature Confusion
May 02, 2025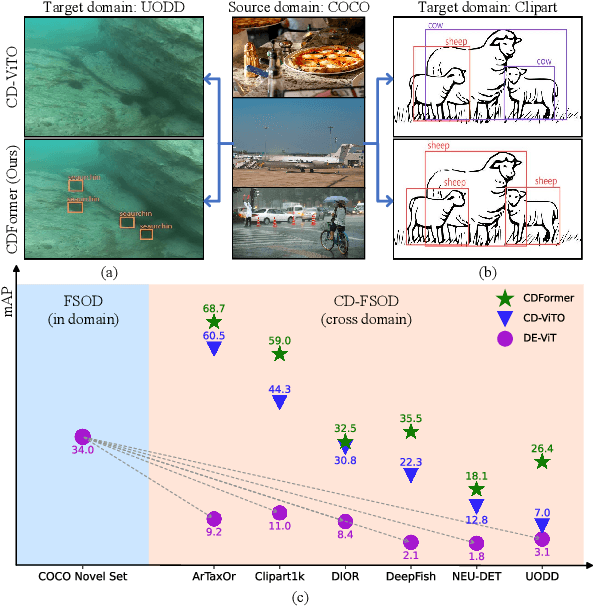
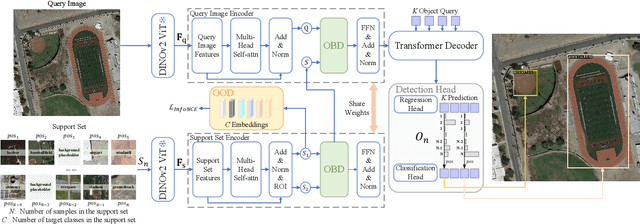

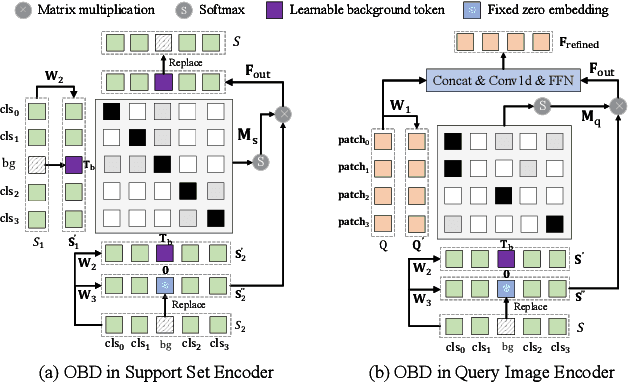
Abstract:Cross-domain few-shot object detection (CD-FSOD) aims to detect novel objects across different domains with limited class instances. Feature confusion, including object-background confusion and object-object confusion, presents significant challenges in both cross-domain and few-shot settings. In this work, we introduce CDFormer, a cross-domain few-shot object detection transformer against feature confusion, to address these challenges. The method specifically tackles feature confusion through two key modules: object-background distinguishing (OBD) and object-object distinguishing (OOD). The OBD module leverages a learnable background token to differentiate between objects and background, while the OOD module enhances the distinction between objects of different classes. Experimental results demonstrate that CDFormer outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches, achieving 12.9% mAP, 11.0% mAP, and 10.4% mAP improvements under the 1/5/10 shot settings, respectively, when fine-tuned.
RestorerID: Towards Tuning-Free Face Restoration with ID Preservation
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Blind face restoration has made great progress in producing high-quality and lifelike images. Yet it remains challenging to preserve the ID information especially when the degradation is heavy. Current reference-guided face restoration approaches either require face alignment or personalized test-tuning, which are unfaithful or time-consuming. In this paper, we propose a tuning-free method named RestorerID that incorporates ID preservation during face restoration. RestorerID is a diffusion model-based method that restores low-quality images with varying levels of degradation by using a single reference image. To achieve this, we propose a unified framework to combine the ID injection with the base blind face restoration model. In addition, we design a novel Face ID Rebalancing Adapter (FIR-Adapter) to tackle the problems of content unconsistency and contours misalignment that are caused by information conflicts between the low-quality input and reference image. Furthermore, by employing an Adaptive ID-Scale Adjusting strategy, RestorerID can produce superior restored images across various levels of degradation. Experimental results on the Celeb-Ref dataset and real-world scenarios demonstrate that RestorerID effectively delivers high-quality face restoration with ID preservation, achieving a superior performance compared to the test-tuning approaches and other reference-guided ones. The code of RestorerID is available at \url{https://github.com/YingJiacheng/RestorerID}.
Centrality-aware Product Retrieval and Ranking
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of improving user experience on e-commerce platforms by enhancing product ranking relevant to users' search queries. Ambiguity and complexity of user queries often lead to a mismatch between the user's intent and retrieved product titles or documents. Recent approaches have proposed the use of Transformer-based models, which need millions of annotated query-title pairs during the pre-training stage, and this data often does not take user intent into account. To tackle this, we curate samples from existing datasets at eBay, manually annotated with buyer-centric relevance scores and centrality scores, which reflect how well the product title matches the users' intent. We introduce a User-intent Centrality Optimization (UCO) approach for existing models, which optimises for the user intent in semantic product search. To that end, we propose a dual-loss based optimisation to handle hard negatives, i.e., product titles that are semantically relevant but do not reflect the user's intent. Our contributions include curating challenging evaluation sets and implementing UCO, resulting in significant product ranking efficiency improvements observed for different evaluation metrics. Our work aims to ensure that the most buyer-centric titles for a query are ranked higher, thereby, enhancing the user experience on e-commerce platforms.
Investigating LLM Applications in E-Commerce
Aug 23, 2024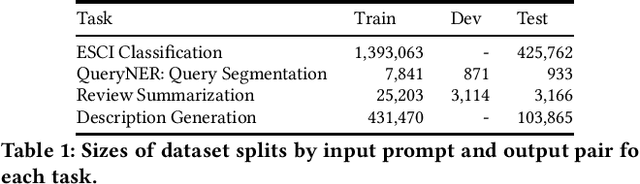
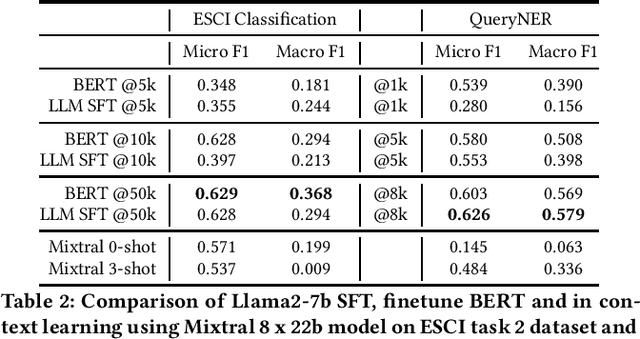
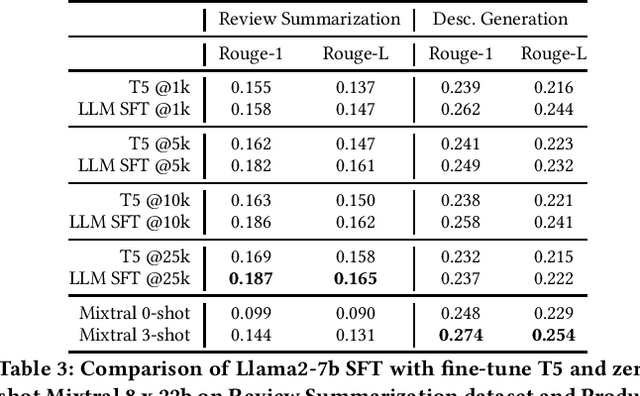

Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized natural language processing in various applications especially in e-commerce. One crucial step before the application of such LLMs in these fields is to understand and compare the performance in different use cases in such tasks. This paper explored the efficacy of LLMs in the e-commerce domain, focusing on instruction-tuning an open source LLM model with public e-commerce datasets of varying sizes and comparing the performance with the conventional models prevalent in industrial applications. We conducted a comprehensive comparison between LLMs and traditional pre-trained language models across specific tasks intrinsic to the e-commerce domain, namely classification, generation, summarization, and named entity recognition (NER). Furthermore, we examined the effectiveness of the current niche industrial application of very large LLM, using in-context learning, in e-commerce specific tasks. Our findings indicate that few-shot inference with very large LLMs often does not outperform fine-tuning smaller pre-trained models, underscoring the importance of task-specific model optimization.Additionally, we investigated different training methodologies such as single-task training, mixed-task training, and LoRA merging both within domain/tasks and between different tasks. Through rigorous experimentation and analysis, this paper offers valuable insights into the potential effectiveness of LLMs to advance natural language processing capabilities within the e-commerce industry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge