Yipeng Zhang
Omni-iEEG: A Large-Scale, Comprehensive iEEG Dataset and Benchmark for Epilepsy Research
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:Epilepsy affects over 50 million people worldwide, and one-third of patients suffer drug-resistant seizures where surgery offers the best chance of seizure freedom. Accurate localization of the epileptogenic zone (EZ) relies on intracranial EEG (iEEG). Clinical workflows, however, remain constrained by labor-intensive manual review. At the same time, existing data-driven approaches are typically developed on single-center datasets that are inconsistent in format and metadata, lack standardized benchmarks, and rarely release pathological event annotations, creating barriers to reproducibility, cross-center validation, and clinical relevance. With extensive efforts to reconcile heterogeneous iEEG formats, metadata, and recordings across publicly available sources, we present $\textbf{Omni-iEEG}$, a large-scale, pre-surgical iEEG resource comprising $\textbf{302 patients}$ and $\textbf{178 hours}$ of high-resolution recordings. The dataset includes harmonized clinical metadata such as seizure onset zones, resections, and surgical outcomes, all validated by board-certified epileptologists. In addition, Omni-iEEG provides over 36K expert-validated annotations of pathological events, enabling robust biomarker studies. Omni-iEEG serves as a bridge between machine learning and epilepsy research. It defines clinically meaningful tasks with unified evaluation metrics grounded in clinical priors, enabling systematic evaluation of models in clinically relevant settings. Beyond benchmarking, we demonstrate the potential of end-to-end modeling on long iEEG segments and highlight the transferability of representations pretrained on non-neurophysiological domains. Together, these contributions establish Omni-iEEG as a foundation for reproducible, generalizable, and clinically translatable epilepsy research. The project page with dataset and code links is available at omni-ieeg.github.io/omni-ieeg.
Self-Supervised Learning from Structural Invariance
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Joint-embedding self-supervised learning (SSL), the key paradigm for unsupervised representation learning from visual data, learns from invariances between semantically-related data pairs. We study the one-to-many mapping problem in SSL, where each datum may be mapped to multiple valid targets. This arises when data pairs come from naturally occurring generative processes, e.g., successive video frames. We show that existing methods struggle to flexibly capture this conditional uncertainty. As a remedy, we introduce a latent variable to account for this uncertainty and derive a variational lower bound on the mutual information between paired embeddings. Our derivation yields a simple regularization term for standard SSL objectives. The resulting method, which we call AdaSSL, applies to both contrastive and distillation-based SSL objectives, and we empirically show its versatility in causal representation learning, fine-grained image understanding, and world modeling on videos.
Scalpel-SAM: A Semi-Supervised Paradigm for Adapting SAM to Infrared Small Object Detection
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Infrared small object detection urgently requires semi-supervised paradigms due to the high cost of annotation. However, existing methods like SAM face significant challenges of domain gaps, inability of encoding physical priors, and inherent architectural complexity. To address this, we designed a Hierarchical MoE Adapter consisting of four white-box neural operators. Building upon this core component, we propose a two-stage paradigm for knowledge distillation and transfer: (1) Prior-Guided Knowledge Distillation, where we use our MoE adapter and 10% of available fully supervised data to distill SAM into an expert teacher (Scalpel-SAM); and (2) Deployment-Oriented Knowledge Transfer, where we use Scalpel-SAM to generate pseudo labels for training lightweight and efficient downstream models. Experiments demonstrate that with minimal annotations, our paradigm enables downstream models to achieve performance comparable to, or even surpassing, their fully supervised counterparts. To our knowledge, this is the first semi-supervised paradigm that systematically addresses the data scarcity issue in IR-SOT using SAM as the teacher model.
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Neural Networks for Few-Shot Credit Risk Assessment
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Quantum Machine Learning (QML) offers a new paradigm for addressing complex financial problems intractable for classical methods. This work specifically tackles the challenge of few-shot credit risk assessment, a critical issue in inclusive finance where data scarcity and imbalance limit the effectiveness of conventional models. To address this, we design and implement a novel hybrid quantum-classical workflow. The methodology first employs an ensemble of classical machine learning models (Logistic Regression, Random Forest, XGBoost) for intelligent feature engineering and dimensionality reduction. Subsequently, a Quantum Neural Network (QNN), trained via the parameter-shift rule, serves as the core classifier. This framework was evaluated through numerical simulations and deployed on the Quafu Quantum Cloud Platform's ScQ-P21 superconducting processor. On a real-world credit dataset of 279 samples, our QNN achieved a robust average AUC of 0.852 +/- 0.027 in simulations and yielded an impressive AUC of 0.88 in the hardware experiment. This performance surpasses a suite of classical benchmarks, with a particularly strong result on the recall metric. This study provides a pragmatic blueprint for applying quantum computing to data-constrained financial scenarios in the NISQ era and offers valuable empirical evidence supporting its potential in high-stakes applications like inclusive finance.
Text to Query Plans for Question Answering on Large Tables
Aug 26, 2025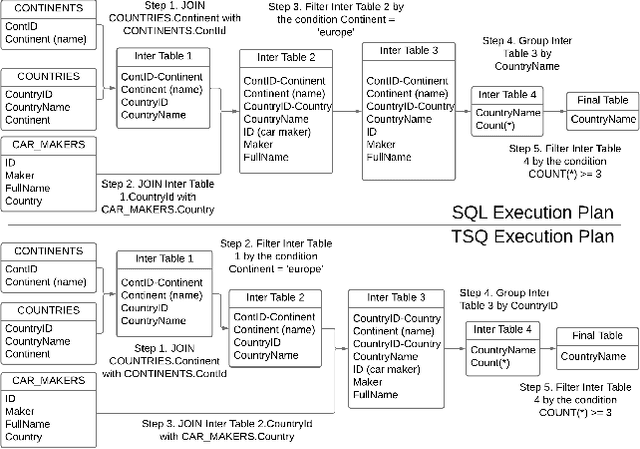
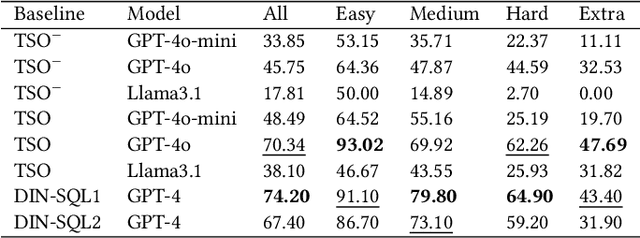
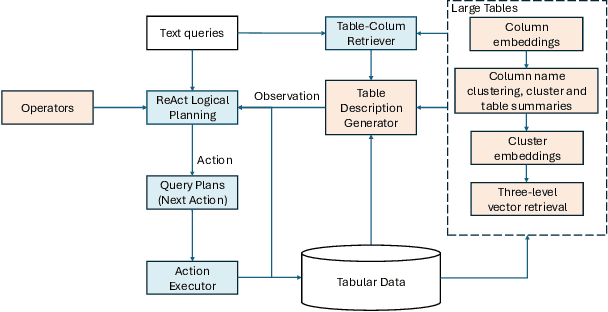

Abstract:Efficient querying and analysis of large tabular datasets remain significant challenges, especially for users without expertise in programming languages like SQL. Text-to-SQL approaches have shown promising performance on benchmark data; however, they inherit SQL's drawbacks, including inefficiency with large datasets and limited support for complex data analyses beyond basic querying. We propose a novel framework that transforms natural language queries into query plans. Our solution is implemented outside traditional databases, allowing us to support classical SQL commands while avoiding SQL's inherent limitations. Additionally, we enable complex analytical functions, such as principal component analysis and anomaly detection, providing greater flexibility and extensibility than traditional SQL capabilities. We leverage LLMs to iteratively interpret queries and construct operation sequences, addressing computational complexity by incrementally building solutions. By executing operations directly on the data, we overcome context length limitations without requiring the entire dataset to be processed by the model. We validate our framework through experiments on both standard databases and large scientific tables, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling extensive datasets and performing sophisticated data analyses.
Bridging Modality Gaps in e-Commerce Products via Vision-Language Alignment
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Item information, such as titles and attributes, is essential for effective user engagement in e-commerce. However, manual or semi-manual entry of structured item specifics often produces inconsistent quality, errors, and slow turnaround, especially for Customer-to-Customer sellers. Generating accurate descriptions directly from item images offers a promising alternative. Existing retrieval-based solutions address some of these issues but often miss fine-grained visual details and struggle with niche or specialized categories. We propose Optimized Preference-Based AI for Listings (OPAL), a framework for generating schema-compliant, high-quality item descriptions from images using a fine-tuned multimodal large language model (MLLM). OPAL addresses key challenges in multimodal e-commerce applications, including bridging modality gaps and capturing detailed contextual information. It introduces two data refinement methods: MLLM-Assisted Conformity Enhancement, which ensures alignment with structured schema requirements, and LLM-Assisted Contextual Understanding, which improves the capture of nuanced and fine-grained information from visual inputs. OPAL uses visual instruction tuning combined with direct preference optimization to fine-tune the MLLM, reducing hallucinations and improving robustness across different backbone architectures. We evaluate OPAL on real-world e-commerce datasets, showing that it consistently outperforms baseline methods in both description quality and schema completion rates. These results demonstrate that OPAL effectively bridges the gap between visual and textual modalities, delivering richer, more accurate, and more consistent item descriptions. This work advances automated listing optimization and supports scalable, high-quality content generation in e-commerce platforms.
Rhomboid Tiling for Geometric Graph Deep Learning
May 14, 2025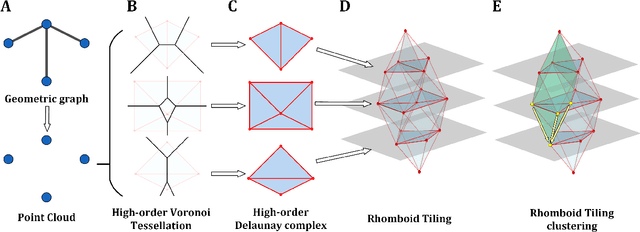
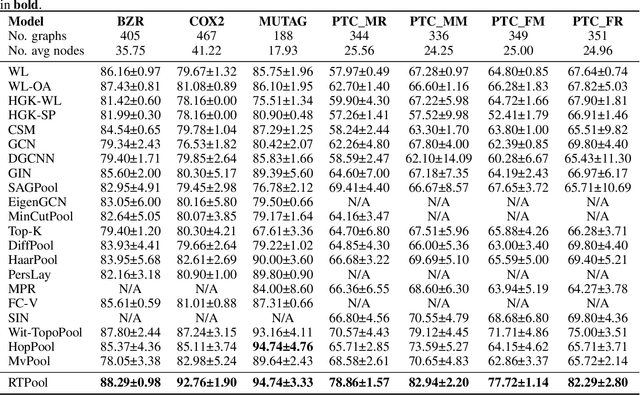
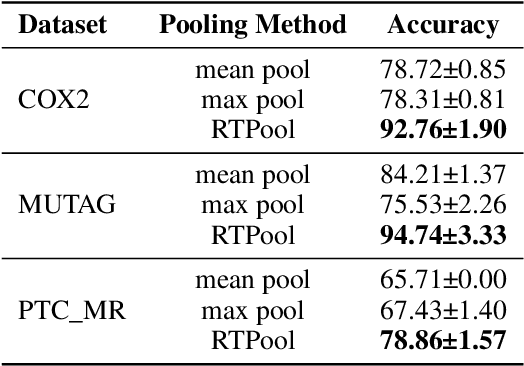
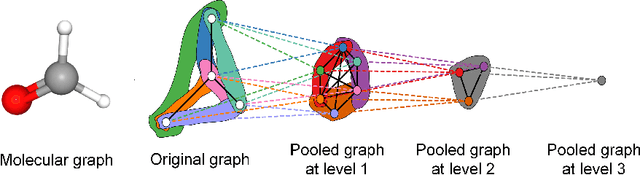
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have proven effective for learning from graph-structured data through their neighborhood-based message passing framework. Many hierarchical graph clustering pooling methods modify this framework by introducing clustering-based strategies, enabling the construction of more expressive and powerful models. However, all of these message passing framework heavily rely on the connectivity structure of graphs, limiting their ability to capture the rich geometric features inherent in geometric graphs. To address this, we propose Rhomboid Tiling (RT) clustering, a novel clustering method based on the rhomboid tiling structure, which performs clustering by leveraging the complex geometric information of the data and effectively extracts its higher-order geometric structures. Moreover, we design RTPool, a hierarchical graph clustering pooling model based on RT clustering for graph classification tasks. The proposed model demonstrates superior performance, outperforming 21 state-of-the-art competitors on all the 7 benchmark datasets.
Modular-Cam: Modular Dynamic Camera-view Video Generation with LLM
Apr 16, 2025
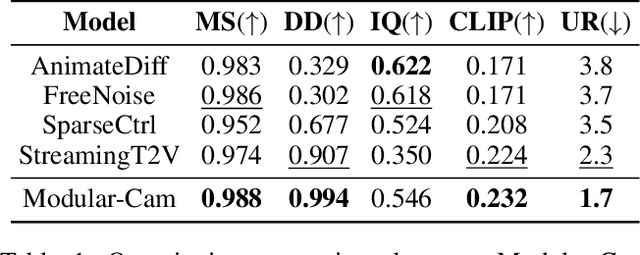
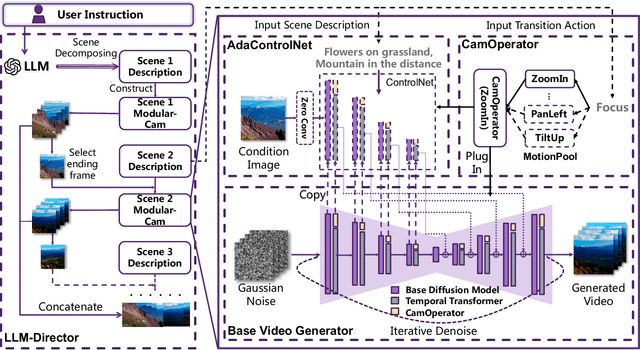
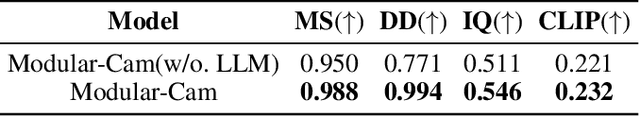
Abstract:Text-to-Video generation, which utilizes the provided text prompt to generate high-quality videos, has drawn increasing attention and achieved great success due to the development of diffusion models recently. Existing methods mainly rely on a pre-trained text encoder to capture the semantic information and perform cross attention with the encoded text prompt to guide the generation of video. However, when it comes to complex prompts that contain dynamic scenes and multiple camera-view transformations, these methods can not decompose the overall information into separate scenes, as well as fail to smoothly change scenes based on the corresponding camera-views. To solve these problems, we propose a novel method, i.e., Modular-Cam. Specifically, to better understand a given complex prompt, we utilize a large language model to analyze user instructions and decouple them into multiple scenes together with transition actions. To generate a video containing dynamic scenes that match the given camera-views, we incorporate the widely-used temporal transformer into the diffusion model to ensure continuity within a single scene and propose CamOperator, a modular network based module that well controls the camera movements. Moreover, we propose AdaControlNet, which utilizes ControlNet to ensure consistency across scenes and adaptively adjusts the color tone of the generated video. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments prove our proposed Modular-Cam's strong capability of generating multi-scene videos together with its ability to achieve fine-grained control of camera movements. Generated results are available at https://modular-cam.github.io.
Towards Self-Improving Systematic Cognition for Next-Generation Foundation MLLMs
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Despite their impressive capabilities, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) face challenges with fine-grained perception and complex reasoning. Prevalent pre-training approaches focus on enhancing perception by training on high-quality image captions due to the extremely high cost of collecting chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning data for improving reasoning. While leveraging advanced MLLMs for caption generation enhances scalability, the outputs often lack comprehensiveness and accuracy. In this paper, we introduce Self-Improving Cognition (SIcog), a self-learning framework designed to construct next-generation foundation MLLMs by enhancing their systematic cognitive capabilities through multimodal pre-training with self-generated data. Specifically, we propose chain-of-description, an approach that improves an MLLM's systematic perception by enabling step-by-step visual understanding, ensuring greater comprehensiveness and accuracy. Additionally, we adopt a structured CoT reasoning technique to enable MLLMs to integrate in-depth multimodal reasoning. To construct a next-generation foundation MLLM with self-improved cognition, SIcog first equips an MLLM with systematic perception and reasoning abilities using minimal external annotations. The enhanced models then generate detailed captions and CoT reasoning data, which are further curated through self-consistency. This curated data is ultimately used to refine the MLLM during multimodal pre-training, facilitating next-generation foundation MLLM construction. Extensive experiments on both low- and high-resolution MLLMs across diverse benchmarks demonstrate that, with merely 213K self-generated pre-training samples, SIcog produces next-generation foundation MLLMs with significantly improved cognition, achieving benchmark-leading performance compared to prevalent pre-training approaches.
Unleashing Correlation and Continuity for Hyperspectral Reconstruction from RGB Images
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Reconstructing Hyperspectral Images (HSI) from RGB images can yield high spatial resolution HSI at a lower cost, demonstrating significant application potential. This paper reveals that local correlation and global continuity of the spectral characteristics are crucial for HSI reconstruction tasks. Therefore, we fully explore these inter-spectral relationships and propose a Correlation and Continuity Network (CCNet) for HSI reconstruction from RGB images. For the correlation of local spectrum, we introduce the Group-wise Spectral Correlation Modeling (GrSCM) module, which efficiently establishes spectral band similarity within a localized range. For the continuity of global spectrum, we design the Neighborhood-wise Spectral Continuity Modeling (NeSCM) module, which employs memory units to recursively model the progressive variation characteristics at the global level. In order to explore the inherent complementarity of these two modules, we design the Patch-wise Adaptive Fusion (PAF) module to efficiently integrate global continuity features into the spectral features in a patch-wise adaptive manner. These innovations enhance the quality of reconstructed HSI. We perform comprehensive comparison and ablation experiments on the mainstream datasets NTIRE2022 and NTIRE2020 for the spectral reconstruction task. Compared to the current advanced spectral reconstruction algorithms, our designed algorithm achieves State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge