Wenwu Zhu
CST
Self-evolving Embodied AI
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Embodied Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an intelligent system formed by agents and their environment through active perception, embodied cognition, and action interaction. Existing embodied AI remains confined to human-crafted setting, in which agents are trained on given memory and construct models for given tasks, enabling fixed embodiments to interact with relatively static environments. Such methods fail in in-the-wild setting characterized by variable embodiments and dynamic open environments. This paper introduces self-evolving embodied AI, a new paradigm in which agents operate based on their changing state and environment with memory self-updating, task self-switching, environment self-prediction, embodiment self-adaptation, and model self-evolution, aiming to achieve continually adaptive intelligence with autonomous evolution. Specifically, we present the definition, framework, components, and mechanisms of self-evolving embodied AI, systematically review state-of-the-art works for realized components, discuss practical applications, and point out future research directions. We believe that self-evolving embodied AI enables agents to autonomously learn and interact with environments in a human-like manner and provide a new perspective toward general artificial intelligence.
Out-of-Distribution Generalization in Graph Foundation Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Graphs are a fundamental data structure for representing relational information in domains such as social networks, molecular systems, and knowledge graphs. However, graph learning models often suffer from limited generalization when applied beyond their training distributions. In practice, distribution shifts may arise from changes in graph structure, domain semantics, available modalities, or task formulations. To address these challenges, graph foundation models (GFMs) have recently emerged, aiming to learn general-purpose representations through large-scale pretraining across diverse graphs and tasks. In this survey, we review recent progress on GFMs from the perspective of out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization. We first discuss the main challenges posed by distribution shifts in graph learning and outline a unified problem setting. We then organize existing approaches based on whether they are designed to operate under a fixed task specification or to support generalization across heterogeneous task formulations, and summarize the corresponding OOD handling strategies and pretraining objectives. Finally, we review common evaluation protocols and discuss open directions for future research. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first survey for OOD generalization in GFMs.
Aerial World Model for Long-horizon Visual Generation and Navigation in 3D Space
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have emerged as powerful embodied agents. One of the core abilities is autonomous navigation in large-scale three-dimensional environments. Existing navigation policies, however, are typically optimized for low-level objectives such as obstacle avoidance and trajectory smoothness, lacking the ability to incorporate high-level semantics into planning. To bridge this gap, we propose ANWM, an aerial navigation world model that predicts future visual observations conditioned on past frames and actions, thereby enabling agents to rank candidate trajectories by their semantic plausibility and navigational utility. ANWM is trained on 4-DoF UAV trajectories and introduces a physics-inspired module: Future Frame Projection (FFP), which projects past frames into future viewpoints to provide coarse geometric priors. This module mitigates representational uncertainty in long-distance visual generation and captures the mapping between 3D trajectories and egocentric observations. Empirical results demonstrate that ANWM significantly outperforms existing world models in long-distance visual forecasting and improves UAV navigation success rates in large-scale environments.
TS-DP: Reinforcement Speculative Decoding For Temporal Adaptive Diffusion Policy Acceleration
Dec 13, 2025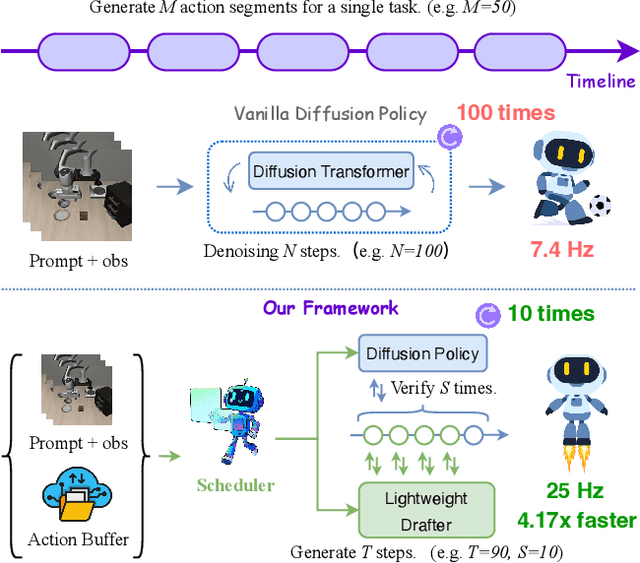
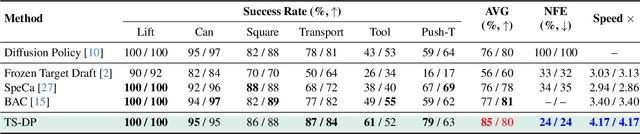
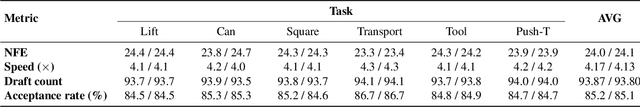
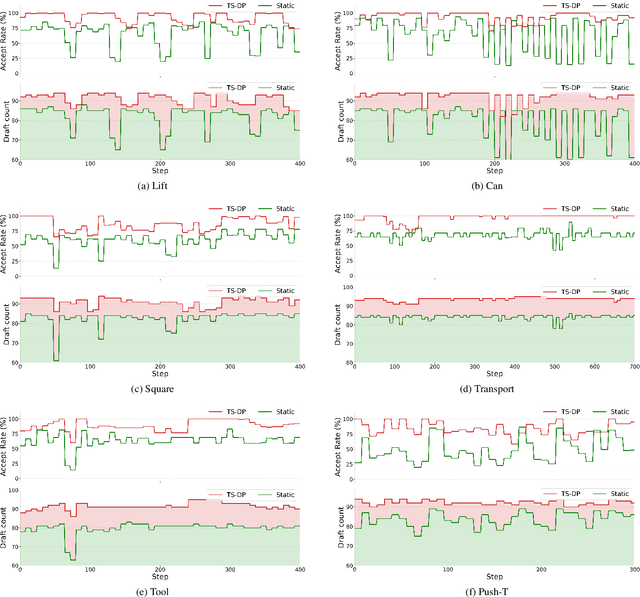
Abstract:Diffusion Policy (DP) excels in embodied control but suffers from high inference latency and computational cost due to multiple iterative denoising steps. The temporal complexity of embodied tasks demands a dynamic and adaptable computation mode. Static and lossy acceleration methods, such as quantization, fail to handle such dynamic embodied tasks, while speculative decoding offers a lossless and adaptive yet underexplored alternative for DP. However, it is non-trivial to address the following challenges: how to match the base model's denoising quality at lower cost under time-varying task difficulty in embodied settings, and how to dynamically and interactively adjust computation based on task difficulty in such environments. In this paper, we propose Temporal-aware Reinforcement-based Speculative Diffusion Policy (TS-DP), the first framework that enables speculative decoding for DP with temporal adaptivity. First, to handle dynamic environments where task difficulty varies over time, we distill a Transformer-based drafter to imitate the base model and replace its costly denoising calls. Second, an RL-based scheduler further adapts to time-varying task difficulty by adjusting speculative parameters to maintain accuracy while improving efficiency. Extensive experiments across diverse embodied environments demonstrate that TS-DP achieves up to 4.17 times faster inference with over 94% accepted drafts, reaching an inference frequency of 25 Hz and enabling real-time diffusion-based control without performance degradation.
SP-VLA: A Joint Model Scheduling and Token Pruning Approach for VLA Model Acceleration
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have attracted increasing attention for their strong control capabilities. However, their high computational cost and low execution frequency hinder their suitability for real-time tasks such as robotic manipulation and autonomous navigation. Existing VLA acceleration methods primarily focus on structural optimization, overlooking the fact that these models operate in sequential decision-making environments. As a result, temporal redundancy in sequential action generation and spatial redundancy in visual input remain unaddressed. To this end, we propose SP-VLA, a unified framework that accelerates VLA models by jointly scheduling models and pruning tokens. Specifically, we design an action-aware model scheduling mechanism that reduces temporal redundancy by dynamically switching between VLA model and a lightweight generator. Inspired by the human motion pattern of focusing on key decision points while relying on intuition for other actions, we categorize VLA actions into deliberative and intuitive, assigning the former to the VLA model and the latter to the lightweight generator, enabling frequency-adaptive execution through collaborative model scheduling. To address spatial redundancy, we further develop a spatio-semantic dual-aware token pruning method. Tokens are classified into spatial and semantic types and pruned based on their dual-aware importance to accelerate VLA inference. These two mechanisms work jointly to guide the VLA in focusing on critical actions and salient visual information, achieving effective acceleration while maintaining high accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves up to 1.5$\times$ acceleration with less than 3% drop in accuracy, outperforming existing approaches in multiple tasks.
Dynamic Mixture of Curriculum LoRA Experts for Continual Multimodal Instruction Tuning
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Continual multimodal instruction tuning is crucial for adapting Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to evolving tasks. However, most existing methods adopt a fixed architecture, struggling with adapting to new tasks due to static model capacity. We propose to evolve the architecture under parameter budgets for dynamic task adaptation, which remains unexplored and imposes two challenges: 1) task architecture conflict, where different tasks require varying layer-wise adaptations, and 2) modality imbalance, where different tasks rely unevenly on modalities, leading to unbalanced updates. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Dynamic Mixture of Curriculum LoRA Experts (D-MoLE) method, which automatically evolves MLLM's architecture with controlled parameter budgets to continually adapt to new tasks while retaining previously learned knowledge. Specifically, we propose a dynamic layer-wise expert allocator, which automatically allocates LoRA experts across layers to resolve architecture conflicts, and routes instructions layer-wisely to facilitate knowledge sharing among experts. Then, we propose a gradient-based inter-modal continual curriculum, which adjusts the update ratio of each module in MLLM based on the difficulty of each modality within the task to alleviate the modality imbalance problem. Extensive experiments show that D-MoLE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving a 15% average improvement over the best baseline. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of continual learning for MLLMs from an architectural perspective.
Towards Multi-modal Graph Large Language Model
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal graphs, which integrate diverse multi-modal features and relations, are ubiquitous in real-world applications. However, existing multi-modal graph learning methods are typically trained from scratch for specific graph data and tasks, failing to generalize across various multi-modal graph data and tasks. To bridge this gap, we explore the potential of Multi-modal Graph Large Language Models (MG-LLM) to unify and generalize across diverse multi-modal graph data and tasks. We propose a unified framework of multi-modal graph data, task, and model, discovering the inherent multi-granularity and multi-scale characteristics in multi-modal graphs. Specifically, we present five key desired characteristics for MG-LLM: 1) unified space for multi-modal structures and attributes, 2) capability of handling diverse multi-modal graph tasks, 3) multi-modal graph in-context learning, 4) multi-modal graph interaction with natural language, and 5) multi-modal graph reasoning. We then elaborate on the key challenges, review related works, and highlight promising future research directions towards realizing these ambitious characteristics. Finally, we summarize existing multi-modal graph datasets pertinent for model training. We believe this paper can contribute to the ongoing advancement of the research towards MG-LLM for generalization across multi-modal graph data and tasks.
Modular Machine Learning: An Indispensable Path towards New-Generation Large Language Models
Apr 28, 2025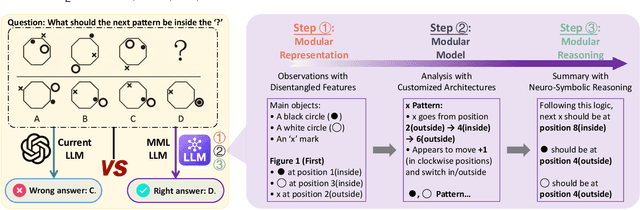
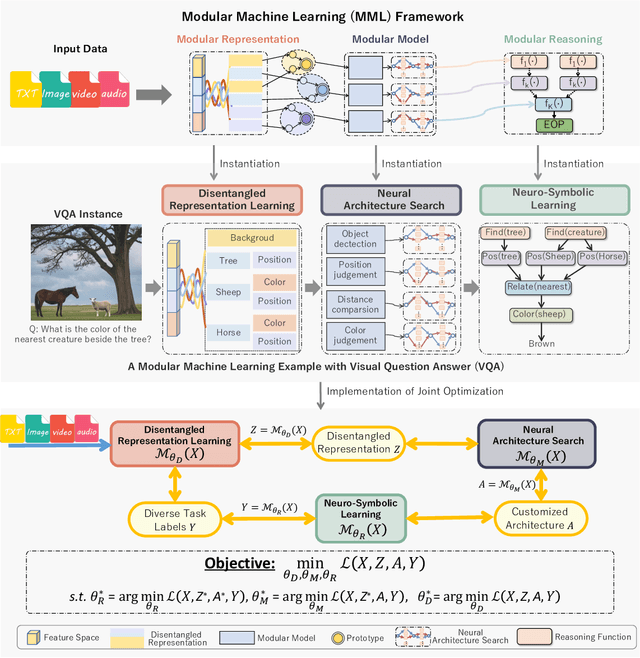
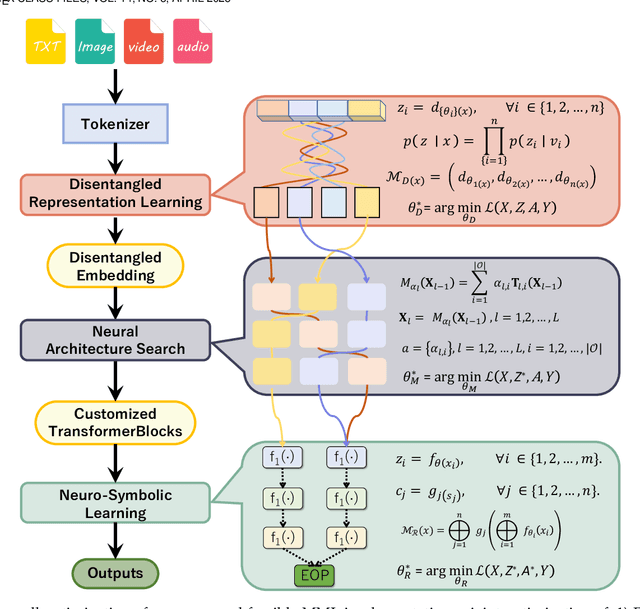
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have dramatically advanced machine learning research including natural language processing, computer vision, data mining, etc., yet they still exhibit critical limitations in reasoning, factual consistency, and interpretability. In this paper, we introduce a novel learning paradigm -- Modular Machine Learning (MML) -- as an essential approach toward new-generation LLMs. MML decomposes the complex structure of LLMs into three interdependent components: modular representation, modular model, and modular reasoning, aiming to enhance LLMs' capability of counterfactual reasoning, mitigating hallucinations, as well as promoting fairness, safety, and transparency. Specifically, the proposed MML paradigm can: i) clarify the internal working mechanism of LLMs through the disentanglement of semantic components; ii) allow for flexible and task-adaptive model design; iii) enable interpretable and logic-driven decision-making process. We present a feasible implementation of MML-based LLMs via leveraging advanced techniques such as disentangled representation learning, neural architecture search and neuro-symbolic learning. We critically identify key challenges, such as the integration of continuous neural and discrete symbolic processes, joint optimization, and computational scalability, present promising future research directions that deserve further exploration. Ultimately, the integration of the MML paradigm with LLMs has the potential to bridge the gap between statistical (deep) learning and formal (logical) reasoning, thereby paving the way for robust, adaptable, and trustworthy AI systems across a wide range of real-world applications.
Embodied-R: Collaborative Framework for Activating Embodied Spatial Reasoning in Foundation Models via Reinforcement Learning
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Humans can perceive and reason about spatial relationships from sequential visual observations, such as egocentric video streams. However, how pretrained models acquire such abilities, especially high-level reasoning, remains unclear. This paper introduces Embodied-R, a collaborative framework combining large-scale Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for perception and small-scale Language Models (LMs) for reasoning. Using Reinforcement Learning (RL) with a novel reward system considering think-answer logical consistency, the model achieves slow-thinking capabilities with limited computational resources. After training on only 5k embodied video samples, Embodied-R with a 3B LM matches state-of-the-art multimodal reasoning models (OpenAI-o1, Gemini-2.5-pro) on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution embodied spatial reasoning tasks. Embodied-R also exhibits emergent thinking patterns such as systematic analysis and contextual integration. We further explore research questions including response length, training on VLM, strategies for reward design, and differences in model generalization after SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning) and RL training.
Modular-Cam: Modular Dynamic Camera-view Video Generation with LLM
Apr 16, 2025
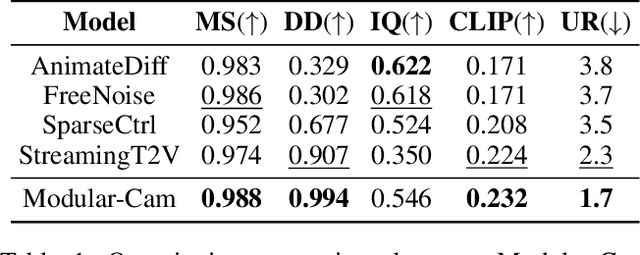
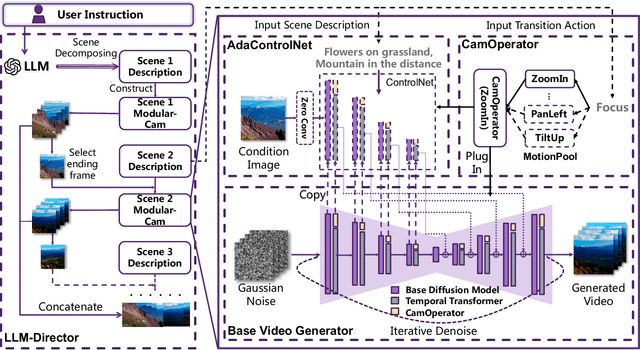
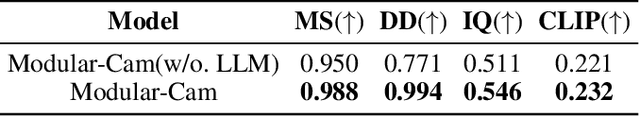
Abstract:Text-to-Video generation, which utilizes the provided text prompt to generate high-quality videos, has drawn increasing attention and achieved great success due to the development of diffusion models recently. Existing methods mainly rely on a pre-trained text encoder to capture the semantic information and perform cross attention with the encoded text prompt to guide the generation of video. However, when it comes to complex prompts that contain dynamic scenes and multiple camera-view transformations, these methods can not decompose the overall information into separate scenes, as well as fail to smoothly change scenes based on the corresponding camera-views. To solve these problems, we propose a novel method, i.e., Modular-Cam. Specifically, to better understand a given complex prompt, we utilize a large language model to analyze user instructions and decouple them into multiple scenes together with transition actions. To generate a video containing dynamic scenes that match the given camera-views, we incorporate the widely-used temporal transformer into the diffusion model to ensure continuity within a single scene and propose CamOperator, a modular network based module that well controls the camera movements. Moreover, we propose AdaControlNet, which utilizes ControlNet to ensure consistency across scenes and adaptively adjusts the color tone of the generated video. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments prove our proposed Modular-Cam's strong capability of generating multi-scene videos together with its ability to achieve fine-grained control of camera movements. Generated results are available at https://modular-cam.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge