Guangyao Li
Crab: A Unified Audio-Visual Scene Understanding Model with Explicit Cooperation
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:In recent years, numerous tasks have been proposed to encourage model to develop specified capability in understanding audio-visual scene, primarily categorized into temporal localization, spatial localization, spatio-temporal reasoning, and pixel-level understanding. Instead, human possesses a unified understanding ability for diversified tasks. Therefore, designing an audio-visual model with general capability to unify these tasks is of great value. However, simply joint training for all tasks can lead to interference due to the heterogeneity of audiovisual data and complex relationship among tasks. We argue that this problem can be solved through explicit cooperation among tasks. To achieve this goal, we propose a unified learning method which achieves explicit inter-task cooperation from both the perspectives of data and model thoroughly. Specifically, considering the labels of existing datasets are simple words, we carefully refine these datasets and construct an Audio-Visual Unified Instruction-tuning dataset with Explicit reasoning process (AV-UIE), which clarifies the cooperative relationship among tasks. Subsequently, to facilitate concrete cooperation in learning stage, an interaction-aware LoRA structure with multiple LoRA heads is designed to learn different aspects of audiovisual data interaction. By unifying the explicit cooperation across the data and model aspect, our method not only surpasses existing unified audio-visual model on multiple tasks, but also outperforms most specialized models for certain tasks. Furthermore, we also visualize the process of explicit cooperation and surprisingly find that each LoRA head has certain audio-visual understanding ability. Code and dataset: https://github.com/GeWu-Lab/Crab
EvoAgent: Agent Autonomous Evolution with Continual World Model for Long-Horizon Tasks
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Completing Long-Horizon (LH) tasks in open-ended worlds is an important yet difficult problem for embodied agents. Existing approaches suffer from two key challenges: (1) they heavily rely on experiences obtained from human-created data or curricula, lacking the ability to continuously update multimodal experiences, and (2) they may encounter catastrophic forgetting issues when faced with new tasks, lacking the ability to continuously update world knowledge. To solve these challenges, this paper presents EvoAgent, an autonomous-evolving agent with a continual World Model (WM), which can autonomously complete various LH tasks across environments through self-planning, self-control, and self-reflection, without human intervention. Our proposed EvoAgent contains three modules, i.e., i) the memory-driven planner which uses an LLM along with the WM and interaction memory, to convert LH tasks into executable sub-tasks; ii) the WM-guided action controller which leverages WM to generate low-level actions and incorporates a self-verification mechanism to update multimodal experiences; iii) the experience-inspired reflector which implements a two-stage curriculum learning algorithm to select experiences for task-adaptive WM updates. Moreover, we develop a continual World Model for EvoAgent, which can continuously update the multimodal experience pool and world knowledge through closed-loop dynamics. We conducted extensive experiments on Minecraft, compared with existing methods, EvoAgent can achieve an average success rate improvement of 105% and reduce ineffective actions by more than 6x.
Adaptive Prompt Learning with SAM for Few-shot Scanning Probe Microscope Image Segmentation
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated strong performance in image segmentation of natural scene images. However, its effectiveness diminishes markedly when applied to specific scientific domains, such as Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM) images. This decline in accuracy can be attributed to the distinct data distribution and limited availability of the data inherent in the scientific images. On the other hand, the acquisition of adequate SPM datasets is both time-intensive and laborious as well as skill-dependent. To address these challenges, we propose an Adaptive Prompt Learning with SAM (APL-SAM) framework tailored for few-shot SPM image segmentation. Our approach incorporates two key innovations to enhance SAM: 1) An Adaptive Prompt Learning module leverages few-shot embeddings derived from limited support set to learn adaptively central representatives, serving as visual prompts. This innovation eliminates the need for time-consuming online user interactions for providing prompts, such as exhaustively marking points and bounding boxes slice by slice; 2) A multi-source, multi-level mask decoder specifically designed for few-shot SPM image segmentation is introduced, which can effectively capture the correspondence between the support and query images. To facilitate comprehensive training and evaluation, we introduce a new dataset, SPM-Seg, curated for SPM image segmentation. Extensive experiments on this dataset reveal that the proposed APL-SAM framework significantly outperforms the original SAM, achieving over a 30% improvement in terms of Dice Similarity Coefficient with only one-shot guidance. Moreover, APL-SAM surpasses state-of-the-art few-shot segmentation methods and even fully supervised approaches in performance. Code and dataset used in this study will be made available upon acceptance.
Multi-weather Cross-view Geo-localization Using Denoising Diffusion Models
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization in GNSS-denied environments aims to determine an unknown location by matching drone-view images with the correct geo-tagged satellite-view images from a large gallery. Recent research shows that learning discriminative image representations under specific weather conditions can significantly enhance performance. However, the frequent occurrence of unseen extreme weather conditions hinders progress. This paper introduces MCGF, a Multi-weather Cross-view Geo-localization Framework designed to dynamically adapt to unseen weather conditions. MCGF establishes a joint optimization between image restoration and geo-localization using denoising diffusion models. For image restoration, MCGF incorporates a shared encoder and a lightweight restoration module to help the backbone eliminate weather-specific information. For geo-localization, MCGF uses EVA-02 as a backbone for feature extraction, with cross-entropy loss for training and cosine distance for testing. Extensive experiments on University160k-WX demonstrate that MCGF achieves competitive results for geo-localization in varying weather conditions.
Boosting Audio Visual Question Answering via Key Semantic-Aware Cues
Jul 30, 2024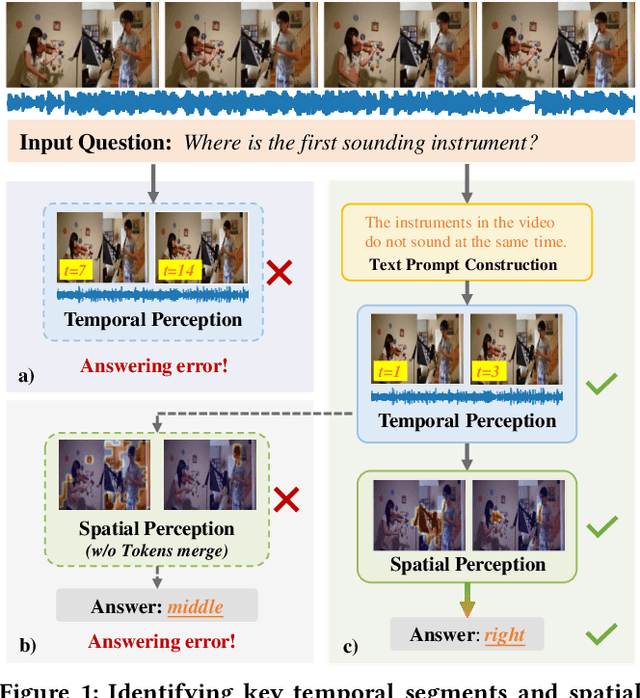
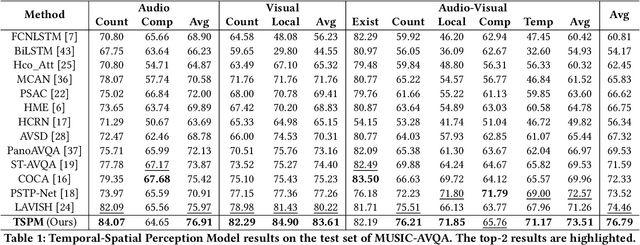
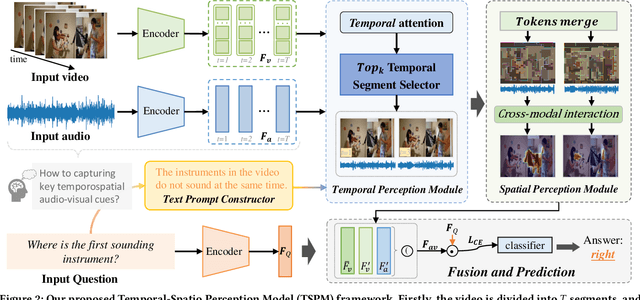
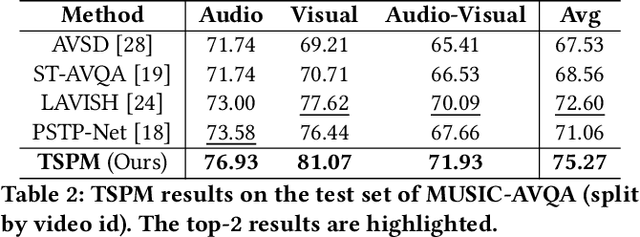
Abstract:The Audio Visual Question Answering (AVQA) task aims to answer questions related to various visual objects, sounds, and their interactions in videos. Such naturally multimodal videos contain rich and complex dynamic audio-visual components, with only a portion of them closely related to the given questions. Hence, effectively perceiving audio-visual cues relevant to the given questions is crucial for correctly answering them. In this paper, we propose a Temporal-Spatial Perception Model (TSPM), which aims to empower the model to perceive key visual and auditory cues related to the questions. Specifically, considering the challenge of aligning non-declarative questions and visual representations into the same semantic space using visual-language pretrained models, we construct declarative sentence prompts derived from the question template, to assist the temporal perception module in better identifying critical segments relevant to the questions. Subsequently, a spatial perception module is designed to merge visual tokens from selected segments to highlight key latent targets, followed by cross-modal interaction with audio to perceive potential sound-aware areas. Finally, the significant temporal-spatial cues from these modules are integrated to answer the question. Extensive experiments on multiple AVQA benchmarks demonstrate that our framework excels not only in understanding audio-visual scenes but also in answering complex questions effectively. Code is available at https://github.com/GeWu-Lab/TSPM.
Ref-AVS: Refer and Segment Objects in Audio-Visual Scenes
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Traditional reference segmentation tasks have predominantly focused on silent visual scenes, neglecting the integral role of multimodal perception and interaction in human experiences. In this work, we introduce a novel task called Reference Audio-Visual Segmentation (Ref-AVS), which seeks to segment objects within the visual domain based on expressions containing multimodal cues. Such expressions are articulated in natural language forms but are enriched with multimodal cues, including audio and visual descriptions. To facilitate this research, we construct the first Ref-AVS benchmark, which provides pixel-level annotations for objects described in corresponding multimodal-cue expressions. To tackle the Ref-AVS task, we propose a new method that adequately utilizes multimodal cues to offer precise segmentation guidance. Finally, we conduct quantitative and qualitative experiments on three test subsets to compare our approach with existing methods from related tasks. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, highlighting its capability to precisely segment objects using multimodal-cue expressions. Dataset is available at \href{https://gewu-lab.github.io/Ref-AVS}{https://gewu-lab.github.io/Ref-AVS}.
CM-PIE: Cross-modal perception for interactive-enhanced audio-visual video parsing
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Audio-visual video parsing is the task of categorizing a video at the segment level with weak labels, and predicting them as audible or visible events. Recent methods for this task leverage the attention mechanism to capture the semantic correlations among the whole video across the audio-visual modalities. However, these approaches have overlooked the importance of individual segments within a video and the relationship among them, and tend to rely on a single modality when learning features. In this paper, we propose a novel interactive-enhanced cross-modal perception method~(CM-PIE), which can learn fine-grained features by applying a segment-based attention module. Furthermore, a cross-modal aggregation block is introduced to jointly optimize the semantic representation of audio and visual signals by enhancing inter-modal interactions. The experimental results show that our model offers improved parsing performance on the Look, Listen, and Parse dataset compared to other methods.
Prompting Segmentation with Sound is Generalizable Audio-Visual Source Localizer
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:Never having seen an object and heard its sound simultaneously, can the model still accurately localize its visual position from the input audio? In this work, we concentrate on the Audio-Visual Localization and Segmentation tasks but under the demanding zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. To achieve this goal, different from existing approaches that mostly employ the encoder-fusion-decoder paradigm to decode localization information from the fused audio-visual feature, we introduce the encoder-prompt-decoder paradigm, aiming to better fit the data scarcity and varying data distribution dilemmas with the help of abundant knowledge from pre-trained models. Specifically, we first propose to construct Semantic-aware Audio Prompt (SAP) to help the visual foundation model focus on sounding objects, meanwhile, the semantic gap between the visual and audio modalities is also encouraged to shrink. Then, we develop a Correlation Adapter (ColA) to keep minimal training efforts as well as maintain adequate knowledge of the visual foundation model. By equipping with these means, extensive experiments demonstrate that this new paradigm outperforms other fusion-based methods in both the unseen class and cross-dataset settings. We hope that our work can further promote the generalization study of Audio-Visual Localization and Segmentation in practical application scenarios.
Progressive Spatio-temporal Perception for Audio-Visual Question Answering
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) task aims to answer questions about different visual objects, sounds, and their associations in videos. Such naturally multi-modal videos are composed of rich and complex dynamic audio-visual components, where most of which could be unrelated to the given questions, or even play as interference in answering the content of interest. Oppositely, only focusing on the question-aware audio-visual content could get rid of influence, meanwhile enabling the model to answer more efficiently. In this paper, we propose a Progressive Spatio-Temporal Perception Network (PSTP-Net), which contains three modules that progressively identify key spatio-temporal regions w.r.t. questions. Specifically, a temporal segment selection module is first introduced to select the most relevant audio-visual segments related to the given question. Then, a spatial region selection module is utilized to choose the most relevant regions associated with the question from the selected temporal segments. To further refine the selection of features, an audio-guided visual attention module is employed to perceive the association between auido and selected spatial regions. Finally, the spatio-temporal features from these modules are integrated for answering the question. Extensive experimental results on the public MUSIC-AVQA and AVQA datasets provide compelling evidence of the effectiveness and efficiency of PSTP-Net. Code is available at: \href{https://github.com/GeWu-Lab/PSTP-Net}{https://github.com/GeWu-Lab/PSTP-Net}
Multi-Scale Attention for Audio Question Answering
May 29, 2023Abstract:Audio question answering (AQA), acting as a widely used proxy task to explore scene understanding, has got more attention. The AQA is challenging for it requires comprehensive temporal reasoning from different scales' events of an audio scene. However, existing methods mostly extend the structures of visual question answering task to audio ones in a simple pattern but may not perform well when perceiving a fine-grained audio scene. To this end, we present a Multi-scale Window Attention Fusion Model (MWAFM) consisting of an asynchronous hybrid attention module and a multi-scale window attention module. The former is designed to aggregate unimodal and cross-modal temporal contexts, while the latter captures sound events of varying lengths and their temporal dependencies for a more comprehensive understanding. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed MWAFM can effectively explore temporal information to facilitate AQA in the fine-grained scene.Code: https://github.com/GeWu-Lab/MWAFM
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge