Weisong Liu
DriveVLA-W0: World Models Amplify Data Scaling Law in Autonomous Driving
Oct 14, 2025



Abstract:Scaling Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models on large-scale data offers a promising path to achieving a more generalized driving intelligence. However, VLA models are limited by a ``supervision deficit'': the vast model capacity is supervised by sparse, low-dimensional actions, leaving much of their representational power underutilized. To remedy this, we propose \textbf{DriveVLA-W0}, a training paradigm that employs world modeling to predict future images. This task generates a dense, self-supervised signal that compels the model to learn the underlying dynamics of the driving environment. We showcase the paradigm's versatility by instantiating it for two dominant VLA archetypes: an autoregressive world model for VLAs that use discrete visual tokens, and a diffusion world model for those operating on continuous visual features. Building on the rich representations learned from world modeling, we introduce a lightweight action expert to address the inference latency for real-time deployment. Extensive experiments on the NAVSIM v1/v2 benchmark and a 680x larger in-house dataset demonstrate that DriveVLA-W0 significantly outperforms BEV and VLA baselines. Crucially, it amplifies the data scaling law, showing that performance gains accelerate as the training dataset size increases.
Prompting Segmentation with Sound is Generalizable Audio-Visual Source Localizer
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:Never having seen an object and heard its sound simultaneously, can the model still accurately localize its visual position from the input audio? In this work, we concentrate on the Audio-Visual Localization and Segmentation tasks but under the demanding zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. To achieve this goal, different from existing approaches that mostly employ the encoder-fusion-decoder paradigm to decode localization information from the fused audio-visual feature, we introduce the encoder-prompt-decoder paradigm, aiming to better fit the data scarcity and varying data distribution dilemmas with the help of abundant knowledge from pre-trained models. Specifically, we first propose to construct Semantic-aware Audio Prompt (SAP) to help the visual foundation model focus on sounding objects, meanwhile, the semantic gap between the visual and audio modalities is also encouraged to shrink. Then, we develop a Correlation Adapter (ColA) to keep minimal training efforts as well as maintain adequate knowledge of the visual foundation model. By equipping with these means, extensive experiments demonstrate that this new paradigm outperforms other fusion-based methods in both the unseen class and cross-dataset settings. We hope that our work can further promote the generalization study of Audio-Visual Localization and Segmentation in practical application scenarios.
S3C: Semi-Supervised VQA Natural Language Explanation via Self-Critical Learning
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:VQA Natural Language Explanation (VQA-NLE) task aims to explain the decision-making process of VQA models in natural language. Unlike traditional attention or gradient analysis, free-text rationales can be easier to understand and gain users' trust. Existing methods mostly use post-hoc or self-rationalization models to obtain a plausible explanation. However, these frameworks are bottlenecked by the following challenges: 1) the reasoning process cannot be faithfully responded to and suffer from the problem of logical inconsistency. 2) Human-annotated explanations are expensive and time-consuming to collect. In this paper, we propose a new Semi-Supervised VQA-NLE via Self-Critical Learning (S3C), which evaluates the candidate explanations by answering rewards to improve the logical consistency between answers and rationales. With a semi-supervised learning framework, the S3C can benefit from a tremendous amount of samples without human-annotated explanations. A large number of automatic measures and human evaluations all show the effectiveness of our method. Meanwhile, the framework achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on the two VQA-NLE datasets.
ODD: A Benchmark Dataset for the NLP-based Opioid Related Aberrant Behavior Detection
Jul 24, 2023



Abstract:Opioid related aberrant behaviors (ORAB) present novel risk factors for opioid overdose. Previously, ORAB have been mainly assessed by survey results and by monitoring drug administrations. Such methods however, cannot scale up and do not cover the entire spectrum of aberrant behaviors. On the other hand, ORAB are widely documented in electronic health record notes. This paper introduces a novel biomedical natural language processing benchmark dataset named ODD, for ORAB Detection Dataset. ODD is an expert-annotated dataset comprising of more than 750 publicly available EHR notes. ODD has been designed to identify ORAB from patients' EHR notes and classify them into nine categories; 1) Confirmed Aberrant Behavior, 2) Suggested Aberrant Behavior, 3) Opioids, 4) Indication, 5) Diagnosed opioid dependency, 6) Benzodiapines, 7) Medication Changes, 8) Central Nervous System-related, and 9) Social Determinants of Health. We explored two state-of-the-art natural language processing (NLP) models (finetuning pretrained language models and prompt-tuning approaches) to identify ORAB. Experimental results show that the prompt-tuning models outperformed the finetuning models in most cateogories and the gains were especially higher among uncommon categories (Suggested aberrant behavior, Diagnosed opioid dependency and Medication change). Although the best model achieved the highest 83.92% on area under precision recall curve, uncommon classes (Suggested Aberrant Behavior, Diagnosed Opioid Dependence, and Medication Change) still have a large room for performance improvement.
Early Prediction of Alzheimers Disease Leveraging Symptom Occurrences from Longitudinal Electronic Health Records of US Military Veterans
Jul 23, 2023



Abstract:Early prediction of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. This study aims to use machine learning approaches to analyze longitudinal electronic health records (EHRs) of patients with AD and identify signs and symptoms that can predict AD onset earlier. We used a case-control design with longitudinal EHRs from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Health Administration (VHA) from 2004 to 2021. Cases were VHA patients with AD diagnosed after 1/1/2016 based on ICD-10-CM codes, matched 1:9 with controls by age, sex and clinical utilization with replacement. We used a panel of AD-related keywords and their occurrences over time in a patient's longitudinal EHRs as predictors for AD prediction with four machine learning models. We performed subgroup analyses by age, sex, and race/ethnicity, and validated the model in a hold-out and "unseen" VHA stations group. Model discrimination, calibration, and other relevant metrics were reported for predictions up to ten years before ICD-based diagnosis. The study population included 16,701 cases and 39,097 matched controls. The average number of AD-related keywords (e.g., "concentration", "speaking") per year increased rapidly for cases as diagnosis approached, from around 10 to over 40, while remaining flat at 10 for controls. The best model achieved high discriminative accuracy (ROCAUC 0.997) for predictions using data from at least ten years before ICD-based diagnoses. The model was well-calibrated (Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit p-value = 0.99) and consistent across subgroups of age, sex and race/ethnicity, except for patients younger than 65 (ROCAUC 0.746). Machine learning models using AD-related keywords identified from EHR notes can predict future AD diagnoses, suggesting its potential use for identifying AD risk using EHR notes, offering an affordable way for early screening on large population.
Enhancing the prediction of disease outcomes using electronic health records and pretrained deep learning models
Dec 22, 2022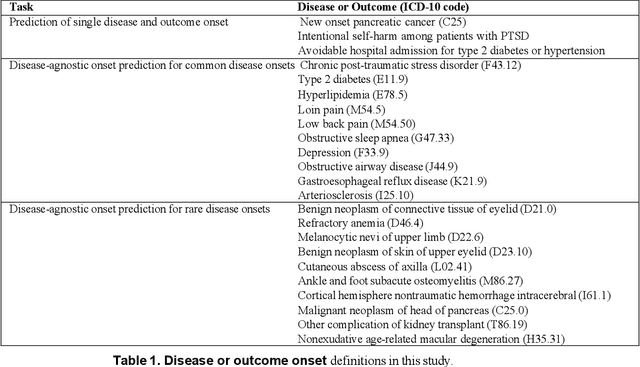
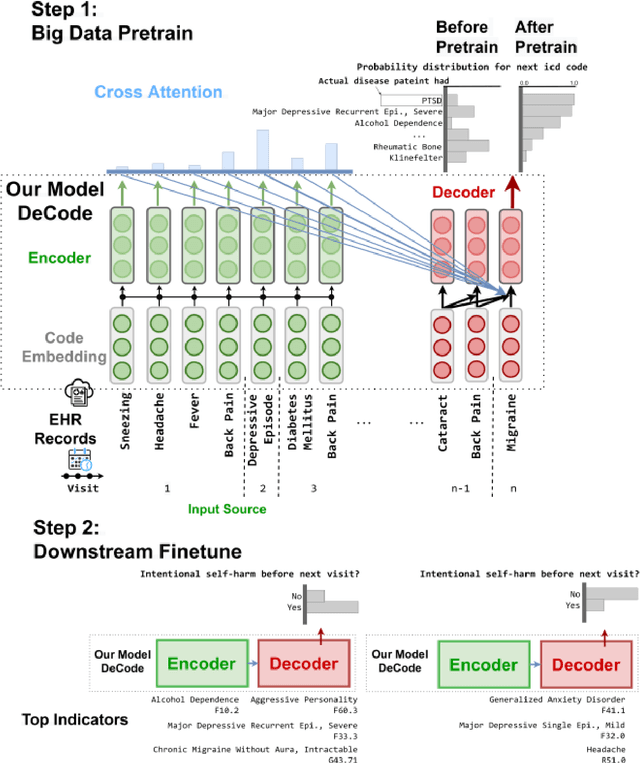
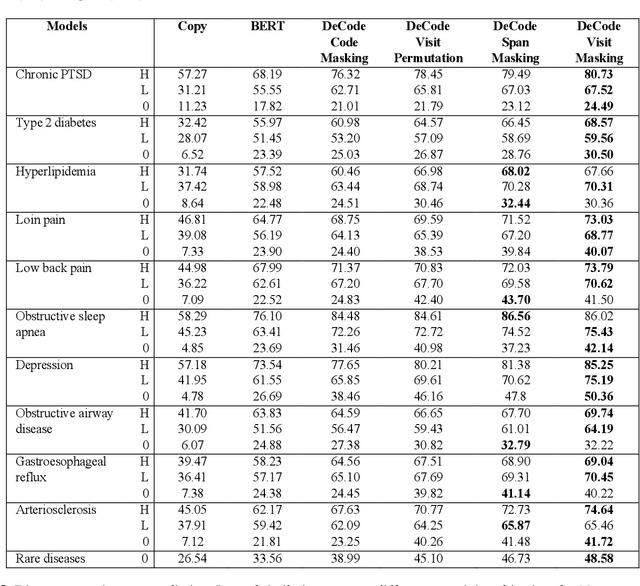

Abstract:Question: Can an encoder-decoder architecture pretrained on a large dataset of longitudinal electronic health records improves patient outcome predictions? Findings: In this prognostic study of 6.8 million patients, our denoising sequence-to-sequence prediction model of multiple outcomes outperformed state-of-the-art models scuh pretrained BERT on a broad range of patient outcomes, including intentional self-harm and pancreatic cancer. Meaning: Deep bidirectional and autoregressive representation improves patient outcome prediction.
Associations Between Natural Language Processing (NLP) Enriched Social Determinants of Health and Suicide Death among US Veterans
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:Importance: Social determinants of health (SDOH) are known to be associated with increased risk of suicidal behaviors, but few studies utilized SDOH from unstructured electronic health record (EHR) notes. Objective: To investigate associations between suicide and recent SDOH, identified using structured and unstructured data. Design: Nested case-control study. Setting: EHR data from the US Veterans Health Administration (VHA). Participants: 6,122,785 Veterans who received care in the US VHA between October 1, 2010, and September 30, 2015. Exposures: Occurrence of SDOH over a maximum span of two years compared with no occurrence of SDOH. Main Outcomes and Measures: Cases of suicide deaths were matched with 4 controls on birth year, cohort entry date, sex, and duration of follow-up. We developed an NLP system to extract SDOH from unstructured notes. Structured data, NLP on unstructured data, and combining them yielded seven, eight and nine SDOH respectively. Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using conditional logistic regression. Results: In our cohort, 8,821 Veterans committed suicide during 23,725,382 person-years of follow-up (incidence rate 37.18 /100,000 person-years). Our cohort was mostly male (92.23%) and white (76.99%). Across the six common SDOH as covariates, NLP-extracted SDOH, on average, covered 84.38% of all SDOH occurrences. All SDOH, measured by structured data and NLP, were significantly associated with increased risk of suicide. The SDOH with the largest effects was legal problems (aOR=2.67, 95% CI=2.46-2.89), followed by violence (aOR=2.26, 95% CI=2.11-2.43). NLP-extracted and structured SDOH were also associated with suicide. Conclusions and Relevance: NLP-extracted SDOH were always significantly associated with increased risk of suicide among Veterans, suggesting the potential of NLP in public health studies.
Automated Identification of Eviction Status from Electronic Health Record Notes
Dec 06, 2022

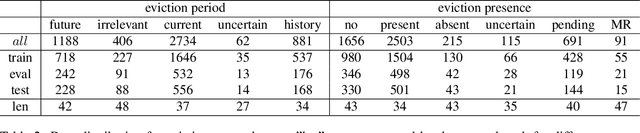

Abstract:Objective: Evictions are involved in a cascade of negative events that can lead to unemployment, homelessness, long-term poverty, and mental health problems. In this study, we developed a natural language processing system to automatically detect eviction incidences and their attributes from electronic health record (EHR) notes. Materials and Methods: We annotated eviction status in 5000 EHR notes from the Veterans Health Administration. We developed a novel model, called Knowledge Injection based on Ripple Effects of Social and Behavioral Determinants of Health (KIRESH), that has shown to substantially outperform other state-of-the-art models such as fine-tuning pre-trained language models like BioBERT and Bio_ClinicalBERT. Moreover, we designed a prompt to further improve the model performance by using the intrinsic connection between the two sub-tasks of eviction presence and period prediction. Finally, we used the Temperature Scaling-based Calibration on our KIRESH-Prompt method to avoid over-confidence issues arising from the imbalance dataset. Results: KIRESH-Prompt achieved a Macro-F1 of 0.6273 (presence) and 0.7115 (period), which was significantly higher than 0.5382 (presence) and 0.67167 (period) for just fine-tuning Bio_ClinicalBERT model. Conclusion and Future Work: KIRESH-Prompt has substantially improved eviction status classification. In future work, we will evaluate the generalizability of the model framework to other applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge