Automated Identification of Eviction Status from Electronic Health Record Notes
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2022

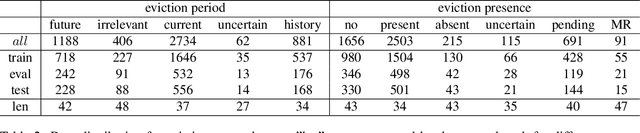

Objective: Evictions are involved in a cascade of negative events that can lead to unemployment, homelessness, long-term poverty, and mental health problems. In this study, we developed a natural language processing system to automatically detect eviction incidences and their attributes from electronic health record (EHR) notes. Materials and Methods: We annotated eviction status in 5000 EHR notes from the Veterans Health Administration. We developed a novel model, called Knowledge Injection based on Ripple Effects of Social and Behavioral Determinants of Health (KIRESH), that has shown to substantially outperform other state-of-the-art models such as fine-tuning pre-trained language models like BioBERT and Bio_ClinicalBERT. Moreover, we designed a prompt to further improve the model performance by using the intrinsic connection between the two sub-tasks of eviction presence and period prediction. Finally, we used the Temperature Scaling-based Calibration on our KIRESH-Prompt method to avoid over-confidence issues arising from the imbalance dataset. Results: KIRESH-Prompt achieved a Macro-F1 of 0.6273 (presence) and 0.7115 (period), which was significantly higher than 0.5382 (presence) and 0.67167 (period) for just fine-tuning Bio_ClinicalBERT model. Conclusion and Future Work: KIRESH-Prompt has substantially improved eviction status classification. In future work, we will evaluate the generalizability of the model framework to other applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge