Yuan Meng
WiSparse: Boosting LLM Inference Efficiency with Weight-Aware Mixed Activation Sparsity
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer strong capabilities but incur high inference costs due to dense computation and memory access. Training-free activation sparsity is a promising approach for efficient LLM inference, yet existing methods often rely solely on activation information and uniform sparsity ratios. This overlooks the critical interplay with weights and inter-block sensitivity variation, leading to suboptimal performance. We identify two key phenomena in modern LLMs: 1) less significant activations may align with highly important weights, and 2) sparsity sensitivity varies non-monotonically across model blocks. We propose Weight-aware Mixed-Granularity Training-free Activation Sparsity (WiSparse), which leverages both activation and weight information for adaptive sparsity allocation. Specifically, we introduce a weight-aware mechanism integrating activation magnitudes with precomputed weight norms to accurately identify salient channels. This is combined with a mixed-granularity allocation scheme: a global budget is distributed across blocks via evolutionary search to protect sensitive regions, then refined within blocks to minimize reconstruction error. We improve sparse kernels and demonstrate effectiveness on three representative models. Notably, at 50% sparsity, WiSparse preserves 97% of Llama3.1's dense performance, surpassing the strongest baseline by 2.23 percentage points while achieving a 21.4% acceleration in end-to-end inference speed. Our research advances the limits of training-free approaches for efficient LLM inference, pushing the boundaries of achievable speedup without training.
DECO: Decoupled Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Bimanual Dexterous Manipulation with a Plugin Tactile Adapter
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Overview of the Proposed DECO Framework.} DECO is a DiT-based policy that decouples multimodal conditioning. Image and action tokens interact via joint self attention, while proprioceptive states and optional conditions are injected through adaptive layer normalization. Tactile signals are injected via cross attention, while a lightweight LoRA-based adapter is used to efficiently fine-tune the pretrained policy. DECO is also accompanied by DECO-50, a bimanual dexterous manipulation dataset with tactile sensing, consisting of 4 scenarios and 28 sub-tasks, covering more than 50 hours of data, approximately 5 million frames, and 8,000 successful trajectories.
Sparse ActionGen: Accelerating Diffusion Policy with Real-time Pruning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Policy has dominated action generation due to its strong capabilities for modeling multi-modal action distributions, but its multi-step denoising processes make it impractical for real-time visuomotor control. Existing caching-based acceleration methods typically rely on $\textit{static}$ schedules that fail to adapt to the $\textit{dynamics}$ of robot-environment interactions, thereby leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose $\underline{\textbf{S}}$parse $\underline{\textbf{A}}$ction$\underline{\textbf{G}}$en ($\textbf{SAG}$) for extremely sparse action generation. To accommodate the iterative interactions, SAG customizes a rollout-adaptive prune-then-reuse mechanism that first identifies prunable computations globally and then reuses cached activations to substitute them during action diffusion. To capture the rollout dynamics, SAG parameterizes an observation-conditioned diffusion pruner for environment-aware adaptation and instantiates it with a highly parameter- and inference-efficient design for real-time prediction. Furthermore, SAG introduces a one-for-all reusing strategy that reuses activations across both timesteps and blocks in a zig-zag manner, minimizing the global redundancy. Extensive experiments on multiple robotic benchmarks demonstrate that SAG achieves up to 4$\times$ generation speedup without sacrificing performance. Project Page: https://sparse-actiongen.github.io/.
SciIF: Benchmarking Scientific Instruction Following Towards Rigorous Scientific Intelligence
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) transition from general knowledge retrieval to complex scientific discovery, their evaluation standards must also incorporate the rigorous norms of scientific inquiry. Existing benchmarks exhibit a critical blind spot: general instruction-following metrics focus on superficial formatting, while domain-specific scientific benchmarks assess only final-answer correctness, often rewarding models that arrive at the right result with the wrong reasons. To address this gap, we introduce scientific instruction following: the capability to solve problems while strictly adhering to the constraints that establish scientific validity. Specifically, we introduce SciIF, a multi-discipline benchmark that evaluates this capability by pairing university-level problems with a fixed catalog of constraints across three pillars: scientific conditions (e.g., boundary checks and assumptions), semantic stability (e.g., unit and symbol conventions), and specific processes(e.g., required numerical methods). Uniquely, SciIF emphasizes auditability, requiring models to provide explicit evidence of constraint satisfaction rather than implicit compliance. By measuring both solution correctness and multi-constraint adherence, SciIF enables finegrained diagnosis of compositional reasoning failures, ensuring that LLMs can function as reliable agents within the strict logical frameworks of science.
TS-DP: Reinforcement Speculative Decoding For Temporal Adaptive Diffusion Policy Acceleration
Dec 13, 2025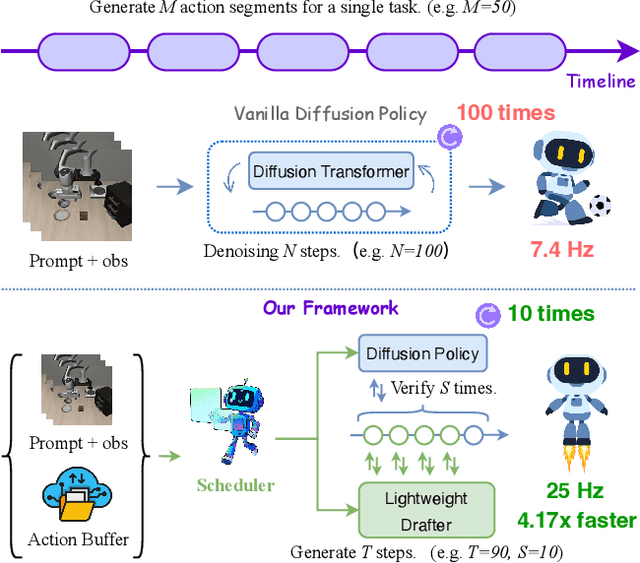
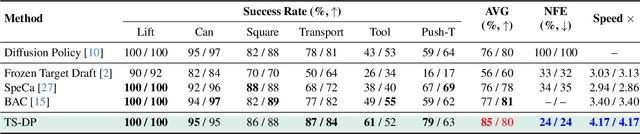
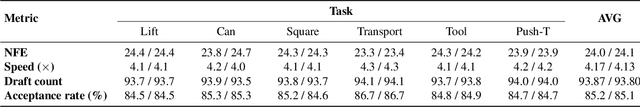
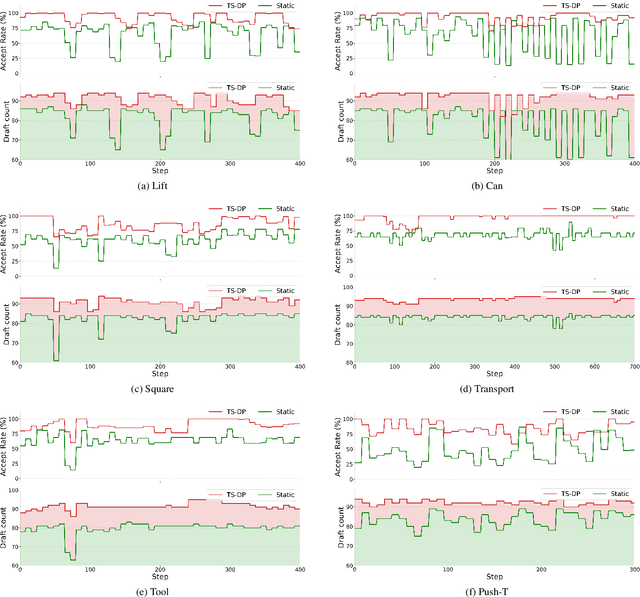
Abstract:Diffusion Policy (DP) excels in embodied control but suffers from high inference latency and computational cost due to multiple iterative denoising steps. The temporal complexity of embodied tasks demands a dynamic and adaptable computation mode. Static and lossy acceleration methods, such as quantization, fail to handle such dynamic embodied tasks, while speculative decoding offers a lossless and adaptive yet underexplored alternative for DP. However, it is non-trivial to address the following challenges: how to match the base model's denoising quality at lower cost under time-varying task difficulty in embodied settings, and how to dynamically and interactively adjust computation based on task difficulty in such environments. In this paper, we propose Temporal-aware Reinforcement-based Speculative Diffusion Policy (TS-DP), the first framework that enables speculative decoding for DP with temporal adaptivity. First, to handle dynamic environments where task difficulty varies over time, we distill a Transformer-based drafter to imitate the base model and replace its costly denoising calls. Second, an RL-based scheduler further adapts to time-varying task difficulty by adjusting speculative parameters to maintain accuracy while improving efficiency. Extensive experiments across diverse embodied environments demonstrate that TS-DP achieves up to 4.17 times faster inference with over 94% accepted drafts, reaching an inference frequency of 25 Hz and enabling real-time diffusion-based control without performance degradation.
A Multi-Stage Large Language Model Framework for Extracting Suicide-Related Social Determinants of Health
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Background: Understanding social determinants of health (SDoH) factors contributing to suicide incidents is crucial for early intervention and prevention. However, data-driven approaches to this goal face challenges such as long-tailed factor distributions, analyzing pivotal stressors preceding suicide incidents, and limited model explainability. Methods: We present a multi-stage large language model framework to enhance SDoH factor extraction from unstructured text. Our approach was compared to other state-of-the-art language models (i.e., pre-trained BioBERT and GPT-3.5-turbo) and reasoning models (i.e., DeepSeek-R1). We also evaluated how the model's explanations help people annotate SDoH factors more quickly and accurately. The analysis included both automated comparisons and a pilot user study. Results: We show that our proposed framework demonstrated performance boosts in the overarching task of extracting SDoH factors and in the finer-grained tasks of retrieving relevant context. Additionally, we show that fine-tuning a smaller, task-specific model achieves comparable or better performance with reduced inference costs. The multi-stage design not only enhances extraction but also provides intermediate explanations, improving model explainability. Conclusions: Our approach improves both the accuracy and transparency of extracting suicide-related SDoH from unstructured texts. These advancements have the potential to support early identification of individuals at risk and inform more effective prevention strategies.
Block-wise Adaptive Caching for Accelerating Diffusion Policy
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Policy has demonstrated strong visuomotor modeling capabilities, but its high computational cost renders it impractical for real-time robotic control. Despite huge redundancy across repetitive denoising steps, existing diffusion acceleration techniques fail to generalize to Diffusion Policy due to fundamental architectural and data divergences. In this paper, we propose Block-wise Adaptive Caching(BAC), a method to accelerate Diffusion Policy by caching intermediate action features. BAC achieves lossless action generation acceleration by adaptively updating and reusing cached features at the block level, based on a key observation that feature similarities vary non-uniformly across timesteps and locks. To operationalize this insight, we first propose the Adaptive Caching Scheduler, designed to identify optimal update timesteps by maximizing the global feature similarities between cached and skipped features. However, applying this scheduler for each block leads to signiffcant error surges due to the inter-block propagation of caching errors, particularly within Feed-Forward Network (FFN) blocks. To mitigate this issue, we develop the Bubbling Union Algorithm, which truncates these errors by updating the upstream blocks with signiffcant caching errors before downstream FFNs. As a training-free plugin, BAC is readily integrable with existing transformer-based Diffusion Policy and vision-language-action models. Extensive experiments on multiple robotic benchmarks demonstrate that BAC achieves up to 3x inference speedup for free.
SP-VLA: A Joint Model Scheduling and Token Pruning Approach for VLA Model Acceleration
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have attracted increasing attention for their strong control capabilities. However, their high computational cost and low execution frequency hinder their suitability for real-time tasks such as robotic manipulation and autonomous navigation. Existing VLA acceleration methods primarily focus on structural optimization, overlooking the fact that these models operate in sequential decision-making environments. As a result, temporal redundancy in sequential action generation and spatial redundancy in visual input remain unaddressed. To this end, we propose SP-VLA, a unified framework that accelerates VLA models by jointly scheduling models and pruning tokens. Specifically, we design an action-aware model scheduling mechanism that reduces temporal redundancy by dynamically switching between VLA model and a lightweight generator. Inspired by the human motion pattern of focusing on key decision points while relying on intuition for other actions, we categorize VLA actions into deliberative and intuitive, assigning the former to the VLA model and the latter to the lightweight generator, enabling frequency-adaptive execution through collaborative model scheduling. To address spatial redundancy, we further develop a spatio-semantic dual-aware token pruning method. Tokens are classified into spatial and semantic types and pruned based on their dual-aware importance to accelerate VLA inference. These two mechanisms work jointly to guide the VLA in focusing on critical actions and salient visual information, achieving effective acceleration while maintaining high accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves up to 1.5$\times$ acceleration with less than 3% drop in accuracy, outperforming existing approaches in multiple tasks.
CPRet: A Dataset, Benchmark, and Model for Retrieval in Competitive Programming
May 19, 2025Abstract:Competitive programming benchmarks are widely used in scenarios such as programming contests and large language model assessments. However, the growing presence of duplicate or highly similar problems raises concerns not only about competition fairness, but also about the validity of competitive programming as a benchmark for model evaluation. In this paper, we propose a new problem -- similar question retrieval -- to address this issue. Due to the lack of both data and models, solving this problem is challenging. To this end, we introduce CPRet, a retrieval-oriented benchmark suite for competitive programming, covering four retrieval tasks: two code-centric (i.e., Text-to-Code and Code-to-Code) and two newly proposed problem-centric tasks (i.e., Problem-to-Duplicate and Simplified-to-Full), built from a combination of automatically crawled problem-solution data and manually curated annotations. Our contribution includes both high-quality training data and temporally separated test sets for reliable evaluation. In addition, we develop two task-specialized retrievers based on this dataset: CPRetriever-Code, trained with a novel Group-InfoNCE loss for problem-code alignment, and CPRetriever-Prob, fine-tuned for identifying problem-level similarity. Both models achieve strong results and are open-sourced for local use. Finally, we analyze LiveCodeBench and find that high-similarity problems inflate model pass rates and reduce differentiation, underscoring the need for similarity-aware evaluation in future benchmarks. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/coldchair/CPRet
Point2Primitive: CAD Reconstruction from Point Cloud by Direct Primitive Prediction
May 04, 2025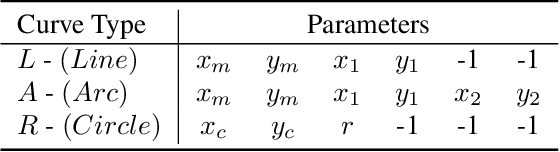
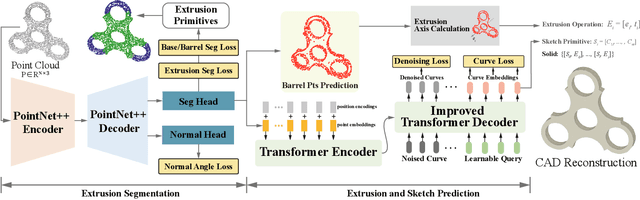
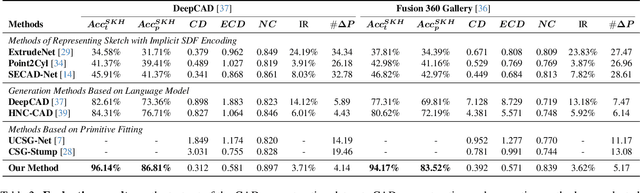
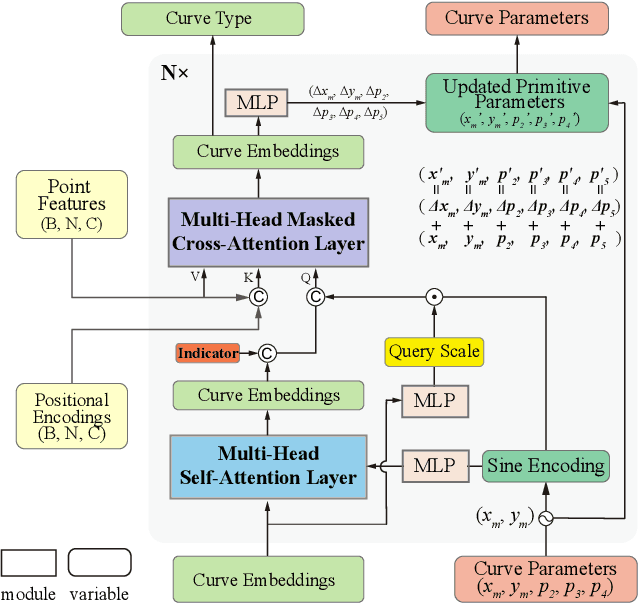
Abstract:Recovering CAD models from point clouds, especially the sketch-extrusion process, can be seen as the process of rebuilding the topology and extrusion primitives. Previous methods utilize implicit fields for sketch representation, leading to shape reconstruction of curved edges. In this paper, we proposed a CAD reconstruction network that produces editable CAD models from input point clouds (Point2Primitive) by directly predicting every element of the extrusion primitives. Point2Primitive can directly detect and predict sketch curves (type and parameter) from point clouds based on an improved transformer. The sketch curve parameters are formulated as position queries and optimized in an autoregressive way, leading to high parameter accuracy. The topology is rebuilt by extrusion segmentation, and each extrusion parameter (sketch and extrusion operation) is recovered by combining the predicted curves and the computed extrusion operation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method is superior in primitive prediction accuracy and CAD reconstruction. The reconstructed shapes are of high geometrical fidelity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge