Zhenshan Bing
DECO: Decoupled Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Bimanual Dexterous Manipulation with a Plugin Tactile Adapter
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Overview of the Proposed DECO Framework.} DECO is a DiT-based policy that decouples multimodal conditioning. Image and action tokens interact via joint self attention, while proprioceptive states and optional conditions are injected through adaptive layer normalization. Tactile signals are injected via cross attention, while a lightweight LoRA-based adapter is used to efficiently fine-tune the pretrained policy. DECO is also accompanied by DECO-50, a bimanual dexterous manipulation dataset with tactile sensing, consisting of 4 scenarios and 28 sub-tasks, covering more than 50 hours of data, approximately 5 million frames, and 8,000 successful trajectories.
TacUMI: A Multi-Modal Universal Manipulation Interface for Contact-Rich Tasks
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Task decomposition is critical for understanding and learning complex long-horizon manipulation tasks. Especially for tasks involving rich physical interactions, relying solely on visual observations and robot proprioceptive information often fails to reveal the underlying event transitions. This raises the requirement for efficient collection of high-quality multi-modal data as well as robust segmentation method to decompose demonstrations into meaningful modules. Building on the idea of the handheld demonstration device Universal Manipulation Interface (UMI), we introduce TacUMI, a multi-modal data collection system that integrates additionally ViTac sensors, force-torque sensor, and pose tracker into a compact, robot-compatible gripper design, which enables synchronized acquisition of all these modalities during human demonstrations. We then propose a multi-modal segmentation framework that leverages temporal models to detect semantically meaningful event boundaries in sequential manipulations. Evaluation on a challenging cable mounting task shows more than 90 percent segmentation accuracy and highlights a remarkable improvement with more modalities, which validates that TacUMI establishes a practical foundation for both scalable collection and segmentation of multi-modal demonstrations in contact-rich tasks.
M4Diffuser: Multi-View Diffusion Policy with Manipulability-Aware Control for Robust Mobile Manipulation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Mobile manipulation requires the coordinated control of a mobile base and a robotic arm while simultaneously perceiving both global scene context and fine-grained object details. Existing single-view approaches often fail in unstructured environments due to limited fields of view, exploration, and generalization abilities. Moreover, classical controllers, although stable, struggle with efficiency and manipulability near singularities. To address these challenges, we propose M4Diffuser, a hybrid framework that integrates a Multi-View Diffusion Policy with a novel Reduced and Manipulability-aware QP (ReM-QP) controller for mobile manipulation. The diffusion policy leverages proprioceptive states and complementary camera perspectives with both close-range object details and global scene context to generate task-relevant end-effector goals in the world frame. These high-level goals are then executed by the ReM-QP controller, which eliminates slack variables for computational efficiency and incorporates manipulability-aware preferences for robustness near singularities. Comprehensive experiments in simulation and real-world environments show that M4Diffuser achieves 7 to 56 percent higher success rates and reduces collisions by 3 to 31 percent over baselines. Our approach demonstrates robust performance for smooth whole-body coordination, and strong generalization to unseen tasks, paving the way for reliable mobile manipulation in unstructured environments. Details of the demo and supplemental material are available on our project website https://sites.google.com/view/m4diffuser.
Estimated Informed Anytime Search for Sampling-Based Planning via Adaptive Sampler
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Path planning in robotics often involves solving continuously valued, high-dimensional problems. Popular informed approaches include graph-based searches, such as A*, and sampling-based methods, such as Informed RRT*, which utilize informed set and anytime strategies to expedite path optimization incrementally. Informed sampling-based planners define informed sets as subsets of the problem domain based on the current best solution cost. However, when no solution is found, these planners re-sample and explore the entire configuration space, which is time-consuming and computationally expensive. This article introduces Multi-Informed Trees (MIT*), a novel planner that constructs estimated informed sets based on prior admissible solution costs before finding the initial solution, thereby accelerating the initial convergence rate. Moreover, MIT* employs an adaptive sampler that dynamically adjusts the sampling strategy based on the exploration process. Furthermore, MIT* utilizes length-related adaptive sparse collision checks to guide lazy reverse search. These features enhance path cost efficiency and computation times while ensuring high success rates in confined scenarios. Through a series of simulations and real-world experiments, it is confirmed that MIT* outperforms existing single-query, sampling-based planners for problems in R^4 to R^16 and has been successfully applied to real-world robot manipulation tasks. A video showcasing our experimental results is available at: https://youtu.be/30RsBIdexTU
Deep Fuzzy Optimization for Batch-Size and Nearest Neighbors in Optimal Robot Motion Planning
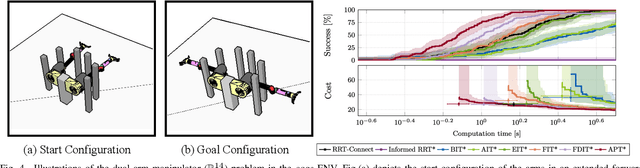
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Efficient motion planning algorithms are essential in robotics. Optimizing essential parameters, such as batch size and nearest neighbor selection in sampling-based methods, can enhance performance in the planning process. However, existing approaches often lack environmental adaptability. Inspired by the method of the deep fuzzy neural networks, this work introduces Learning-based Informed Trees (LIT*), a sampling-based deep fuzzy learning-based planner that dynamically adjusts batch size and nearest neighbor parameters to obstacle distributions in the configuration spaces. By encoding both global and local ratios via valid and invalid states, LIT* differentiates between obstacle-sparse and obstacle-dense regions, leading to lower-cost paths and reduced computation time. Experimental results in high-dimensional spaces demonstrate that LIT* achieves faster convergence and improved solution quality. It outperforms state-of-the-art single-query, sampling-based planners in environments ranging from R^8 to R^14 and is successfully validated on a dual-arm robot manipulation task. A video showcasing our experimental results is available at: https://youtu.be/NrNs9zebWWk
Genetic Informed Trees (GIT*): Path Planning via Reinforced Genetic Programming Heuristics
Aug 28, 2025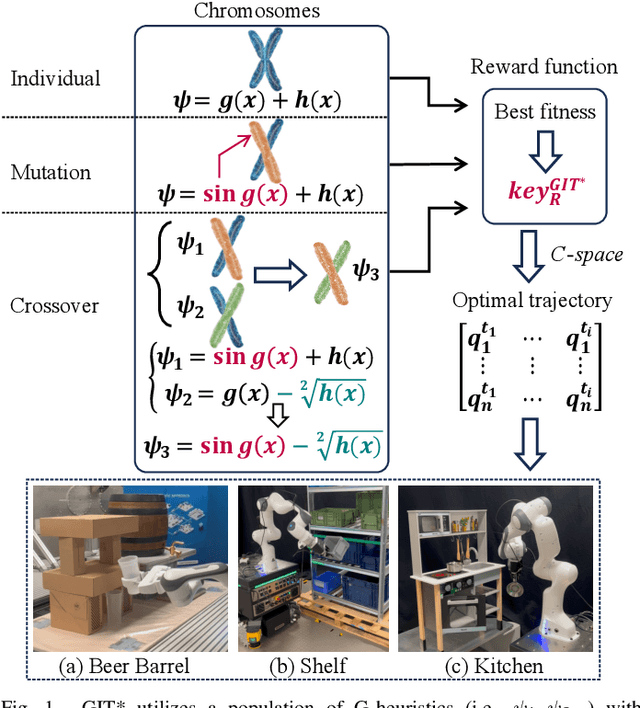
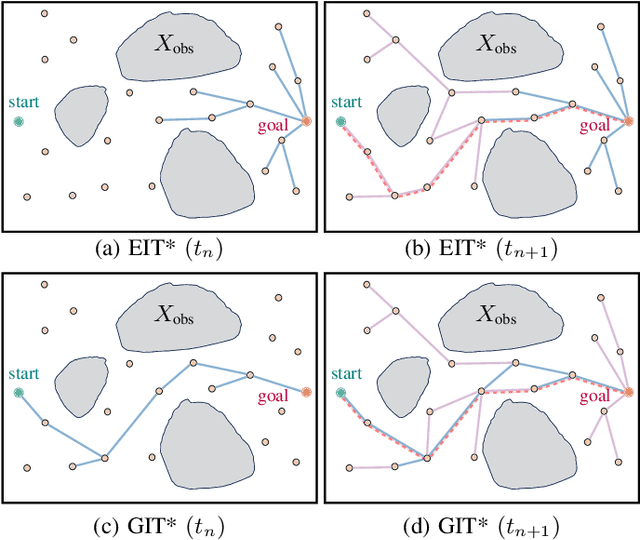
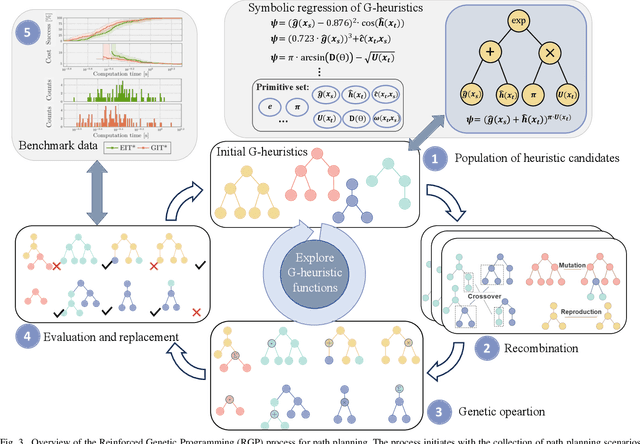
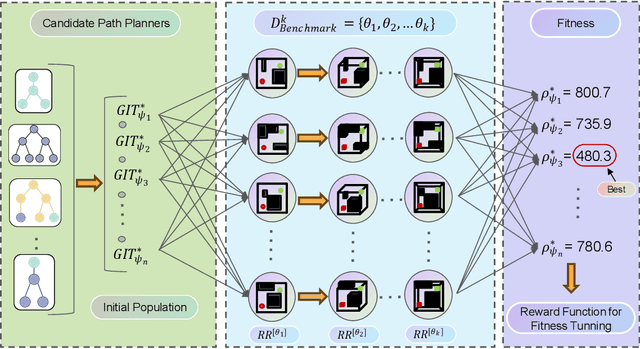
Abstract:Optimal path planning involves finding a feasible state sequence between a start and a goal that optimizes an objective. This process relies on heuristic functions to guide the search direction. While a robust function can improve search efficiency and solution quality, current methods often overlook available environmental data and simplify the function structure due to the complexity of information relationships. This study introduces Genetic Informed Trees (GIT*), which improves upon Effort Informed Trees (EIT*) by integrating a wider array of environmental data, such as repulsive forces from obstacles and the dynamic importance of vertices, to refine heuristic functions for better guidance. Furthermore, we integrated reinforced genetic programming (RGP), which combines genetic programming with reward system feedback to mutate genotype-generative heuristic functions for GIT*. RGP leverages a multitude of data types, thereby improving computational efficiency and solution quality within a set timeframe. Comparative analyses demonstrate that GIT* surpasses existing single-query, sampling-based planners in problems ranging from R^4 to R^16 and was tested on a real-world mobile manipulation task. A video showcasing our experimental results is available at https://youtu.be/URjXbc_BiYg
Language-Enhanced Mobile Manipulation for Efficient Object Search in Indoor Environments
Aug 28, 2025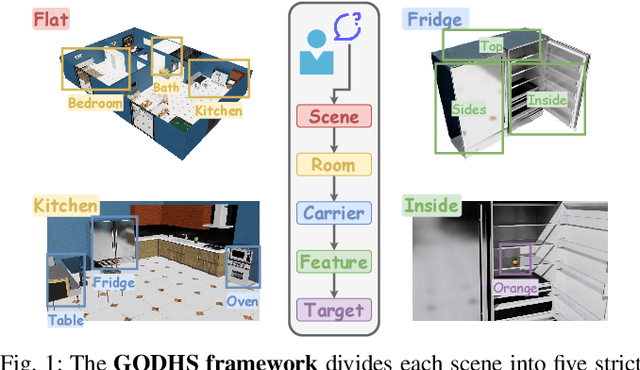
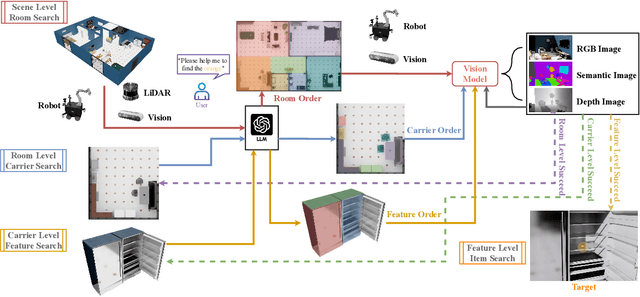
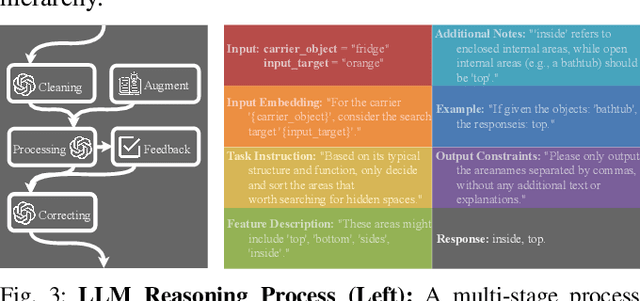

Abstract:Enabling robots to efficiently search for and identify objects in complex, unstructured environments is critical for diverse applications ranging from household assistance to industrial automation. However, traditional scene representations typically capture only static semantics and lack interpretable contextual reasoning, limiting their ability to guide object search in completely unfamiliar settings. To address this challenge, we propose a language-enhanced hierarchical navigation framework that tightly integrates semantic perception and spatial reasoning. Our method, Goal-Oriented Dynamically Heuristic-Guided Hierarchical Search (GODHS), leverages large language models (LLMs) to infer scene semantics and guide the search process through a multi-level decision hierarchy. Reliability in reasoning is achieved through the use of structured prompts and logical constraints applied at each stage of the hierarchy. For the specific challenges of mobile manipulation, we introduce a heuristic-based motion planner that combines polar angle sorting with distance prioritization to efficiently generate exploration paths. Comprehensive evaluations in Isaac Sim demonstrate the feasibility of our framework, showing that GODHS can locate target objects with higher search efficiency compared to conventional, non-semantic search strategies. Website and Video are available at: https://drapandiger.github.io/GODHS
Tree-Based Grafting Approach for Bidirectional Motion Planning with Local Subsets Optimization
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Bidirectional motion planning often reduces planning time compared to its unidirectional counterparts. It requires connecting the forward and reverse search trees to form a continuous path. However, this process could fail and restart the asymmetric bidirectional search due to the limitations of lazy-reverse search. To address this challenge, we propose Greedy GuILD Grafting Trees (G3T*), a novel path planner that grafts invalid edge connections at both ends to re-establish tree-based connectivity, enabling rapid path convergence. G3T* employs a greedy approach using the minimum Lebesgue measure of guided incremental local densification (GuILD) subsets to optimize paths efficiently. Furthermore, G3T* dynamically adjusts the sampling distribution between the informed set and GuILD subsets based on historical and current cost improvements, ensuring asymptotic optimality. These features enhance the forward search's growth towards the reverse tree, achieving faster convergence and lower solution costs. Benchmark experiments across dimensions from R^2 to R^8 and real-world robotic evaluations demonstrate G3T*'s superior performance compared to existing single-query sampling-based planners. A video showcasing our experimental results is available at: https://youtu.be/3mfCRL5SQIU
APT*: Asymptotically Optimal Motion Planning via Adaptively Prolated Elliptical R-Nearest Neighbors
Aug 27, 2025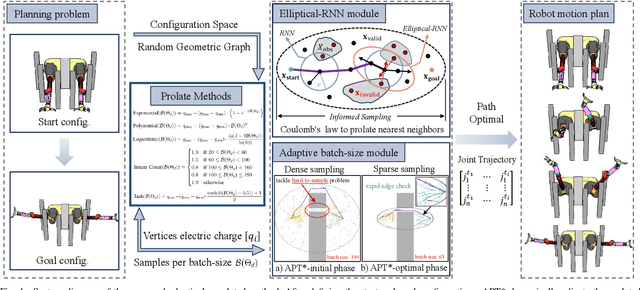
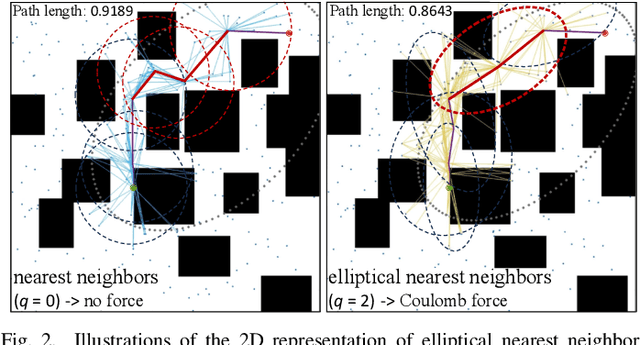
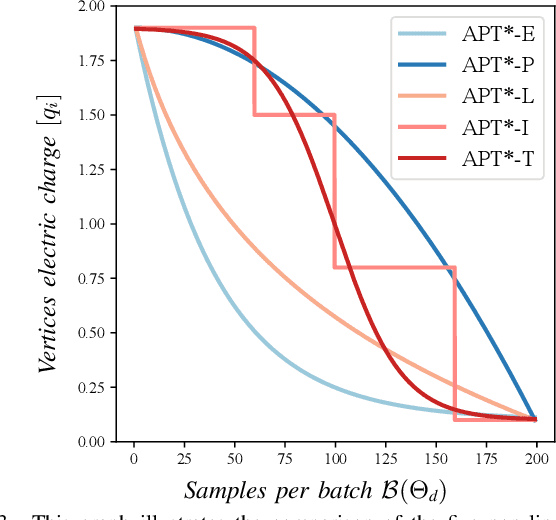
Abstract:Optimal path planning aims to determine a sequence of states from a start to a goal while accounting for planning objectives. Popular methods often integrate fixed batch sizes and neglect information on obstacles, which is not problem-specific. This study introduces Adaptively Prolated Trees (APT*), a novel sampling-based motion planner that extends based on Force Direction Informed Trees (FDIT*), integrating adaptive batch-sizing and elliptical $r$-nearest neighbor modules to dynamically modulate the path searching process based on environmental feedback. APT* adjusts batch sizes based on the hypervolume of the informed sets and considers vertices as electric charges that obey Coulomb's law to define virtual forces via neighbor samples, thereby refining the prolate nearest neighbor selection. These modules employ non-linear prolate methods to adaptively adjust the electric charges of vertices for force definition, thereby improving the convergence rate with lower solution costs. Comparative analyses show that APT* outperforms existing single-query sampling-based planners in dimensions from $\mathbb{R}^4$ to $\mathbb{R}^{16}$, and it was further validated through a real-world robot manipulation task. A video showcasing our experimental results is available at: https://youtu.be/gCcUr8LiEw4
Elliptical K-Nearest Neighbors -- Path Optimization via Coulomb's Law and Invalid Vertices in C-space Obstacles
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Path planning has long been an important and active research area in robotics. To address challenges in high-dimensional motion planning, this study introduces the Force Direction Informed Trees (FDIT*), a sampling-based planner designed to enhance speed and cost-effectiveness in pathfinding. FDIT* builds upon the state-of-the-art informed sampling planner, the Effort Informed Trees (EIT*), by capitalizing on often-overlooked information in invalid vertices. It incorporates principles of physical force, particularly Coulomb's law. This approach proposes the elliptical $k$-nearest neighbors search method, enabling fast convergence navigation and avoiding high solution cost or infeasible paths by exploring more problem-specific search-worthy areas. It demonstrates benefits in search efficiency and cost reduction, particularly in confined, high-dimensional environments. It can be viewed as an extension of nearest neighbors search techniques. Fusing invalid vertex data with physical dynamics facilitates force-direction-based search regions, resulting in an improved convergence rate to the optimum. FDIT* outperforms existing single-query, sampling-based planners on the tested problems in R^4 to R^16 and has been demonstrated on a real-world mobile manipulation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge