Shixiang Tang
SciIF: Benchmarking Scientific Instruction Following Towards Rigorous Scientific Intelligence
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) transition from general knowledge retrieval to complex scientific discovery, their evaluation standards must also incorporate the rigorous norms of scientific inquiry. Existing benchmarks exhibit a critical blind spot: general instruction-following metrics focus on superficial formatting, while domain-specific scientific benchmarks assess only final-answer correctness, often rewarding models that arrive at the right result with the wrong reasons. To address this gap, we introduce scientific instruction following: the capability to solve problems while strictly adhering to the constraints that establish scientific validity. Specifically, we introduce SciIF, a multi-discipline benchmark that evaluates this capability by pairing university-level problems with a fixed catalog of constraints across three pillars: scientific conditions (e.g., boundary checks and assumptions), semantic stability (e.g., unit and symbol conventions), and specific processes(e.g., required numerical methods). Uniquely, SciIF emphasizes auditability, requiring models to provide explicit evidence of constraint satisfaction rather than implicit compliance. By measuring both solution correctness and multi-constraint adherence, SciIF enables finegrained diagnosis of compositional reasoning failures, ensuring that LLMs can function as reliable agents within the strict logical frameworks of science.
SciEvalKit: An Open-source Evaluation Toolkit for Scientific General Intelligence
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce SciEvalKit, a unified benchmarking toolkit designed to evaluate AI models for science across a broad range of scientific disciplines and task capabilities. Unlike general-purpose evaluation platforms, SciEvalKit focuses on the core competencies of scientific intelligence, including Scientific Multimodal Perception, Scientific Multimodal Reasoning, Scientific Multimodal Understanding, Scientific Symbolic Reasoning, Scientific Code Generation, Science Hypothesis Generation and Scientific Knowledge Understanding. It supports six major scientific domains, spanning from physics and chemistry to astronomy and materials science. SciEvalKit builds a foundation of expert-grade scientific benchmarks, curated from real-world, domain-specific datasets, ensuring that tasks reflect authentic scientific challenges. The toolkit features a flexible, extensible evaluation pipeline that enables batch evaluation across models and datasets, supports custom model and dataset integration, and provides transparent, reproducible, and comparable results. By bridging capability-based evaluation and disciplinary diversity, SciEvalKit offers a standardized yet customizable infrastructure to benchmark the next generation of scientific foundation models and intelligent agents. The toolkit is open-sourced and actively maintained to foster community-driven development and progress in AI4Science.
Omni-Weather: Unified Multimodal Foundation Model for Weather Generation and Understanding
Dec 25, 2025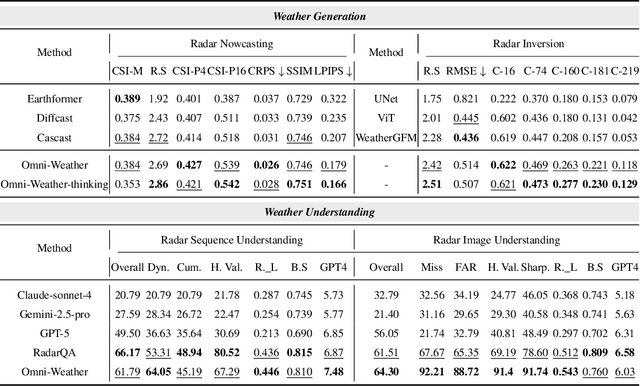
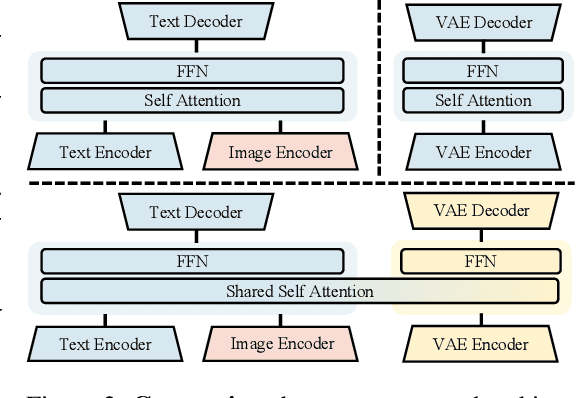
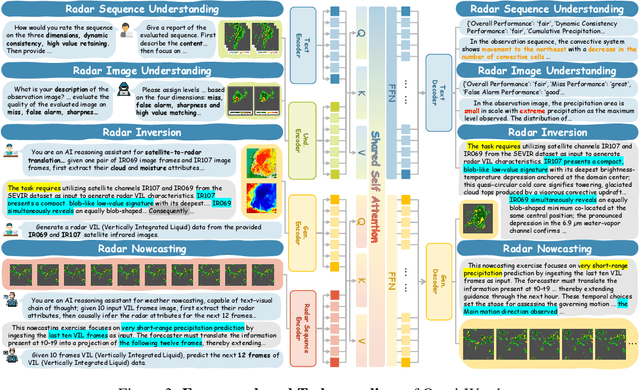
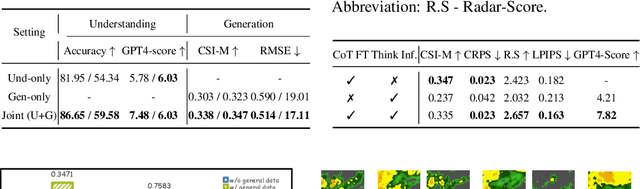
Abstract:Weather modeling requires both accurate prediction and mechanistic interpretation, yet existing methods treat these goals in isolation, separating generation from understanding. To address this gap, we present Omni-Weather, the first multimodal foundation model that unifies weather generation and understanding within a single architecture. Omni-Weather integrates a radar encoder for weather generation tasks, followed by unified processing using a shared self-attention mechanism. Moreover, we construct a Chain-of-Thought dataset for causal reasoning in weather generation, enabling interpretable outputs and improved perceptual quality. Extensive experiments show Omni-Weather achieves state-of-the-art performance in both weather generation and understanding. Our findings further indicate that generative and understanding tasks in the weather domain can mutually enhance each other. Omni-Weather also demonstrates the feasibility and value of unifying weather generation and understanding.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
Visionary: The World Model Carrier Built on WebGPU-Powered Gaussian Splatting Platform
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Neural rendering, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), has evolved rapidly and become a key component for building world models. However, existing viewer solutions remain fragmented, heavy, or constrained by legacy pipelines, resulting in high deployment friction and limited support for dynamic content and generative models. In this work, we present Visionary, an open, web-native platform for real-time various Gaussian Splatting and meshes rendering. Built on an efficient WebGPU renderer with per-frame ONNX inference, Visionary enables dynamic neural processing while maintaining a lightweight, "click-to-run" browser experience. It introduces a standardized Gaussian Generator contract, which not only supports standard 3DGS rendering but also allows plug-and-play algorithms to generate or update Gaussians each frame. Such inference also enables us to apply feedforward generative post-processing. The platform further offers a plug in three.js library with a concise TypeScript API for seamless integration into existing web applications. Experiments show that, under identical 3DGS assets, Visionary achieves superior rendering efficiency compared to current Web viewers due to GPU-based primitive sorting. It already supports multiple variants, including MLP-based 3DGS, 4DGS, neural avatars, and style transformation or enhancement networks. By unifying inference and rendering directly in the browser, Visionary significantly lowers the barrier to reproduction, comparison, and deployment of 3DGS-family methods, serving as a unified World Model Carrier for both reconstructive and generative paradigms.
ARCHE: A Novel Task to Evaluate LLMs on Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in scientific domains. While they can produce reasoning-like content via methods such as chain-of-thought prompting, these outputs are typically unstructured and informal, obscuring whether models truly understand the fundamental reasoning paradigms that underpin scientific inference. To address this, we introduce a novel task named Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction (ARCHE), in which models must decompose complex reasoning arguments into combinations of standard reasoning paradigms in the form of a Reasoning Logic Tree (RLT). In RLT, all reasoning steps are explicitly categorized as one of three variants of Peirce's fundamental inference modes: deduction, induction, or abduction. To facilitate this task, we release ARCHE Bench, a new benchmark derived from 70 Nature Communications articles, including more than 1,900 references and 38,000 viewpoints. We propose two logic-aware evaluation metrics: Entity Coverage (EC) for content completeness and Reasoning Edge Accuracy (REA) for step-by-step logical validity. Evaluations on 10 leading LLMs on ARCHE Bench reveal that models exhibit a trade-off between REA and EC, and none are yet able to extract a complete and standard reasoning chain. These findings highlight a substantial gap between the abilities of current reasoning models and the rigor required for scientific argumentation.
MicroRCA-Agent: Microservice Root Cause Analysis Method Based on Large Language Model Agents
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:This paper presents MicroRCA-Agent, an innovative solution for microservice root cause analysis based on large language model agents, which constructs an intelligent fault root cause localization system with multimodal data fusion. The technical innovations are embodied in three key aspects: First, we combine the pre-trained Drain log parsing algorithm with multi-level data filtering mechanism to efficiently compress massive logs into high-quality fault features. Second, we employ a dual anomaly detection approach that integrates Isolation Forest unsupervised learning algorithms with status code validation to achieve comprehensive trace anomaly identification. Third, we design a statistical symmetry ratio filtering mechanism coupled with a two-stage LLM analysis strategy to enable full-stack phenomenon summarization across node-service-pod hierarchies. The multimodal root cause analysis module leverages carefully designed cross-modal prompts to deeply integrate multimodal anomaly information, fully exploiting the cross-modal understanding and logical reasoning capabilities of large language models to generate structured analysis results encompassing fault components, root cause descriptions, and reasoning trace. Comprehensive ablation studies validate the complementary value of each modal data and the effectiveness of the system architecture. The proposed solution demonstrates superior performance in complex microservice fault scenarios, achieving a final score of 50.71. The code has been released at: https://github.com/tangpan360/MicroRCA-Agent.
Interleaving Reasoning for Better Text-to-Image Generation
Sep 09, 2025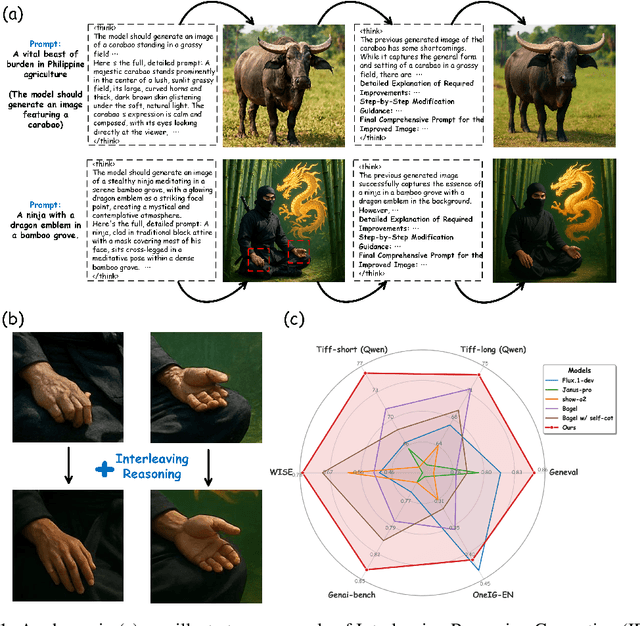
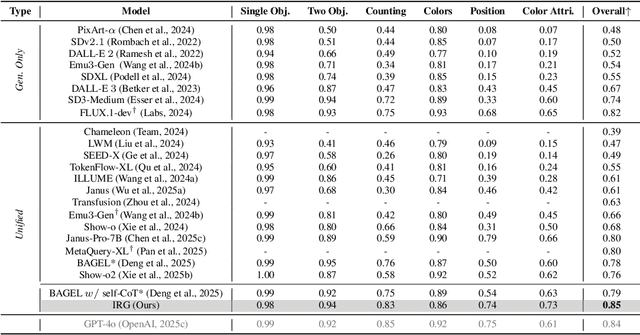

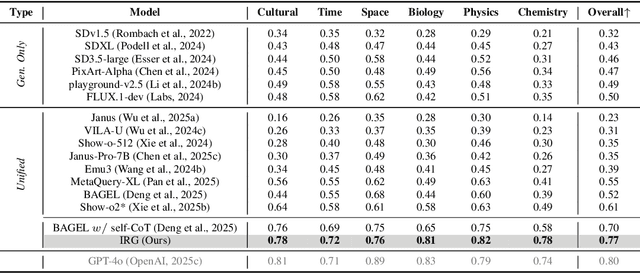
Abstract:Unified multimodal understanding and generation models recently have achieve significant improvement in image generation capability, yet a large gap remains in instruction following and detail preservation compared to systems that tightly couple comprehension with generation such as GPT-4o. Motivated by recent advances in interleaving reasoning, we explore whether such reasoning can further improve Text-to-Image (T2I) generation. We introduce Interleaving Reasoning Generation (IRG), a framework that alternates between text-based thinking and image synthesis: the model first produces a text-based thinking to guide an initial image, then reflects on the result to refine fine-grained details, visual quality, and aesthetics while preserving semantics. To train IRG effectively, we propose Interleaving Reasoning Generation Learning (IRGL), which targets two sub-goals: (1) strengthening the initial think-and-generate stage to establish core content and base quality, and (2) enabling high-quality textual reflection and faithful implementation of those refinements in a subsequent image. We curate IRGL-300K, a dataset organized into six decomposed learning modes that jointly cover learning text-based thinking, and full thinking-image trajectories. Starting from a unified foundation model that natively emits interleaved text-image outputs, our two-stage training first builds robust thinking and reflection, then efficiently tunes the IRG pipeline in the full thinking-image trajectory data. Extensive experiments show SoTA performance, yielding absolute gains of 5-10 points on GenEval, WISE, TIIF, GenAI-Bench, and OneIG-EN, alongside substantial improvements in visual quality and fine-grained fidelity. The code, model weights and datasets will be released in: https://github.com/Osilly/Interleaving-Reasoning-Generation .
A Survey of Scientific Large Language Models: From Data Foundations to Agent Frontiers
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) are transforming how knowledge is represented, integrated, and applied in scientific research, yet their progress is shaped by the complex nature of scientific data. This survey presents a comprehensive, data-centric synthesis that reframes the development of Sci-LLMs as a co-evolution between models and their underlying data substrate. We formulate a unified taxonomy of scientific data and a hierarchical model of scientific knowledge, emphasizing the multimodal, cross-scale, and domain-specific challenges that differentiate scientific corpora from general natural language processing datasets. We systematically review recent Sci-LLMs, from general-purpose foundations to specialized models across diverse scientific disciplines, alongside an extensive analysis of over 270 pre-/post-training datasets, showing why Sci-LLMs pose distinct demands -- heterogeneous, multi-scale, uncertainty-laden corpora that require representations preserving domain invariance and enabling cross-modal reasoning. On evaluation, we examine over 190 benchmark datasets and trace a shift from static exams toward process- and discovery-oriented assessments with advanced evaluation protocols. These data-centric analyses highlight persistent issues in scientific data development and discuss emerging solutions involving semi-automated annotation pipelines and expert validation. Finally, we outline a paradigm shift toward closed-loop systems where autonomous agents based on Sci-LLMs actively experiment, validate, and contribute to a living, evolving knowledge base. Collectively, this work provides a roadmap for building trustworthy, continually evolving artificial intelligence (AI) systems that function as a true partner in accelerating scientific discovery.
Mimicking the Physicist's Eye:A VLM-centric Approach for Physics Formula Discovery
Aug 24, 2025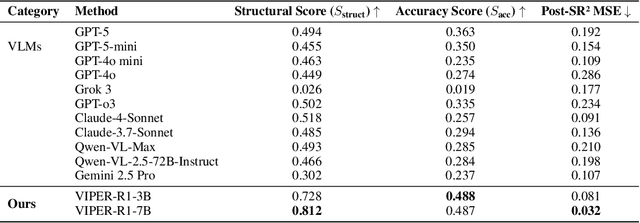
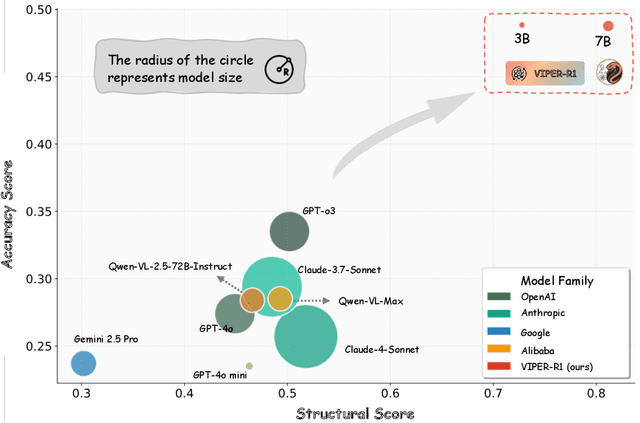
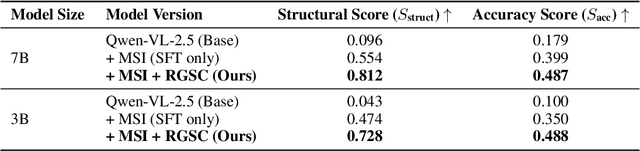
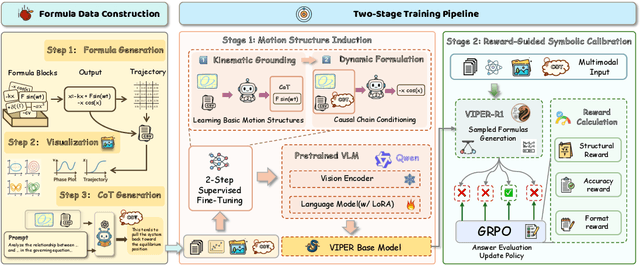
Abstract:Automated discovery of physical laws from observational data in the real world is a grand challenge in AI. Current methods, relying on symbolic regression or LLMs, are limited to uni-modal data and overlook the rich, visual phenomenological representations of motion that are indispensable to physicists. This "sensory deprivation" severely weakens their ability to interpret the inherent spatio-temporal patterns within dynamic phenomena. To address this gap, we propose VIPER-R1, a multimodal model that performs Visual Induction for Physics-based Equation Reasoning to discover fundamental symbolic formulas. It integrates visual perception, trajectory data, and symbolic reasoning to emulate the scientific discovery process. The model is trained via a curriculum of Motion Structure Induction (MSI), using supervised fine-tuning to interpret kinematic phase portraits and to construct hypotheses guided by a Causal Chain of Thought (C-CoT), followed by Reward-Guided Symbolic Calibration (RGSC) to refine the formula structure with reinforcement learning. During inference, the trained VIPER-R1 acts as an agent: it first posits a high-confidence symbolic ansatz, then proactively invokes an external symbolic regression tool to perform Symbolic Residual Realignment (SR^2). This final step, analogous to a physicist's perturbation analysis, reconciles the theoretical model with empirical data. To support this research, we introduce PhysSymbol, a new 5,000-instance multimodal corpus. Experiments show that VIPER-R1 consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines in accuracy and interpretability, enabling more precise discovery of physical laws. Project page: https://jiaaqiliu.github.io/VIPER-R1/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge