Jinouwen Zhang
SciIF: Benchmarking Scientific Instruction Following Towards Rigorous Scientific Intelligence
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) transition from general knowledge retrieval to complex scientific discovery, their evaluation standards must also incorporate the rigorous norms of scientific inquiry. Existing benchmarks exhibit a critical blind spot: general instruction-following metrics focus on superficial formatting, while domain-specific scientific benchmarks assess only final-answer correctness, often rewarding models that arrive at the right result with the wrong reasons. To address this gap, we introduce scientific instruction following: the capability to solve problems while strictly adhering to the constraints that establish scientific validity. Specifically, we introduce SciIF, a multi-discipline benchmark that evaluates this capability by pairing university-level problems with a fixed catalog of constraints across three pillars: scientific conditions (e.g., boundary checks and assumptions), semantic stability (e.g., unit and symbol conventions), and specific processes(e.g., required numerical methods). Uniquely, SciIF emphasizes auditability, requiring models to provide explicit evidence of constraint satisfaction rather than implicit compliance. By measuring both solution correctness and multi-constraint adherence, SciIF enables finegrained diagnosis of compositional reasoning failures, ensuring that LLMs can function as reliable agents within the strict logical frameworks of science.
LabUtopia: High-Fidelity Simulation and Hierarchical Benchmark for Scientific Embodied Agents
May 28, 2025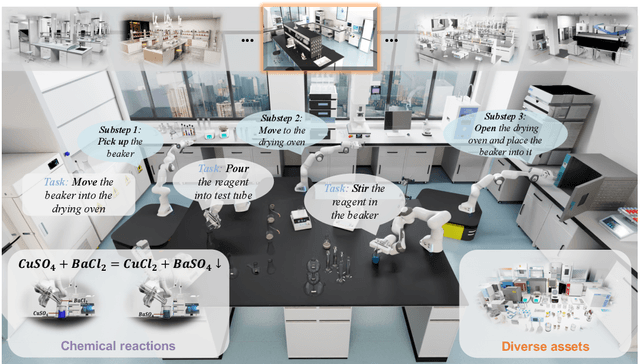
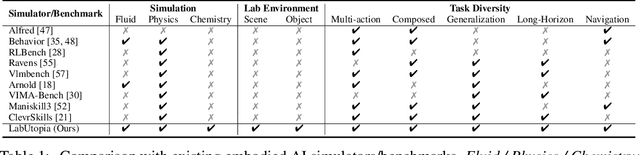
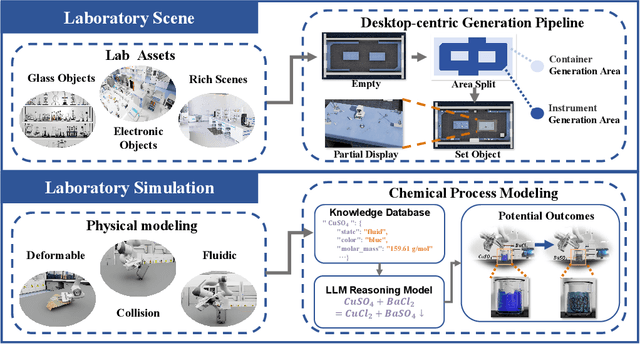
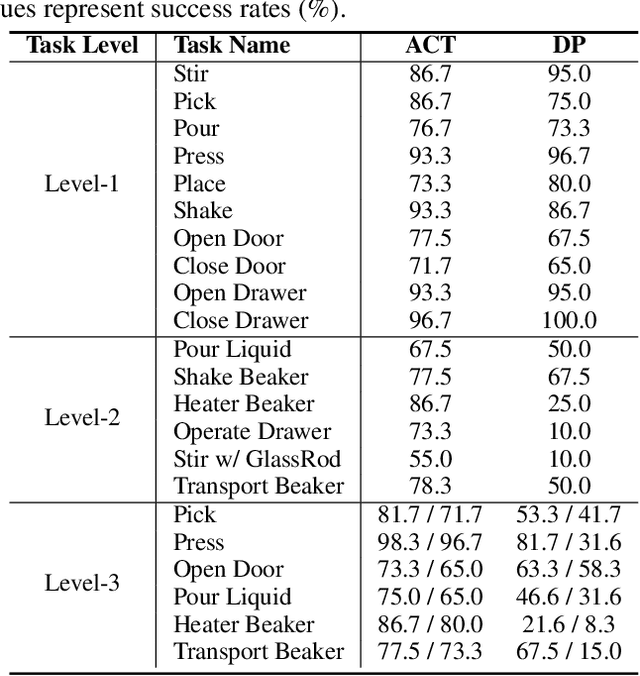
Abstract:Scientific embodied agents play a crucial role in modern laboratories by automating complex experimental workflows. Compared to typical household environments, laboratory settings impose significantly higher demands on perception of physical-chemical transformations and long-horizon planning, making them an ideal testbed for advancing embodied intelligence. However, its development has been long hampered by the lack of suitable simulator and benchmarks. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing LabUtopia, a comprehensive simulation and benchmarking suite designed to facilitate the development of generalizable, reasoning-capable embodied agents in laboratory settings. Specifically, it integrates i) LabSim, a high-fidelity simulator supporting multi-physics and chemically meaningful interactions; ii) LabScene, a scalable procedural generator for diverse scientific scenes; and iii) LabBench, a hierarchical benchmark spanning five levels of complexity from atomic actions to long-horizon mobile manipulation. LabUtopia supports 30 distinct tasks and includes more than 200 scene and instrument assets, enabling large-scale training and principled evaluation in high-complexity environments. We demonstrate that LabUtopia offers a powerful platform for advancing the integration of perception, planning, and control in scientific-purpose agents and provides a rigorous testbed for exploring the practical capabilities and generalization limits of embodied intelligence in future research.
Revisiting Generative Policies: A Simpler Reinforcement Learning Algorithmic Perspective
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Generative models, particularly diffusion models, have achieved remarkable success in density estimation for multimodal data, drawing significant interest from the reinforcement learning (RL) community, especially in policy modeling in continuous action spaces. However, existing works exhibit significant variations in training schemes and RL optimization objectives, and some methods are only applicable to diffusion models. In this study, we compare and analyze various generative policy training and deployment techniques, identifying and validating effective designs for generative policy algorithms. Specifically, we revisit existing training objectives and classify them into two categories, each linked to a simpler approach. The first approach, Generative Model Policy Optimization (GMPO), employs a native advantage-weighted regression formulation as the training objective, which is significantly simpler than previous methods. The second approach, Generative Model Policy Gradient (GMPG), offers a numerically stable implementation of the native policy gradient method. We introduce a standardized experimental framework named GenerativeRL. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed methods achieve state-of-the-art performance on various offline-RL datasets, offering a unified and practical guideline for training and deploying generative policies.
Pretrained Reversible Generation as Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Recent generative models based on score matching and flow matching have significantly advanced generation tasks, but their potential in discriminative tasks remains underexplored. Previous approaches, such as generative classifiers, have not fully leveraged the capabilities of these models for discriminative tasks due to their intricate designs. We propose Pretrained Reversible Generation (PRG), which extracts unsupervised representations by reversing the generative process of a pretrained continuous flow model. PRG effectively reuses unsupervised generative models, leveraging their high capacity to serve as robust and generalizable feature extractors for downstream tasks. Our method consistently outperforms prior approaches across multiple benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance among generative model-based methods, including 78\% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet. Extensive ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge