Yuhao Zhou
SciEvalKit: An Open-source Evaluation Toolkit for Scientific General Intelligence
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce SciEvalKit, a unified benchmarking toolkit designed to evaluate AI models for science across a broad range of scientific disciplines and task capabilities. Unlike general-purpose evaluation platforms, SciEvalKit focuses on the core competencies of scientific intelligence, including Scientific Multimodal Perception, Scientific Multimodal Reasoning, Scientific Multimodal Understanding, Scientific Symbolic Reasoning, Scientific Code Generation, Science Hypothesis Generation and Scientific Knowledge Understanding. It supports six major scientific domains, spanning from physics and chemistry to astronomy and materials science. SciEvalKit builds a foundation of expert-grade scientific benchmarks, curated from real-world, domain-specific datasets, ensuring that tasks reflect authentic scientific challenges. The toolkit features a flexible, extensible evaluation pipeline that enables batch evaluation across models and datasets, supports custom model and dataset integration, and provides transparent, reproducible, and comparable results. By bridging capability-based evaluation and disciplinary diversity, SciEvalKit offers a standardized yet customizable infrastructure to benchmark the next generation of scientific foundation models and intelligent agents. The toolkit is open-sourced and actively maintained to foster community-driven development and progress in AI4Science.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
AgentPRM: Process Reward Models for LLM Agents via Step-Wise Promise and Progress
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Despite rapid development, large language models (LLMs) still encounter challenges in multi-turn decision-making tasks (i.e., agent tasks) like web shopping and browser navigation, which require making a sequence of intelligent decisions based on environmental feedback. Previous work for LLM agents typically relies on elaborate prompt engineering or fine-tuning with expert trajectories to improve performance. In this work, we take a different perspective: we explore constructing process reward models (PRMs) to evaluate each decision and guide the agent's decision-making process. Unlike LLM reasoning, where each step is scored based on correctness, actions in agent tasks do not have a clear-cut correctness. Instead, they should be evaluated based on their proximity to the goal and the progress they have made. Building on this insight, we propose a re-defined PRM for agent tasks, named AgentPRM, to capture both the interdependence between sequential decisions and their contribution to the final goal. This enables better progress tracking and exploration-exploitation balance. To scalably obtain labeled data for training AgentPRM, we employ a Temporal Difference-based (TD-based) estimation method combined with Generalized Advantage Estimation (GAE), which proves more sample-efficient than prior methods. Extensive experiments across different agentic tasks show that AgentPRM is over $8\times$ more compute-efficient than baselines, and it demonstrates robust improvement when scaling up test-time compute. Moreover, we perform detailed analyses to show how our method works and offer more insights, e.g., applying AgentPRM to the reinforcement learning of LLM agents.
Data Efficient Any Transformer-to-Mamba Distillation via Attention Bridge
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:State-space models (SSMs) have emerged as efficient alternatives to Transformers for sequence modeling, offering superior scalability through recurrent structures. However, their training remains costly and the ecosystem around them is far less mature than that of Transformers. Moreover, the structural heterogeneity between SSMs and Transformers makes it challenging to efficiently distill knowledge from pretrained attention models. In this work, we propose Cross-architecture distillation via Attention Bridge (CAB), a novel data-efficient distillation framework that efficiently transfers attention knowledge from Transformer teachers to state-space student models. Unlike conventional knowledge distillation that transfers knowledge only at the output level, CAB enables token-level supervision via a lightweight bridge and flexible layer-wise alignment, improving both efficiency and transferability. We further introduce flexible layer-wise alignment strategies to accommodate architectural discrepancies between teacher and student. Extensive experiments across vision and language domains demonstrate that our method consistently improves the performance of state-space models, even under limited training data, outperforming both standard and cross-architecture distillation methods. Our findings suggest that attention-based knowledge can be efficiently transferred to recurrent models, enabling rapid utilization of Transformer expertise for building a stronger SSM community.
Deploying Models to Non-participating Clients in Federated Learning without Fine-tuning: A Hypernetwork-based Approach
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for privacy-preserving collaborative learning, yet data heterogeneity remains a critical challenge. While existing methods achieve progress in addressing data heterogeneity for participating clients, they fail to generalize to non-participating clients with in-domain distribution shifts and resource constraints. To mitigate this issue, we present HyperFedZero, a novel method that dynamically generates specialized models via a hypernetwork conditioned on distribution-aware embeddings. Our approach explicitly incorporates distribution-aware inductive biases into the model's forward pass, extracting robust distribution embeddings using a NoisyEmbed-enhanced extractor with a Balancing Penalty, effectively preventing feature collapse. The hypernetwork then leverages these embeddings to generate specialized models chunk-by-chunk for non-participating clients, ensuring adaptability to their unique data distributions. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets and models demonstrate HyperFedZero's remarkable performance, surpassing competing methods consistently with minimal computational, storage, and communication overhead. Moreover, ablation studies and visualizations further validate the necessity of each component, confirming meaningful adaptations and validating the effectiveness of HyperFedZero.
Speech-Language Models with Decoupled Tokenizers and Multi-Token Prediction
Jun 14, 2025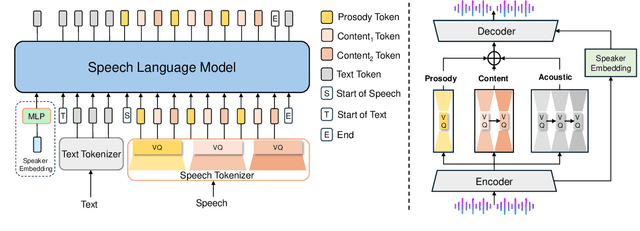
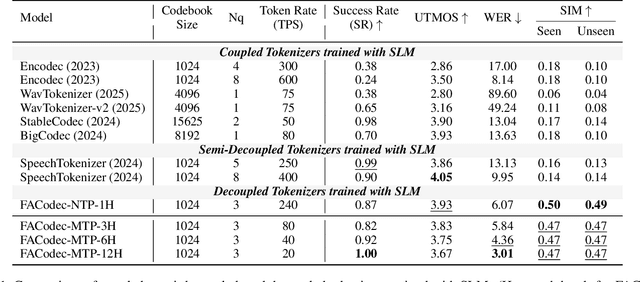
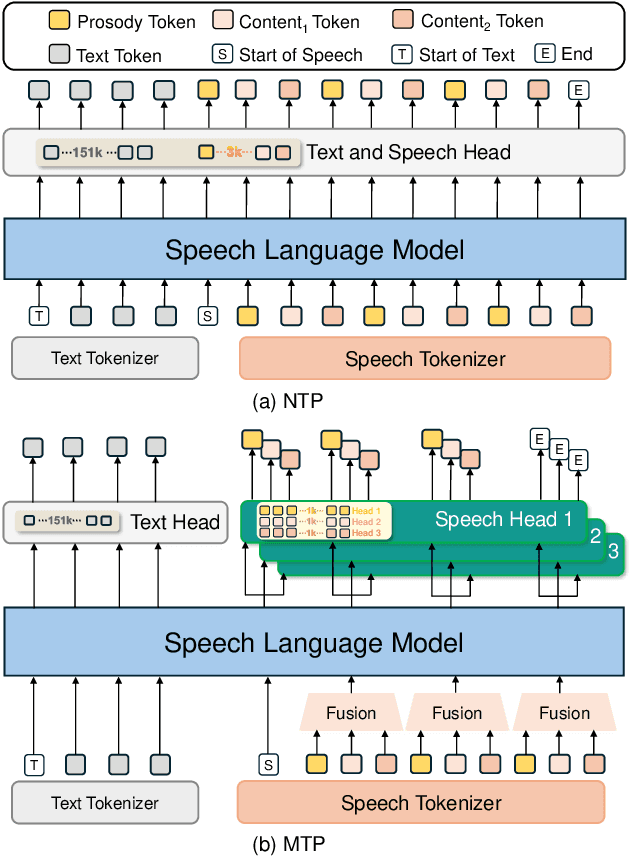
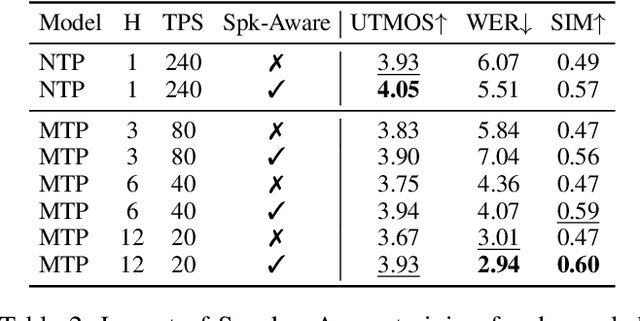
Abstract:Speech-language models (SLMs) offer a promising path toward unifying speech and text understanding and generation. However, challenges remain in achieving effective cross-modal alignment and high-quality speech generation. In this work, we systematically investigate the impact of key components (i.e., speech tokenizers, speech heads, and speaker modeling) on the performance of LLM-centric SLMs. We compare coupled, semi-decoupled, and fully decoupled speech tokenizers under a fair SLM framework and find that decoupled tokenization significantly improves alignment and synthesis quality. To address the information density mismatch between speech and text, we introduce multi-token prediction (MTP) into SLMs, enabling each hidden state to decode multiple speech tokens. This leads to up to 12$\times$ faster decoding and a substantial drop in word error rate (from 6.07 to 3.01). Furthermore, we propose a speaker-aware generation paradigm and introduce RoleTriviaQA, a large-scale role-playing knowledge QA benchmark with diverse speaker identities. Experiments demonstrate that our methods enhance both knowledge understanding and speaker consistency.
Scientists' First Exam: Probing Cognitive Abilities of MLLM via Perception, Understanding, and Reasoning
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Scientific discoveries increasingly rely on complex multimodal reasoning based on information-intensive scientific data and domain-specific expertise. Empowered by expert-level scientific benchmarks, scientific Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) hold the potential to significantly enhance this discovery process in realistic workflows. However, current scientific benchmarks mostly focus on evaluating the knowledge understanding capabilities of MLLMs, leading to an inadequate assessment of their perception and reasoning abilities. To address this gap, we present the Scientists' First Exam (SFE) benchmark, designed to evaluate the scientific cognitive capacities of MLLMs through three interconnected levels: scientific signal perception, scientific attribute understanding, scientific comparative reasoning. Specifically, SFE comprises 830 expert-verified VQA pairs across three question types, spanning 66 multimodal tasks across five high-value disciplines. Extensive experiments reveal that current state-of-the-art GPT-o3 and InternVL-3 achieve only 34.08% and 26.52% on SFE, highlighting significant room for MLLMs to improve in scientific realms. We hope the insights obtained in SFE will facilitate further developments in AI-enhanced scientific discoveries.
MSEarth: A Benchmark for Multimodal Scientific Comprehension of Earth Science
May 27, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has unlocked new opportunities to tackle complex scientific challenges. Despite this progress, their application in addressing earth science problems, especially at the graduate level, remains underexplored. A significant barrier is the absence of benchmarks that capture the depth and contextual complexity of geoscientific reasoning. Current benchmarks often rely on synthetic datasets or simplistic figure-caption pairs, which do not adequately reflect the intricate reasoning and domain-specific insights required for real-world scientific applications. To address these gaps, we introduce MSEarth, a multimodal scientific benchmark curated from high-quality, open-access scientific publications. MSEarth encompasses the five major spheres of Earth science: atmosphere, cryosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, featuring over 7K figures with refined captions. These captions are crafted from the original figure captions and enriched with discussions and reasoning from the papers, ensuring the benchmark captures the nuanced reasoning and knowledge-intensive content essential for advanced scientific tasks. MSEarth supports a variety of tasks, including scientific figure captioning, multiple choice questions, and open-ended reasoning challenges. By bridging the gap in graduate-level benchmarks, MSEarth provides a scalable and high-fidelity resource to enhance the development and evaluation of MLLMs in scientific reasoning. The benchmark is publicly available to foster further research and innovation in this field. Resources related to this benchmark can be found at https://huggingface.co/MSEarth and https://github.com/xiangyu-mm/MSEarth.
REPA Works Until It Doesn't: Early-Stopped, Holistic Alignment Supercharges Diffusion Training
May 22, 2025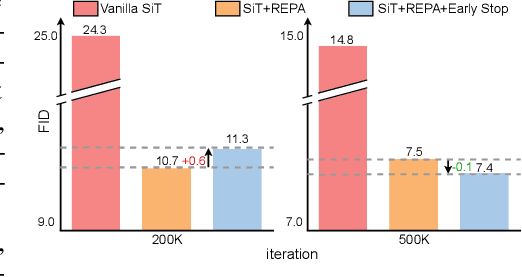
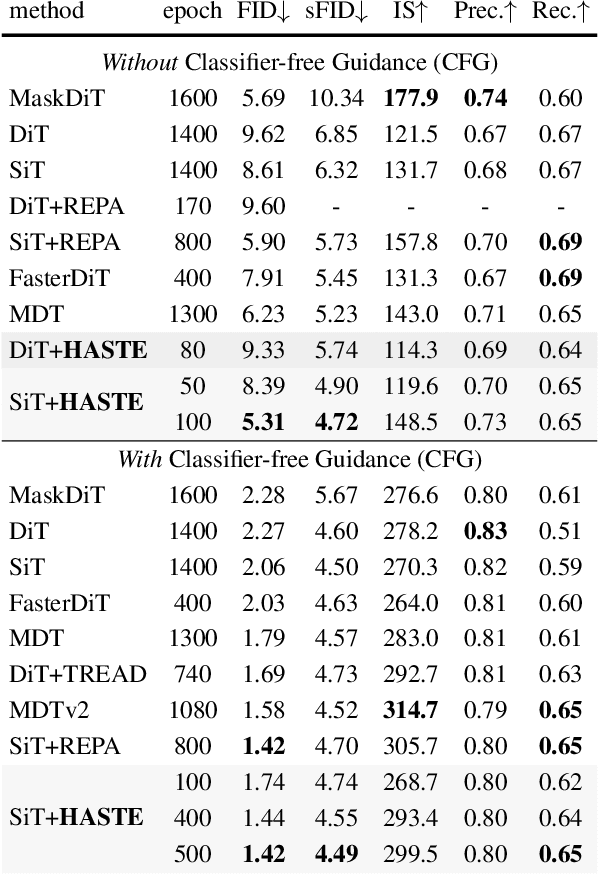

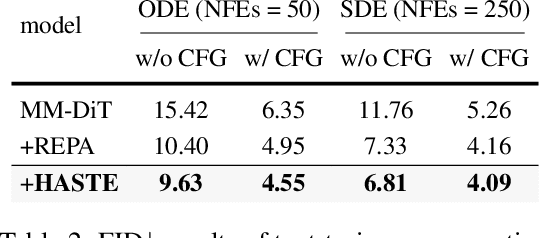
Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) deliver state-of-the-art image quality, yet their training remains notoriously slow. A recent remedy -- representation alignment (REPA) that matches DiT hidden features to those of a non-generative teacher (e.g. DINO) -- dramatically accelerates the early epochs but plateaus or even degrades performance later. We trace this failure to a capacity mismatch: once the generative student begins modelling the joint data distribution, the teacher's lower-dimensional embeddings and attention patterns become a straitjacket rather than a guide. We then introduce HASTE (Holistic Alignment with Stage-wise Termination for Efficient training), a two-phase schedule that keeps the help and drops the hindrance. Phase I applies a holistic alignment loss that simultaneously distills attention maps (relational priors) and feature projections (semantic anchors) from the teacher into mid-level layers of the DiT, yielding rapid convergence. Phase II then performs one-shot termination that deactivates the alignment loss, once a simple trigger such as a fixed iteration is hit, freeing the DiT to focus on denoising and exploit its generative capacity. HASTE speeds up training of diverse DiTs without architecture changes. On ImageNet 256X256, it reaches the vanilla SiT-XL/2 baseline FID in 50 epochs and matches REPA's best FID in 500 epochs, amounting to a 28X reduction in optimization steps. HASTE also improves text-to-image DiTs on MS-COCO, demonstrating to be a simple yet principled recipe for efficient diffusion training across various tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/NUS-HPC-AI-Lab/HASTE .
EarthSE: A Benchmark Evaluating Earth Scientific Exploration Capability for Large Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) drive interest in scientific applications, necessitating specialized benchmarks such as Earth science. Existing benchmarks either present a general science focus devoid of Earth science specificity or cover isolated subdomains, lacking holistic evaluation. Furthermore, current benchmarks typically neglect the assessment of LLMs' capabilities in open-ended scientific exploration. In this paper, we present a comprehensive and professional benchmark for the Earth sciences, designed to evaluate the capabilities of LLMs in scientific exploration within this domain, spanning from fundamental to advanced levels. Leveraging a corpus of 100,000 research papers, we first construct two Question Answering (QA) datasets: Earth-Iron, which offers extensive question coverage for broad assessment, and Earth-Silver, which features a higher level of difficulty to evaluate professional depth. These datasets encompass five Earth spheres, 114 disciplines, and 11 task categories, assessing foundational knowledge crucial for scientific exploration. Most notably, we introduce Earth-Gold with new metrics, a dataset comprising open-ended multi-turn dialogues specifically designed to evaluate the advanced capabilities of LLMs in scientific exploration, including methodology induction, limitation analysis, and concept proposal. Extensive experiments reveal limitations in 11 leading LLMs across different domains and tasks, highlighting considerable room for improvement in their scientific exploration capabilities. The benchmark is available on https://huggingface.co/ai-earth .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge