Xiaokai Bai
Wavelet-based Multi-View Fusion of 4D Radar Tensor and Camera for Robust 3D Object Detection
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:4D millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar has been widely adopted in autonomous driving and robot perception due to its low cost and all-weather robustness. However, its inherent sparsity and limited semantic richness significantly constrain perception capability. Recently, fusing camera data with 4D radar has emerged as a promising cost effective solution, by exploiting the complementary strengths of the two modalities. Nevertheless, point-cloud-based radar often suffer from information loss introduced by multi-stage signal processing, while directly utilizing raw 4D radar data incurs prohibitive computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose WRCFormer, a novel 3D object detection framework that fuses raw radar cubes with camera inputs via multi-view representations of the decoupled radar cube. Specifically, we design a Wavelet Attention Module as the basic module of wavelet-based Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) to enhance the representation of sparse radar signals and image data. We further introduce a two-stage query-based, modality-agnostic fusion mechanism termed Geometry-guided Progressive Fusion to efficiently integrate multi-view features from both modalities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WRCFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on the K-Radar benchmarks, surpassing the best model by approximately 2.4% in all scenarios and 1.6% in the sleet scenario, highlighting its robustness under adverse weather conditions.
Recurrent Cross-View Object Geo-Localization
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Cross-view object geo-localization (CVOGL) aims to determine the location of a specific object in high-resolution satellite imagery given a query image with a point prompt. Existing approaches treat CVOGL as a one-shot detection task, directly regressing object locations from cross-view information aggregation, but they are vulnerable to feature noise and lack mechanisms for error correction. In this paper, we propose ReCOT, a Recurrent Cross-view Object geo-localization Transformer, which reformulates CVOGL as a recurrent localization task. ReCOT introduces a set of learnable tokens that encode task-specific intent from the query image and prompt embeddings, and iteratively attend to the reference features to refine the predicted location. To enhance this recurrent process, we incorporate two complementary modules: (1) a SAM-based knowledge distillation strategy that transfers segmentation priors from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to provide clearer semantic guidance without additional inference cost, and (2) a Reference Feature Enhancement Module (RFEM) that introduces a hierarchical attention to emphasize object-relevant regions in the reference features. Extensive experiments on standard CVOGL benchmarks demonstrate that ReCOT achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance while reducing parameters by 60% compared to previous SOTA approaches.
S-BEVLoc: BEV-based Self-supervised Framework for Large-scale LiDAR Global Localization
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:LiDAR-based global localization is an essential component of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), which helps loop closure and re-localization. Current approaches rely on ground-truth poses obtained from GPS or SLAM odometry to supervise network training. Despite the great success of these supervised approaches, substantial cost and effort are required for high-precision ground-truth pose acquisition. In this work, we propose S-BEVLoc, a novel self-supervised framework based on bird's-eye view (BEV) for LiDAR global localization, which eliminates the need for ground-truth poses and is highly scalable. We construct training triplets from single BEV images by leveraging the known geographic distances between keypoint-centered BEV patches. Convolutional neural network (CNN) is used to extract local features, and NetVLAD is employed to aggregate global descriptors. Moreover, we introduce SoftCos loss to enhance learning from the generated triplets. Experimental results on the large-scale KITTI and NCLT datasets show that S-BEVLoc achieves state-of-the-art performance in place recognition, loop closure, and global localization tasks, while offering scalability that would require extra effort for supervised approaches.
Structure-Aware Radar-Camera Depth Estimation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Monocular depth estimation aims to determine the depth of each pixel from an RGB image captured by a monocular camera. The development of deep learning has significantly advanced this field by facilitating the learning of depth features from some well-annotated datasets \cite{Geiger_Lenz_Stiller_Urtasun_2013,silberman2012indoor}. Eigen \textit{et al.} \cite{eigen2014depth} first introduce a multi-scale fusion network for depth regression. Following this, subsequent improvements have come from reinterpreting the regression task as a classification problem \cite{bhat2021adabins,Li_Wang_Liu_Jiang_2022}, incorporating additional priors \cite{shao2023nddepth,yang2023gedepth}, and developing more effective objective function \cite{xian2020structure,Yin_Liu_Shen_Yan_2019}. Despite these advances, generalizing to unseen domains remains a challenge. Recently, several methods have employed affine-invariant loss to enable multi-dataset joint training \cite{MiDaS,ZeroDepth,guizilini2023towards,Dany}. Among them, Depth Anything \cite{Dany} has shown leading performance in zero-shot monocular depth estimation. While it struggles to estimate accurate metric depth due to the lack of explicit depth cues, it excels at extracting structural information from unseen images, producing structure-detailed monocular depth.
Doracamom: Joint 3D Detection and Occupancy Prediction with Multi-view 4D Radars and Cameras for Omnidirectional Perception
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:3D object detection and occupancy prediction are critical tasks in autonomous driving, attracting significant attention. Despite the potential of recent vision-based methods, they encounter challenges under adverse conditions. Thus, integrating cameras with next-generation 4D imaging radar to achieve unified multi-task perception is highly significant, though research in this domain remains limited. In this paper, we propose Doracamom, the first framework that fuses multi-view cameras and 4D radar for joint 3D object detection and semantic occupancy prediction, enabling comprehensive environmental perception. Specifically, we introduce a novel Coarse Voxel Queries Generator that integrates geometric priors from 4D radar with semantic features from images to initialize voxel queries, establishing a robust foundation for subsequent Transformer-based refinement. To leverage temporal information, we design a Dual-Branch Temporal Encoder that processes multi-modal temporal features in parallel across BEV and voxel spaces, enabling comprehensive spatio-temporal representation learning. Furthermore, we propose a Cross-Modal BEV-Voxel Fusion module that adaptively fuses complementary features through attention mechanisms while employing auxiliary tasks to enhance feature quality. Extensive experiments on the OmniHD-Scenes, View-of-Delft (VoD), and TJ4DRadSet datasets demonstrate that Doracamom achieves state-of-the-art performance in both tasks, establishing new benchmarks for multi-modal 3D perception. Code and models will be publicly available.
OmniHD-Scenes: A Next-Generation Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving
Dec 14, 2024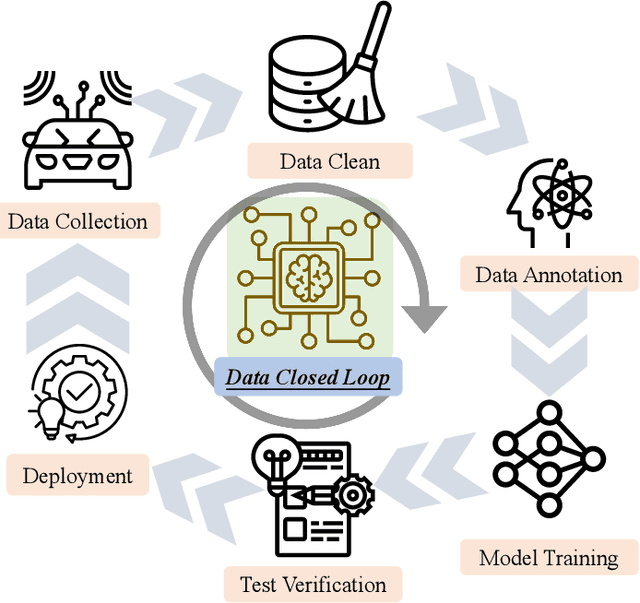

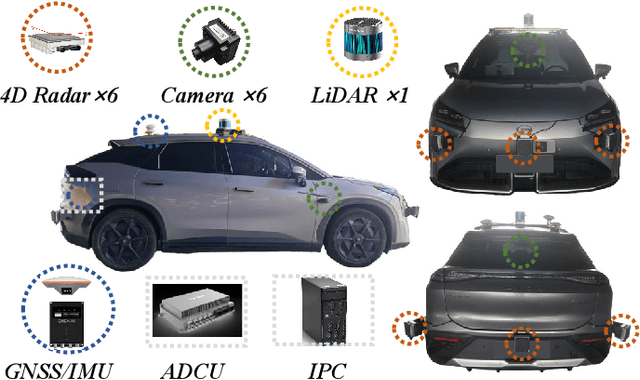
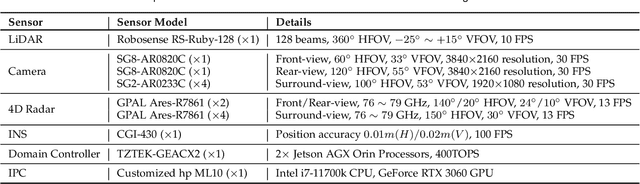
Abstract:The rapid advancement of deep learning has intensified the need for comprehensive data for use by autonomous driving algorithms. High-quality datasets are crucial for the development of effective data-driven autonomous driving solutions. Next-generation autonomous driving datasets must be multimodal, incorporating data from advanced sensors that feature extensive data coverage, detailed annotations, and diverse scene representation. To address this need, we present OmniHD-Scenes, a large-scale multimodal dataset that provides comprehensive omnidirectional high-definition data. The OmniHD-Scenes dataset combines data from 128-beam LiDAR, six cameras, and six 4D imaging radar systems to achieve full environmental perception. The dataset comprises 1501 clips, each approximately 30-s long, totaling more than 450K synchronized frames and more than 5.85 million synchronized sensor data points. We also propose a novel 4D annotation pipeline. To date, we have annotated 200 clips with more than 514K precise 3D bounding boxes. These clips also include semantic segmentation annotations for static scene elements. Additionally, we introduce a novel automated pipeline for generation of the dense occupancy ground truth, which effectively leverages information from non-key frames. Alongside the proposed dataset, we establish comprehensive evaluation metrics, baseline models, and benchmarks for 3D detection and semantic occupancy prediction. These benchmarks utilize surround-view cameras and 4D imaging radar to explore cost-effective sensor solutions for autonomous driving applications. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our low-cost sensor configuration and its robustness under adverse conditions. Data will be released at https://www.2077ai.com/OmniHD-Scenes.
Rethinking Early-Fusion Strategies for Improved Multispectral Object Detection
May 25, 2024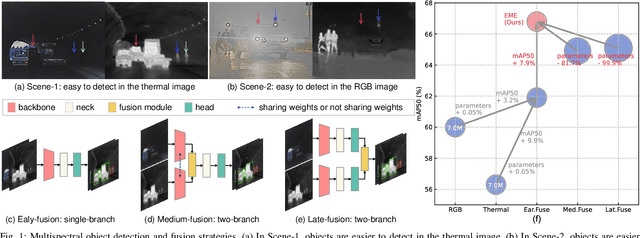
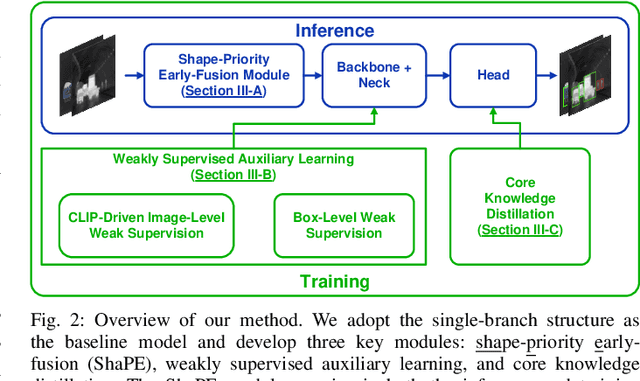
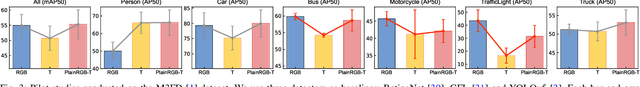
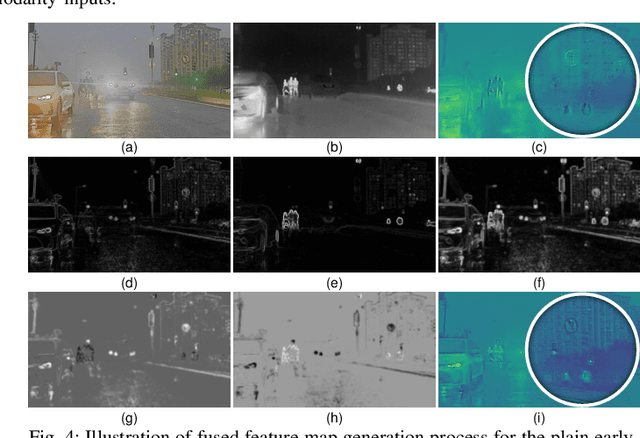
Abstract:Most recent multispectral object detectors employ a two-branch structure to extract features from RGB and thermal images. While the two-branch structure achieves better performance than a single-branch structure, it overlooks inference efficiency. This conflict is increasingly aggressive, as recent works solely pursue higher performance rather than both performance and efficiency. In this paper, we address this issue by improving the performance of efficient single-branch structures. We revisit the reasons causing the performance gap between these structures. For the first time, we reveal the information interference problem in the naive early-fusion strategy adopted by previous single-branch structures. Besides, we find that the domain gap between multispectral images, and weak feature representation of the single-branch structure are also key obstacles for performance. Focusing on these three problems, we propose corresponding solutions, including a novel shape-priority early-fusion strategy, a weakly supervised learning method, and a core knowledge distillation technique. Experiments demonstrate that single-branch networks equipped with these three contributions achieve significant performance enhancements while retaining high efficiency. Our code will be available at \url{https://github.com/XueZ-phd/Efficient-RGB-T-Early-Fusion-Detection}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge