Runwei Guan
4D-CAAL: 4D Radar-Camera Calibration and Auto-Labeling for Autonomous Driving
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:4D radar has emerged as a critical sensor for autonomous driving, primarily due to its enhanced capabilities in elevation measurement and higher resolution compared to traditional 3D radar. Effective integration of 4D radar with cameras requires accurate extrinsic calibration, and the development of radar-based perception algorithms demands large-scale annotated datasets. However, existing calibration methods often employ separate targets optimized for either visual or radar modalities, complicating correspondence establishment. Furthermore, manually labeling sparse radar data is labor-intensive and unreliable. To address these challenges, we propose 4D-CAAL, a unified framework for 4D radar-camera calibration and auto-labeling. Our approach introduces a novel dual-purpose calibration target design, integrating a checkerboard pattern on the front surface for camera detection and a corner reflector at the center of the back surface for radar detection. We develop a robust correspondence matching algorithm that aligns the checkerboard center with the strongest radar reflection point, enabling accurate extrinsic calibration. Subsequently, we present an auto-labeling pipeline that leverages the calibrated sensor relationship to transfer annotations from camera-based segmentations to radar point clouds through geometric projection and multi-feature optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves high calibration accuracy while significantly reducing manual annotation effort, thereby accelerating the development of robust multi-modal perception systems for autonomous driving.
Wavelet-based Multi-View Fusion of 4D Radar Tensor and Camera for Robust 3D Object Detection
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:4D millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar has been widely adopted in autonomous driving and robot perception due to its low cost and all-weather robustness. However, its inherent sparsity and limited semantic richness significantly constrain perception capability. Recently, fusing camera data with 4D radar has emerged as a promising cost effective solution, by exploiting the complementary strengths of the two modalities. Nevertheless, point-cloud-based radar often suffer from information loss introduced by multi-stage signal processing, while directly utilizing raw 4D radar data incurs prohibitive computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose WRCFormer, a novel 3D object detection framework that fuses raw radar cubes with camera inputs via multi-view representations of the decoupled radar cube. Specifically, we design a Wavelet Attention Module as the basic module of wavelet-based Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) to enhance the representation of sparse radar signals and image data. We further introduce a two-stage query-based, modality-agnostic fusion mechanism termed Geometry-guided Progressive Fusion to efficiently integrate multi-view features from both modalities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that WRCFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on the K-Radar benchmarks, surpassing the best model by approximately 2.4% in all scenarios and 1.6% in the sleet scenario, highlighting its robustness under adverse weather conditions.
MMDrive: Interactive Scene Understanding Beyond Vision with Multi-representational Fusion
Dec 16, 2025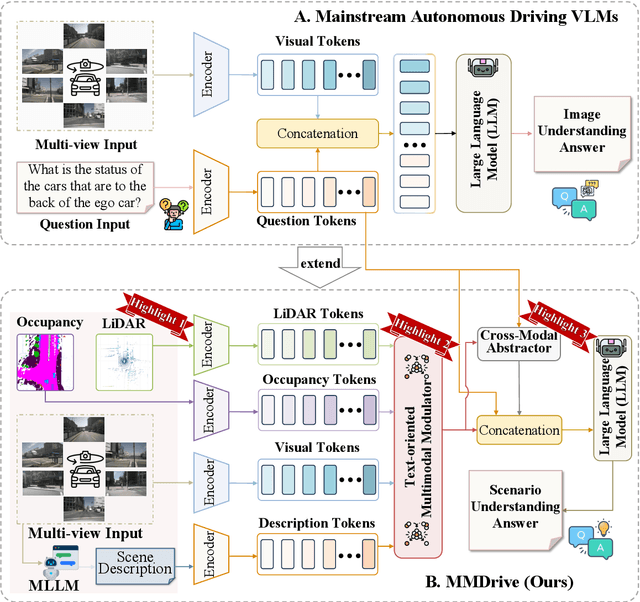
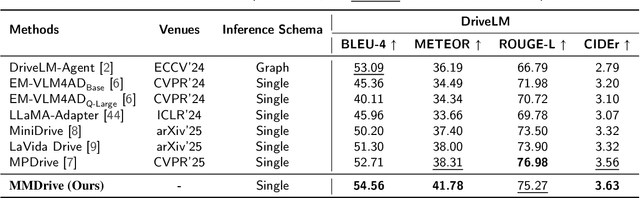

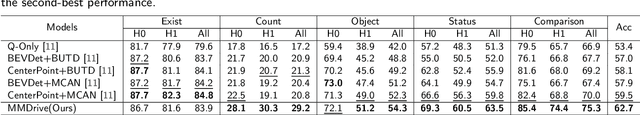
Abstract:Vision-language models enable the understanding and reasoning of complex traffic scenarios through multi-source information fusion, establishing it as a core technology for autonomous driving. However, existing vision-language models are constrained by the image understanding paradigm in 2D plane, which restricts their capability to perceive 3D spatial information and perform deep semantic fusion, resulting in suboptimal performance in complex autonomous driving environments. This study proposes MMDrive, an multimodal vision-language model framework that extends traditional image understanding to a generalized 3D scene understanding framework. MMDrive incorporates three complementary modalities, including occupancy maps, LiDAR point clouds, and textual scene descriptions. To this end, it introduces two novel components for adaptive cross-modal fusion and key information extraction. Specifically, the Text-oriented Multimodal Modulator dynamically weights the contributions of each modality based on the semantic cues in the question, guiding context-aware feature integration. The Cross-Modal Abstractor employs learnable abstract tokens to generate compact, cross-modal summaries that highlight key regions and essential semantics. Comprehensive evaluations on the DriveLM and NuScenes-QA benchmarks demonstrate that MMDrive achieves significant performance gains over existing vision-language models for autonomous driving, with a BLEU-4 score of 54.56 and METEOR of 41.78 on DriveLM, and an accuracy score of 62.7% on NuScenes-QA. MMDrive effectively breaks the traditional image-only understanding barrier, enabling robust multimodal reasoning in complex driving environments and providing a new foundation for interpretable autonomous driving scene understanding.
Da Yu: Towards USV-Based Image Captioning for Waterway Surveillance and Scene Understanding
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Automated waterway environment perception is crucial for enabling unmanned surface vessels (USVs) to understand their surroundings and make informed decisions. Most existing waterway perception models primarily focus on instance-level object perception paradigms (e.g., detection, segmentation). However, due to the complexity of waterway environments, current perception datasets and models fail to achieve global semantic understanding of waterways, limiting large-scale monitoring and structured log generation. With the advancement of vision-language models (VLMs), we leverage image captioning to introduce WaterCaption, the first captioning dataset specifically designed for waterway environments. WaterCaption focuses on fine-grained, multi-region long-text descriptions, providing a new research direction for visual geo-understanding and spatial scene cognition. Exactly, it includes 20.2k image-text pair data with 1.8 million vocabulary size. Additionally, we propose Da Yu, an edge-deployable multi-modal large language model for USVs, where we propose a novel vision-to-language projector called Nano Transformer Adaptor (NTA). NTA effectively balances computational efficiency with the capacity for both global and fine-grained local modeling of visual features, thereby significantly enhancing the model's ability to generate long-form textual outputs. Da Yu achieves an optimal balance between performance and efficiency, surpassing state-of-the-art models on WaterCaption and several other captioning benchmarks.
CornerPoint3D: Look at the Nearest Corner Instead of the Center
Apr 03, 2025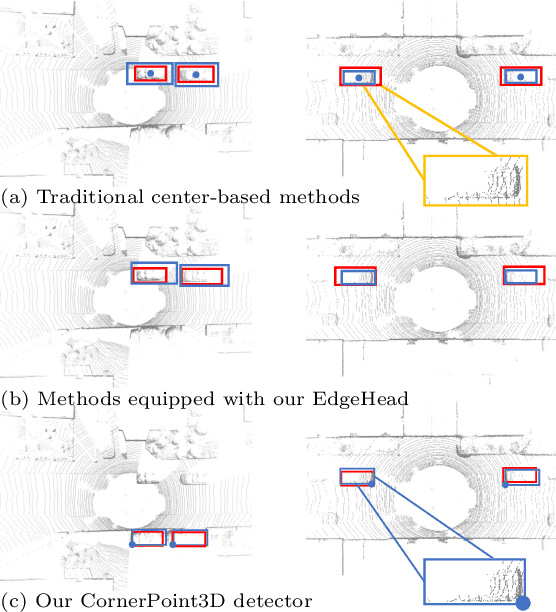
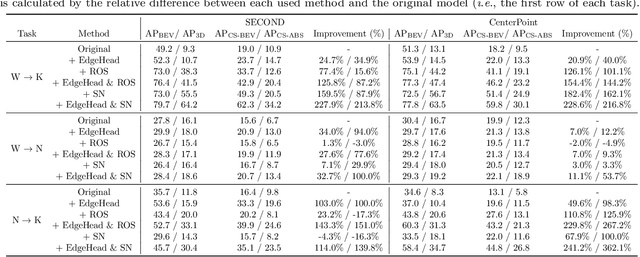
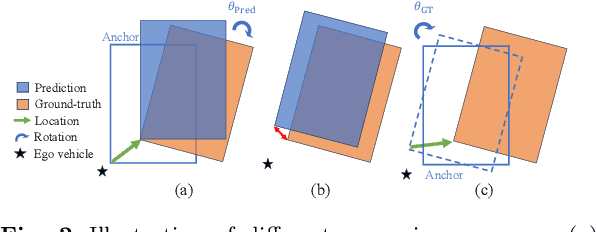
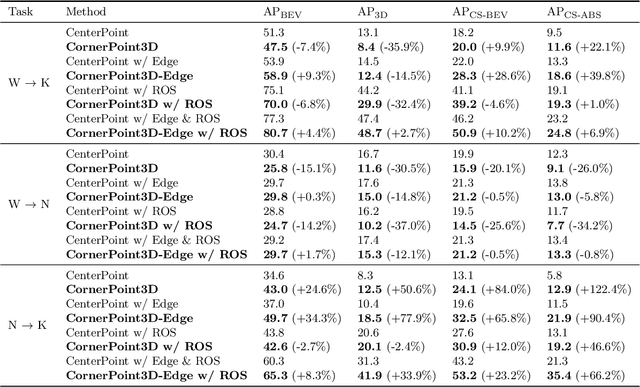
Abstract:3D object detection aims to predict object centers, dimensions, and rotations from LiDAR point clouds. Despite its simplicity, LiDAR captures only the near side of objects, making center-based detectors prone to poor localization accuracy in cross-domain tasks with varying point distributions. Meanwhile, existing evaluation metrics designed for single-domain assessment also suffer from overfitting due to dataset-specific size variations. A key question arises: Do we really need models to maintain excellent performance in the entire 3D bounding boxes after being applied across domains? Actually, one of our main focuses is on preventing collisions between vehicles and other obstacles, especially in cross-domain scenarios where correctly predicting the sizes is much more difficult. To address these issues, we rethink cross-domain 3D object detection from a practical perspective. We propose two new metrics that evaluate a model's ability to detect objects' closer-surfaces to the LiDAR sensor. Additionally, we introduce EdgeHead, a refinement head that guides models to focus more on learnable closer surfaces, significantly improving cross-domain performance under both our new and traditional BEV/3D metrics. Furthermore, we argue that predicting the nearest corner rather than the object center enhances robustness. We propose a novel 3D object detector, coined as CornerPoint3D, which is built upon CenterPoint and uses heatmaps to supervise the learning and detection of the nearest corner of each object. Our proposed methods realize a balanced trade-off between the detection quality of entire bounding boxes and the locating accuracy of closer surfaces to the LiDAR sensor, outperforming the traditional center-based detector CenterPoint in multiple cross-domain tasks and providing a more practically reasonable and robust cross-domain 3D object detection solution.
OptiPMB: Enhancing 3D Multi-Object Tracking with Optimized Poisson Multi-Bernoulli Filtering
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Accurate 3D multi-object tracking (MOT) is crucial for autonomous driving, as it enables robust perception, navigation, and planning in complex environments. While deep learning-based solutions have demonstrated impressive 3D MOT performance, model-based approaches remain appealing for their simplicity, interpretability, and data efficiency. Conventional model-based trackers typically rely on random vector-based Bayesian filters within the tracking-by-detection (TBD) framework but face limitations due to heuristic data association and track management schemes. In contrast, random finite set (RFS)-based Bayesian filtering handles object birth, survival, and death in a theoretically sound manner, facilitating interpretability and parameter tuning. In this paper, we present OptiPMB, a novel RFS-based 3D MOT method that employs an optimized Poisson multi-Bernoulli (PMB) filter while incorporating several key innovative designs within the TBD framework. Specifically, we propose a measurement-driven hybrid adaptive birth model for improved track initialization, employ adaptive detection probability parameters to effectively maintain tracks for occluded objects, and optimize density pruning and track extraction modules to further enhance overall tracking performance. Extensive evaluations on nuScenes and KITTI datasets show that OptiPMB achieves superior tracking accuracy compared with state-of-the-art methods, thereby establishing a new benchmark for model-based 3D MOT and offering valuable insights for future research on RFS-based trackers in autonomous driving.
Cognitive Disentanglement for Referring Multi-Object Tracking
Mar 14, 2025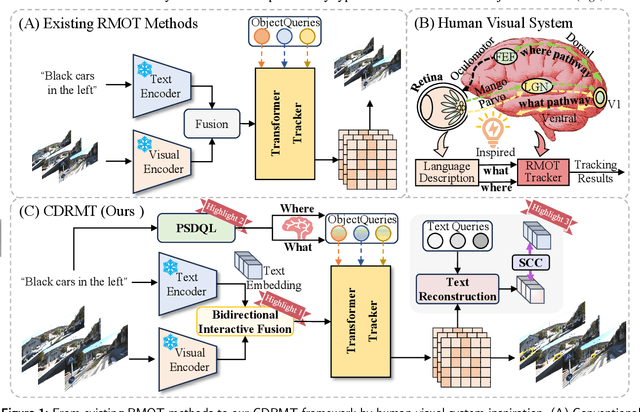
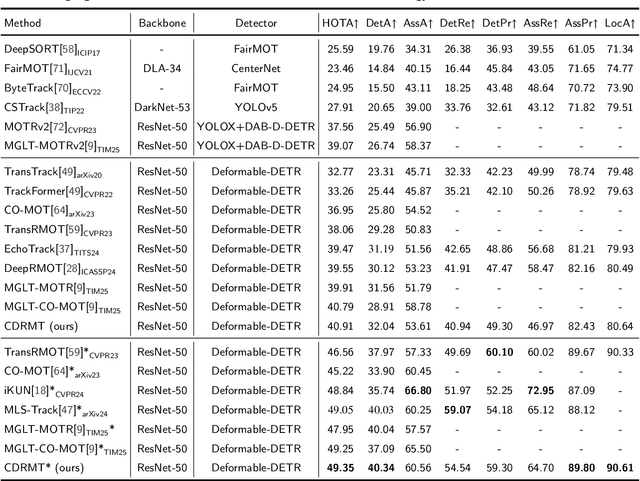
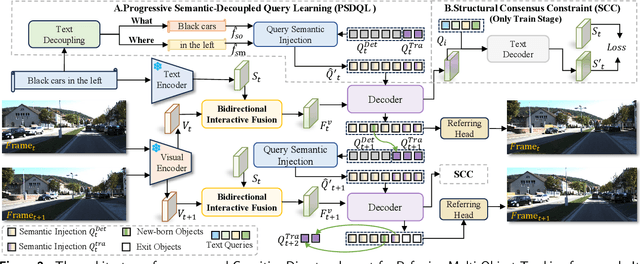
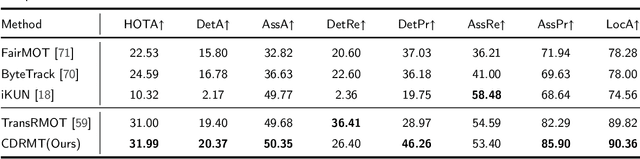
Abstract:As a significant application of multi-source information fusion in intelligent transportation perception systems, Referring Multi-Object Tracking (RMOT) involves localizing and tracking specific objects in video sequences based on language references. However, existing RMOT approaches often treat language descriptions as holistic embeddings and struggle to effectively integrate the rich semantic information contained in language expressions with visual features. This limitation is especially apparent in complex scenes requiring comprehensive understanding of both static object attributes and spatial motion information. In this paper, we propose a Cognitive Disentanglement for Referring Multi-Object Tracking (CDRMT) framework that addresses these challenges. It adapts the "what" and "where" pathways from human visual processing system to RMOT tasks. Specifically, our framework comprises three collaborative components: (1)The Bidirectional Interactive Fusion module first establishes cross-modal connections while preserving modality-specific characteristics; (2) Building upon this foundation, the Progressive Semantic-Decoupled Query Learning mechanism hierarchically injects complementary information into object queries, progressively refining object understanding from coarse to fine-grained semantic levels; (3) Finally, the Structural Consensus Constraint enforces bidirectional semantic consistency between visual features and language descriptions, ensuring that tracked objects faithfully reflect the referring expression. Extensive experiments on different benchmark datasets demonstrate that CDRMT achieves substantial improvements over state-of-the-art methods, with average gains of 6.0% in HOTA score on Refer-KITTI and 3.2% on Refer-KITTI-V2. Our approach advances the state-of-the-art in RMOT while simultaneously providing new insights into multi-source information fusion.
Talk2PC: Enhancing 3D Visual Grounding through LiDAR and Radar Point Clouds Fusion for Autonomous Driving
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Embodied outdoor scene understanding forms the foundation for autonomous agents to perceive, analyze, and react to dynamic driving environments. However, existing 3D understanding is predominantly based on 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs), collecting and processing limited scene-aware contexts. Instead, compared to the 2D planar visual information, point cloud sensors like LiDAR offer rich depth information and fine-grained 3D representations of objects. Meanwhile, the emerging 4D millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar is capable of detecting the motion trend, velocity, and reflection intensity of each object. Therefore, the integration of these two modalities provides more flexible querying conditions for natural language, enabling more accurate 3D visual grounding. To this end, in this paper, we exploratively propose a novel method called TPCNet, the first outdoor 3D visual grounding model upon the paradigm of prompt-guided point cloud sensor combination, including both LiDAR and radar contexts. To adaptively balance the features of these two sensors required by the prompt, we have designed a multi-fusion paradigm called Two-Stage Heterogeneous Modal Adaptive Fusion. Specifically, this paradigm initially employs Bidirectional Agent Cross-Attention (BACA), which feeds dual-sensor features, characterized by global receptive fields, to the text features for querying. Additionally, we have designed a Dynamic Gated Graph Fusion (DGGF) module to locate the regions of interest identified by the queries. To further enhance accuracy, we innovatively devise an C3D-RECHead, based on the nearest object edge. Our experiments have demonstrated that our TPCNet, along with its individual modules, achieves the state-of-the-art performance on both the Talk2Radar and Talk2Car datasets.
Doracamom: Joint 3D Detection and Occupancy Prediction with Multi-view 4D Radars and Cameras for Omnidirectional Perception
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:3D object detection and occupancy prediction are critical tasks in autonomous driving, attracting significant attention. Despite the potential of recent vision-based methods, they encounter challenges under adverse conditions. Thus, integrating cameras with next-generation 4D imaging radar to achieve unified multi-task perception is highly significant, though research in this domain remains limited. In this paper, we propose Doracamom, the first framework that fuses multi-view cameras and 4D radar for joint 3D object detection and semantic occupancy prediction, enabling comprehensive environmental perception. Specifically, we introduce a novel Coarse Voxel Queries Generator that integrates geometric priors from 4D radar with semantic features from images to initialize voxel queries, establishing a robust foundation for subsequent Transformer-based refinement. To leverage temporal information, we design a Dual-Branch Temporal Encoder that processes multi-modal temporal features in parallel across BEV and voxel spaces, enabling comprehensive spatio-temporal representation learning. Furthermore, we propose a Cross-Modal BEV-Voxel Fusion module that adaptively fuses complementary features through attention mechanisms while employing auxiliary tasks to enhance feature quality. Extensive experiments on the OmniHD-Scenes, View-of-Delft (VoD), and TJ4DRadSet datasets demonstrate that Doracamom achieves state-of-the-art performance in both tasks, establishing new benchmarks for multi-modal 3D perception. Code and models will be publicly available.
3rd Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision (MaCVi) 2025: Challenge Results
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:The 3rd Workshop on Maritime Computer Vision (MaCVi) 2025 addresses maritime computer vision for Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USV) and underwater. This report offers a comprehensive overview of the findings from the challenges. We provide both statistical and qualitative analyses, evaluating trends from over 700 submissions. All datasets, evaluation code, and the leaderboard are available to the public at https://macvi.org/workshop/macvi25.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge