Xiaohao Cai
SEIS: Subspace-based Equivariance and Invariance Scores for Neural Representations
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Understanding how neural representations respond to geometric transformations is essential for evaluating whether learned features preserve meaningful spatial structure. Existing approaches primarily assess robustness by comparing model outputs under transformed inputs, offering limited insight into how geometric information is organized within internal representations and failing to distinguish between information loss and re-encoding. In this work, we introduce SEIS (Subspace-based Equivariance and Invariance Scores), a subspace metric for analyzing layer-wise feature representations under geometric transformations, disentangling equivariance from invariance without requiring labels or explicit knowledge of the transformation. Synthetic validation confirms that SEIS correctly recovers known transformations. Applied to trained classification networks, SEIS reveals a transition from equivariance in early layers to invariance in deeper layers, and that data augmentation increases invariance while preserving equivariance. We further show that multi-task learning induces synergistic gains in both properties at the shared encoder, and skip connections restore equivariance lost during decoding.
CALM: Culturally Self-Aware Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Cultural awareness in language models is the capacity to understand and adapt to diverse cultural contexts. However, most existing approaches treat culture as static background knowledge, overlooking its dynamic and evolving nature. This limitation reduces their reliability in downstream tasks that demand genuine cultural sensitivity. In this work, we introduce CALM, a novel framework designed to endow language models with cultural self-awareness. CALM disentangles task semantics from explicit cultural concepts and latent cultural signals, shaping them into structured cultural clusters through contrastive learning. These clusters are then aligned via cross-attention to establish fine-grained interactions among related cultural features and are adaptively integrated through a Mixture-of-Experts mechanism along culture-specific dimensions. The resulting unified representation is fused with the model's original knowledge to construct a culturally grounded internal identity state, which is further enhanced through self-prompted reflective learning, enabling continual adaptation and self-correction. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple cross-cultural benchmark datasets demonstrate that CALM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
GRASPTrack: Geometry-Reasoned Association via Segmentation and Projection for Multi-Object Tracking
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Multi-object tracking (MOT) in monocular videos is fundamentally challenged by occlusions and depth ambiguity, issues that conventional tracking-by-detection (TBD) methods struggle to resolve owing to a lack of geometric awareness. To address these limitations, we introduce GRASPTrack, a novel depth-aware MOT framework that integrates monocular depth estimation and instance segmentation into a standard TBD pipeline to generate high-fidelity 3D point clouds from 2D detections, thereby enabling explicit 3D geometric reasoning. These 3D point clouds are then voxelized to enable a precise and robust Voxel-Based 3D Intersection-over-Union (IoU) for spatial association. To further enhance tracking robustness, our approach incorporates Depth-aware Adaptive Noise Compensation, which dynamically adjusts the Kalman filter process noise based on occlusion severity for more reliable state estimation. Additionally, we propose a Depth-enhanced Observation-Centric Momentum, which extends the motion direction consistency from the image plane into 3D space to improve motion-based association cues, particularly for objects with complex trajectories. Extensive experiments on the MOT17, MOT20, and DanceTrack benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance, significantly improving tracking robustness in complex scenes with frequent occlusions and intricate motion patterns.
MOGO: Residual Quantized Hierarchical Causal Transformer for High-Quality and Real-Time 3D Human Motion Generation
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in transformer-based text-to-motion generation have led to impressive progress in synthesizing high-quality human motion. Nevertheless, jointly achieving high fidelity, streaming capability, real-time responsiveness, and scalability remains a fundamental challenge. In this paper, we propose MOGO (Motion Generation with One-pass), a novel autoregressive framework tailored for efficient and real-time 3D motion generation. MOGO comprises two key components: (1) MoSA-VQ, a motion scale-adaptive residual vector quantization module that hierarchically discretizes motion sequences with learnable scaling to produce compact yet expressive representations; and (2) RQHC-Transformer, a residual quantized hierarchical causal transformer that generates multi-layer motion tokens in a single forward pass, significantly reducing inference latency. To enhance semantic fidelity, we further introduce a text condition alignment mechanism that improves motion decoding under textual control. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets including HumanML3D, KIT-ML, and CMP demonstrate that MOGO achieves competitive or superior generation quality compared to state-of-the-art transformer-based methods, while offering substantial improvements in real-time performance, streaming generation, and generalization under zero-shot settings.
Less but Better: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Personality Detection
Apr 07, 2025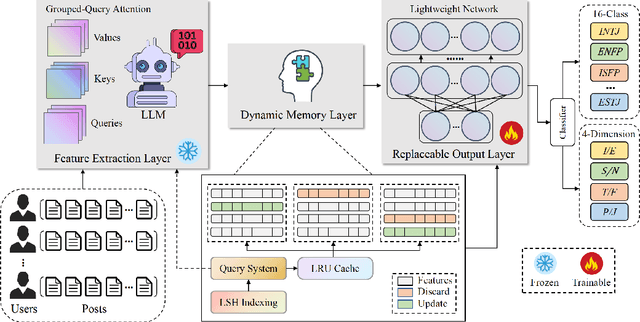
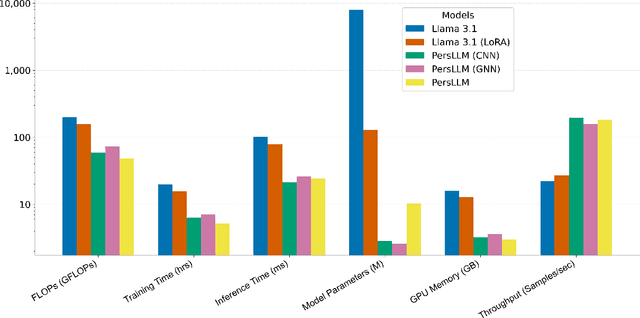
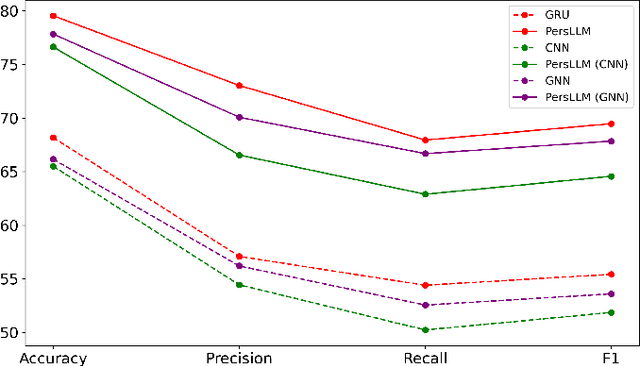
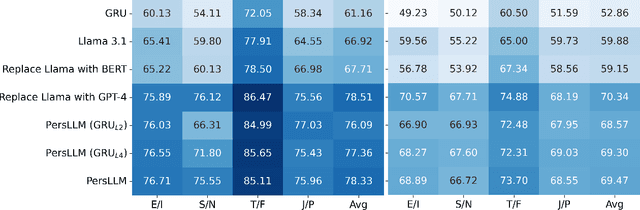
Abstract:Personality detection automatically identifies an individual's personality from various data sources, such as social media texts. However, as the parameter scale of language models continues to grow, the computational cost becomes increasingly difficult to manage. Fine-tuning also grows more complex, making it harder to justify the effort and reliably predict outcomes. We introduce a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning framework, PersLLM, to address these challenges. In PersLLM, a large language model (LLM) extracts high-dimensional representations from raw data and stores them in a dynamic memory layer. PersLLM then updates the downstream layers with a replaceable output network, enabling flexible adaptation to various personality detection scenarios. By storing the features in the memory layer, we eliminate the need for repeated complex computations by the LLM. Meanwhile, the lightweight output network serves as a proxy for evaluating the overall effectiveness of the framework, improving the predictability of results. Experimental results on key benchmark datasets like Kaggle and Pandora show that PersLLM significantly reduces computational cost while maintaining competitive performance and strong adaptability.
CornerPoint3D: Look at the Nearest Corner Instead of the Center
Apr 03, 2025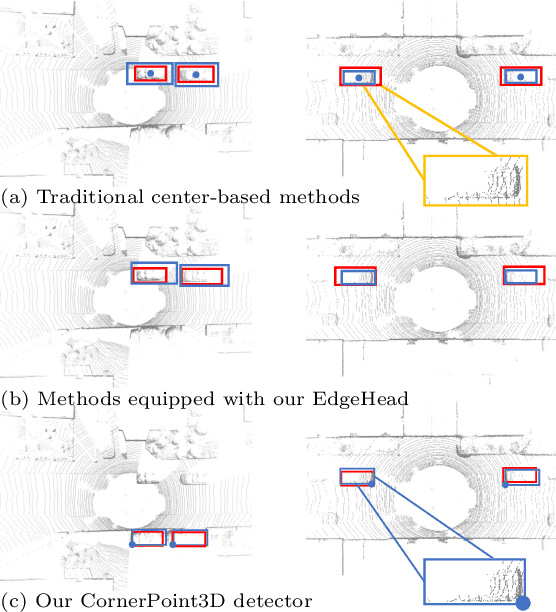
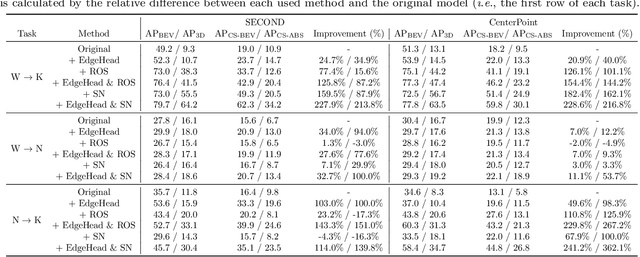
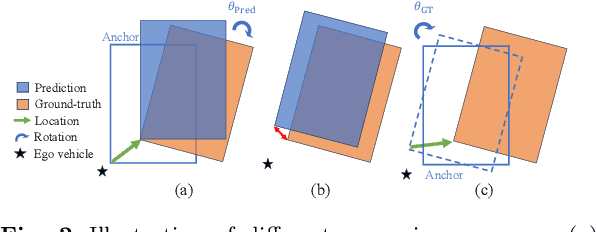
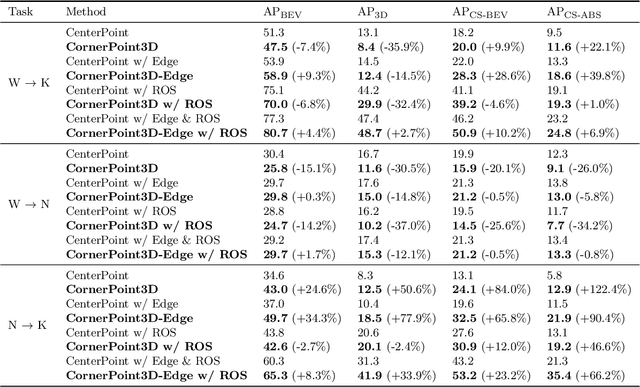
Abstract:3D object detection aims to predict object centers, dimensions, and rotations from LiDAR point clouds. Despite its simplicity, LiDAR captures only the near side of objects, making center-based detectors prone to poor localization accuracy in cross-domain tasks with varying point distributions. Meanwhile, existing evaluation metrics designed for single-domain assessment also suffer from overfitting due to dataset-specific size variations. A key question arises: Do we really need models to maintain excellent performance in the entire 3D bounding boxes after being applied across domains? Actually, one of our main focuses is on preventing collisions between vehicles and other obstacles, especially in cross-domain scenarios where correctly predicting the sizes is much more difficult. To address these issues, we rethink cross-domain 3D object detection from a practical perspective. We propose two new metrics that evaluate a model's ability to detect objects' closer-surfaces to the LiDAR sensor. Additionally, we introduce EdgeHead, a refinement head that guides models to focus more on learnable closer surfaces, significantly improving cross-domain performance under both our new and traditional BEV/3D metrics. Furthermore, we argue that predicting the nearest corner rather than the object center enhances robustness. We propose a novel 3D object detector, coined as CornerPoint3D, which is built upon CenterPoint and uses heatmaps to supervise the learning and detection of the nearest corner of each object. Our proposed methods realize a balanced trade-off between the detection quality of entire bounding boxes and the locating accuracy of closer surfaces to the LiDAR sensor, outperforming the traditional center-based detector CenterPoint in multiple cross-domain tasks and providing a more practically reasonable and robust cross-domain 3D object detection solution.
LL4G: Self-Supervised Dynamic Optimization for Graph-Based Personality Detection
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Graph-based personality detection constructs graph structures from textual data, particularly social media posts. Current methods often struggle with sparse or noisy data and rely on static graphs, limiting their ability to capture dynamic changes between nodes and relationships. This paper introduces LL4G, a self-supervised framework leveraging large language models (LLMs) to optimize graph neural networks (GNNs). LLMs extract rich semantic features to generate node representations and to infer explicit and implicit relationships. The graph structure adaptively adds nodes and edges based on input data, continuously optimizing itself. The GNN then uses these optimized representations for joint training on node reconstruction, edge prediction, and contrastive learning tasks. This integration of semantic and structural information generates robust personality profiles. Experimental results on Kaggle and Pandora datasets show LL4G outperforms state-of-the-art models.
tCURLoRA: Tensor CUR Decomposition Based Low-Rank Parameter Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 04, 2025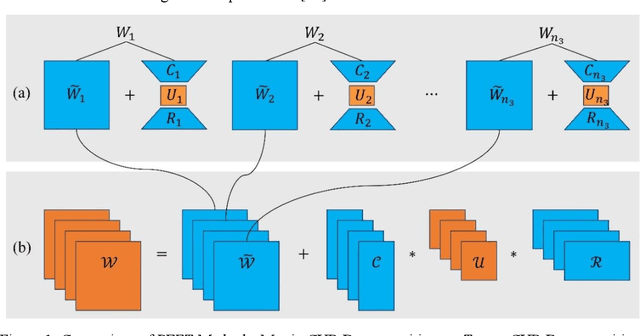

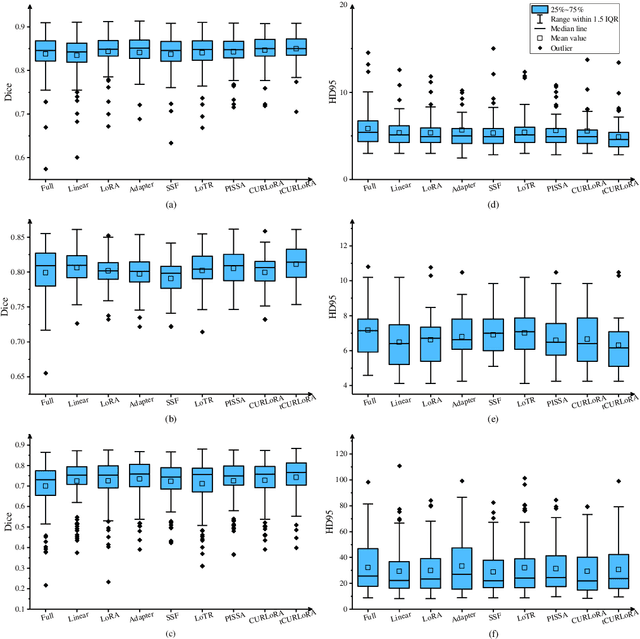
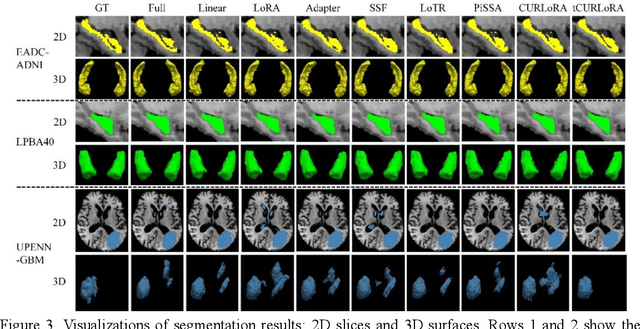
Abstract:Transfer learning, by leveraging knowledge from pre-trained models, has significantly enhanced the performance of target tasks. However, as deep neural networks scale up, full fine-tuning introduces substantial computational and storage challenges in resource-constrained environments, limiting its widespread adoption. To address this, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods have been developed to reduce computational complexity and storage requirements by minimizing the number of updated parameters. While matrix decomposition-based PEFT methods, such as LoRA, show promise, they struggle to fully capture the high-dimensional structural characteristics of model weights. In contrast, high-dimensional tensors offer a more natural representation of neural network weights, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of higher-order features and multi-dimensional interactions. In this paper, we propose tCURLoRA, a novel fine-tuning method based on tensor CUR decomposition. By concatenating pre-trained weight matrices into a three-dimensional tensor and applying tensor CUR decomposition, we update only the lower-order tensor components during fine-tuning, effectively reducing computational and storage overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that tCURLoRA outperforms existing PEFT methods in medical image segmentation tasks.
GAMED: Knowledge Adaptive Multi-Experts Decoupling for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal fake news detection often involves modelling heterogeneous data sources, such as vision and language. Existing detection methods typically rely on fusion effectiveness and cross-modal consistency to model the content, complicating understanding how each modality affects prediction accuracy. Additionally, these methods are primarily based on static feature modelling, making it difficult to adapt to the dynamic changes and relationships between different data modalities. This paper develops a significantly novel approach, GAMED, for multimodal modelling, which focuses on generating distinctive and discriminative features through modal decoupling to enhance cross-modal synergies, thereby optimizing overall performance in the detection process. GAMED leverages multiple parallel expert networks to refine features and pre-embed semantic knowledge to improve the experts' ability in information selection and viewpoint sharing. Subsequently, the feature distribution of each modality is adaptively adjusted based on the respective experts' opinions. GAMED also introduces a novel classification technique to dynamically manage contributions from different modalities, while improving the explainability of decisions. Experimental results on the Fakeddit and Yang datasets demonstrate that GAMED performs better than recently developed state-of-the-art models. The source code can be accessed at https://github.com/slz0925/GAMED.
Revisiting Cross-Domain Problem for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Aug 22, 2024

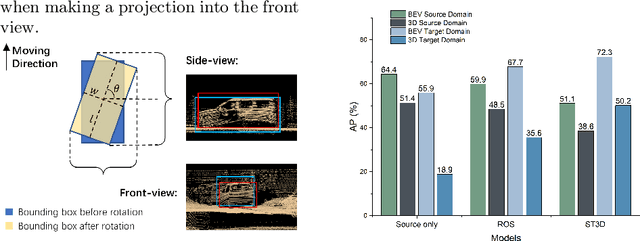
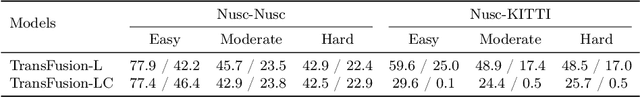
Abstract:Deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks and transformers have been widely applied to solve 3D object detection problems in the domain of autonomous driving. While existing models have achieved outstanding performance on most open benchmarks, the generalization ability of these deep networks is still in doubt. To adapt models to other domains including different cities, countries, and weather, retraining with the target domain data is currently necessary, which hinders the wide application of autonomous driving. In this paper, we deeply analyze the cross-domain performance of the state-of-the-art models. We observe that most models will overfit the training domains and it is challenging to adapt them to other domains directly. Existing domain adaptation methods for 3D object detection problems are actually shifting the models' knowledge domain instead of improving their generalization ability. We then propose additional evaluation metrics -- the side-view and front-view AP -- to better analyze the core issues of the methods' heavy drops in accuracy levels. By using the proposed metrics and further evaluating the cross-domain performance in each dimension, we conclude that the overfitting problem happens more obviously on the front-view surface and the width dimension which usually faces the sensor and has more 3D points surrounding it. Meanwhile, our experiments indicate that the density of the point cloud data also significantly influences the models' cross-domain performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge