Guanming Chen
CALM: Culturally Self-Aware Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Cultural awareness in language models is the capacity to understand and adapt to diverse cultural contexts. However, most existing approaches treat culture as static background knowledge, overlooking its dynamic and evolving nature. This limitation reduces their reliability in downstream tasks that demand genuine cultural sensitivity. In this work, we introduce CALM, a novel framework designed to endow language models with cultural self-awareness. CALM disentangles task semantics from explicit cultural concepts and latent cultural signals, shaping them into structured cultural clusters through contrastive learning. These clusters are then aligned via cross-attention to establish fine-grained interactions among related cultural features and are adaptively integrated through a Mixture-of-Experts mechanism along culture-specific dimensions. The resulting unified representation is fused with the model's original knowledge to construct a culturally grounded internal identity state, which is further enhanced through self-prompted reflective learning, enabling continual adaptation and self-correction. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple cross-cultural benchmark datasets demonstrate that CALM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Less but Better: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models for Personality Detection
Apr 07, 2025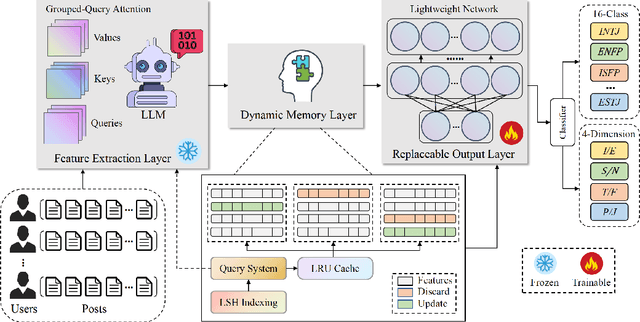
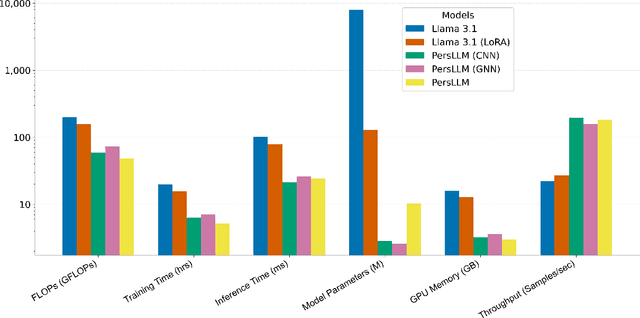
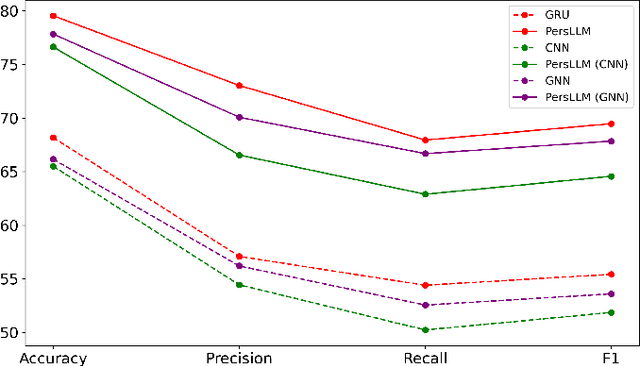
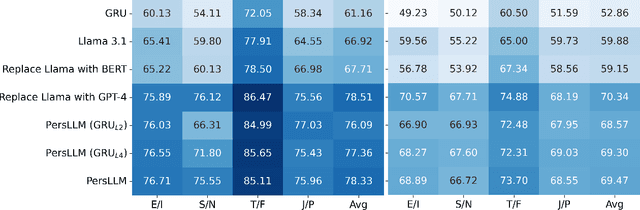
Abstract:Personality detection automatically identifies an individual's personality from various data sources, such as social media texts. However, as the parameter scale of language models continues to grow, the computational cost becomes increasingly difficult to manage. Fine-tuning also grows more complex, making it harder to justify the effort and reliably predict outcomes. We introduce a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning framework, PersLLM, to address these challenges. In PersLLM, a large language model (LLM) extracts high-dimensional representations from raw data and stores them in a dynamic memory layer. PersLLM then updates the downstream layers with a replaceable output network, enabling flexible adaptation to various personality detection scenarios. By storing the features in the memory layer, we eliminate the need for repeated complex computations by the LLM. Meanwhile, the lightweight output network serves as a proxy for evaluating the overall effectiveness of the framework, improving the predictability of results. Experimental results on key benchmark datasets like Kaggle and Pandora show that PersLLM significantly reduces computational cost while maintaining competitive performance and strong adaptability.
LL4G: Self-Supervised Dynamic Optimization for Graph-Based Personality Detection
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Graph-based personality detection constructs graph structures from textual data, particularly social media posts. Current methods often struggle with sparse or noisy data and rely on static graphs, limiting their ability to capture dynamic changes between nodes and relationships. This paper introduces LL4G, a self-supervised framework leveraging large language models (LLMs) to optimize graph neural networks (GNNs). LLMs extract rich semantic features to generate node representations and to infer explicit and implicit relationships. The graph structure adaptively adds nodes and edges based on input data, continuously optimizing itself. The GNN then uses these optimized representations for joint training on node reconstruction, edge prediction, and contrastive learning tasks. This integration of semantic and structural information generates robust personality profiles. Experimental results on Kaggle and Pandora datasets show LL4G outperforms state-of-the-art models.
GAMED: Knowledge Adaptive Multi-Experts Decoupling for Multimodal Fake News Detection
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal fake news detection often involves modelling heterogeneous data sources, such as vision and language. Existing detection methods typically rely on fusion effectiveness and cross-modal consistency to model the content, complicating understanding how each modality affects prediction accuracy. Additionally, these methods are primarily based on static feature modelling, making it difficult to adapt to the dynamic changes and relationships between different data modalities. This paper develops a significantly novel approach, GAMED, for multimodal modelling, which focuses on generating distinctive and discriminative features through modal decoupling to enhance cross-modal synergies, thereby optimizing overall performance in the detection process. GAMED leverages multiple parallel expert networks to refine features and pre-embed semantic knowledge to improve the experts' ability in information selection and viewpoint sharing. Subsequently, the feature distribution of each modality is adaptively adjusted based on the respective experts' opinions. GAMED also introduces a novel classification technique to dynamically manage contributions from different modalities, while improving the explainability of decisions. Experimental results on the Fakeddit and Yang datasets demonstrate that GAMED performs better than recently developed state-of-the-art models. The source code can be accessed at https://github.com/slz0925/GAMED.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge