Yuhan Wang
RIS-Aided Wireless Amodal Sensing for Single-View 3D Reconstruction
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Amodal sensing is critical for various real-world sensing applications because it can recover the complete shapes of partially occluded objects in complex environments. Among various amodal sensing paradigms, wireless amodal sensing is a potential solution due to its advantages of environmental robustness, privacy preservation, and low cost. However, the sensing data obtained by wireless system is sparse for shape reconstruction because of the low spatial resolution, and this issue is further intensified in complex environments with occlusion. To address this issue, we propose a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-aided wireless amodal sensing scheme that leverages a large-scale RIS to enhance the spatial resolution and create reflection paths that can bypass the obstacles. A generative learning model is also employed to reconstruct the complete shape based on the sensing data captured from the viewpoint of the RIS. In such a system, it is challenging to optimize the RIS phase shifts because the relationship between RIS phase shifts and amodal sensing accuracy is complex and the closed-form expression is unknown. To tackle this challenge, we develop an error prediction model that learns the mapping from RIS phase shifts to amodal sensing accuracy, and optimizes RIS phase shifts based on this mapping. Experimental results on the benchmark dataset show that our method achieves at least a 56.73% reduction in reconstruction error compared to conventional schemes under the same number of RIS configurations.
Building Audio-Visual Digital Twins with Smartphones
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Digital twins today are almost entirely visual, overlooking acoustics-a core component of spatial realism and interaction. We introduce AV-Twin, the first practical system that constructs editable audio-visual digital twins using only commodity smartphones. AV-Twin combines mobile RIR capture and a visual-assisted acoustic field model to efficiently reconstruct room acoustics. It further recovers per-surface material properties through differentiable acoustic rendering, enabling users to modify materials, geometry, and layout while automatically updating both audio and visuals. Together, these capabilities establish a practical path toward fully modifiable audio-visual digital twins for real-world environments.
MA-CBP: A Criminal Behavior Prediction Framework Based on Multi-Agent Asynchronous Collaboration
Aug 08, 2025



Abstract:With the acceleration of urbanization, criminal behavior in public scenes poses an increasingly serious threat to social security. Traditional anomaly detection methods based on feature recognition struggle to capture high-level behavioral semantics from historical information, while generative approaches based on Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail to meet real-time requirements. To address these challenges, we propose MA-CBP, a criminal behavior prediction framework based on multi-agent asynchronous collaboration. This framework transforms real-time video streams into frame-level semantic descriptions, constructs causally consistent historical summaries, and fuses adjacent image frames to perform joint reasoning over long- and short-term contexts. The resulting behavioral decisions include key elements such as event subjects, locations, and causes, enabling early warning of potential criminal activity. In addition, we construct a high-quality criminal behavior dataset that provides multi-scale language supervision, including frame-level, summary-level, and event-level semantic annotations. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance on multiple datasets and offers a promising solution for risk warning in urban public safety scenarios.
GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M: A Million-Scale, GPT-Generated Image Dataset
Jul 28, 2025
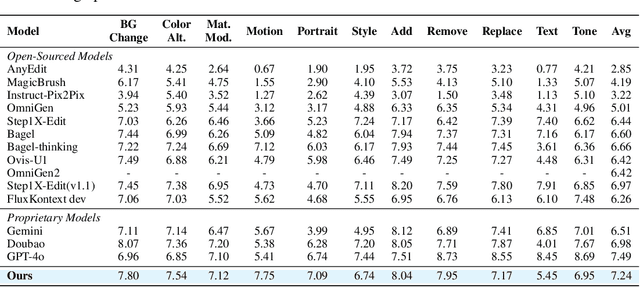
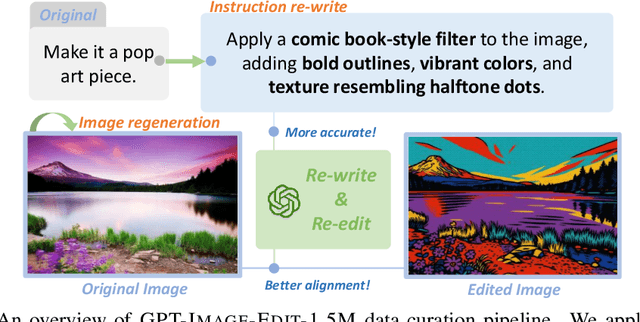
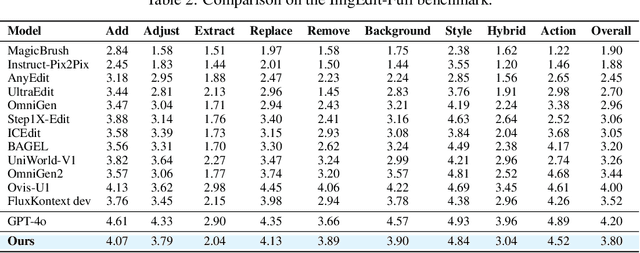
Abstract:Recent advancements in large multimodal models like GPT-4o have set a new standard for high-fidelity, instruction-guided image editing. However, the proprietary nature of these models and their training data creates a significant barrier for open-source research. To bridge this gap, we introduce GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M, a publicly available, large-scale image-editing corpus containing more than 1.5 million high-quality triplets (instruction, source image, edited image). We systematically construct this dataset by leveraging the versatile capabilities of GPT-4o to unify and refine three popular image-editing datasets: OmniEdit, HQ-Edit, and UltraEdit. Specifically, our methodology involves 1) regenerating output images to enhance visual quality and instruction alignment, and 2) selectively rewriting prompts to improve semantic clarity. To validate the efficacy of our dataset, we fine-tune advanced open-source models on GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M. The empirical results are exciting, e.g., the fine-tuned FluxKontext achieves highly competitive performance across a comprehensive suite of benchmarks, including 7.24 on GEdit-EN, 3.80 on ImgEdit-Full, and 8.78 on Complex-Edit, showing stronger instruction following and higher perceptual quality while maintaining identity. These scores markedly exceed all previously published open-source methods and substantially narrow the gap to leading proprietary models. We hope the full release of GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M can help to catalyze further open research in instruction-guided image editing.
Enhancing Transferability and Consistency in Cross-Domain Recommendations via Supervised Disentanglement
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Cross-domain recommendation (CDR) aims to alleviate the data sparsity by transferring knowledge across domains. Disentangled representation learning provides an effective solution to model complex user preferences by separating intra-domain features (domain-shared and domain-specific features), thereby enhancing robustness and interpretability. However, disentanglement-based CDR methods employing generative modeling or GNNs with contrastive objectives face two key challenges: (i) pre-separation strategies decouple features before extracting collaborative signals, disrupting intra-domain interactions and introducing noise; (ii) unsupervised disentanglement objectives lack explicit task-specific guidance, resulting in limited consistency and suboptimal alignment. To address these challenges, we propose DGCDR, a GNN-enhanced encoder-decoder framework. To handle challenge (i), DGCDR first applies GNN to extract high-order collaborative signals, providing enriched representations as a robust foundation for disentanglement. The encoder then dynamically disentangles features into domain-shared and -specific spaces, preserving collaborative information during the separation process. To handle challenge (ii), the decoder introduces an anchor-based supervision that leverages hierarchical feature relationships to enhance intra-domain consistency and cross-domain alignment. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that DGCDR achieves state-of-the-art performance, with improvements of up to 11.59% across key metrics. Qualitative analyses further validate its superior disentanglement quality and transferability. Our source code and datasets are available on GitHub for further comparison.
Harnessing EHRs for Diffusion-based Anomaly Detection on Chest X-rays
May 22, 2025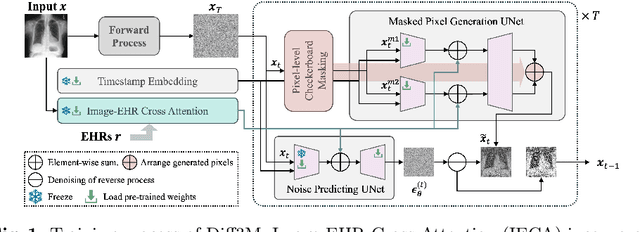
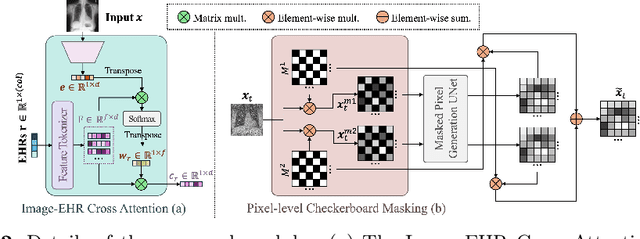
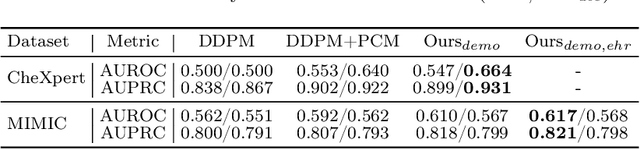
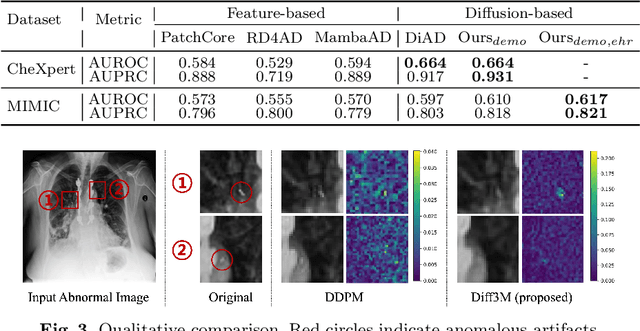
Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) in medical imaging is crucial for identifying pathological abnormalities without requiring extensive labeled data. However, existing diffusion-based UAD models rely solely on imaging features, limiting their ability to distinguish between normal anatomical variations and pathological anomalies. To address this, we propose Diff3M, a multi-modal diffusion-based framework that integrates chest X-rays and structured Electronic Health Records (EHRs) for enhanced anomaly detection. Specifically, we introduce a novel image-EHR cross-attention module to incorporate structured clinical context into the image generation process, improving the model's ability to differentiate normal from abnormal features. Additionally, we develop a static masking strategy to enhance the reconstruction of normal-like images from anomalies. Extensive evaluations on CheXpert and MIMIC-CXR/IV demonstrate that Diff3M achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing UAD methods in medical imaging. Our code is available at this http URL https://github.com/nth221/Diff3M
TCSinger 2: Customizable Multilingual Zero-shot Singing Voice Synthesis
May 20, 2025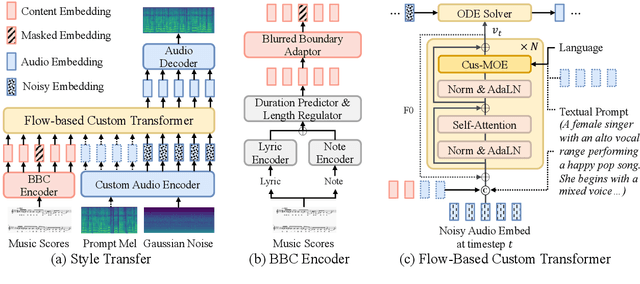
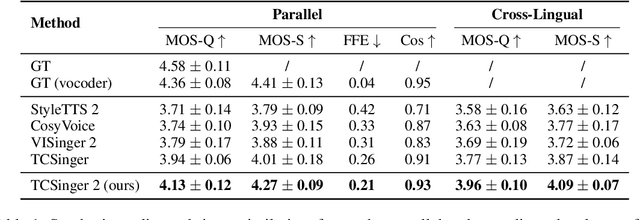
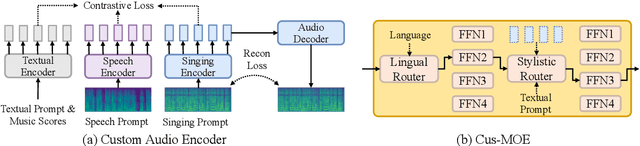
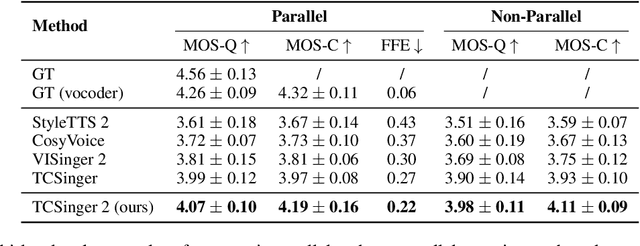
Abstract:Customizable multilingual zero-shot singing voice synthesis (SVS) has various potential applications in music composition and short video dubbing. However, existing SVS models overly depend on phoneme and note boundary annotations, limiting their robustness in zero-shot scenarios and producing poor transitions between phonemes and notes. Moreover, they also lack effective multi-level style control via diverse prompts. To overcome these challenges, we introduce TCSinger 2, a multi-task multilingual zero-shot SVS model with style transfer and style control based on various prompts. TCSinger 2 mainly includes three key modules: 1) Blurred Boundary Content (BBC) Encoder, predicts duration, extends content embedding, and applies masking to the boundaries to enable smooth transitions. 2) Custom Audio Encoder, uses contrastive learning to extract aligned representations from singing, speech, and textual prompts. 3) Flow-based Custom Transformer, leverages Cus-MOE, with F0 supervision, enhancing both the synthesis quality and style modeling of the generated singing voice. Experimental results show that TCSinger 2 outperforms baseline models in both subjective and objective metrics across multiple related tasks.
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:This paper presents MedSegFactory, a versatile medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across modalities and tasks. It aims to serve as an unlimited data repository, supplying image-mask pairs to enhance existing segmentation tools. The core of MedSegFactory is a dual-stream diffusion model, where one stream synthesizes medical images and the other generates corresponding segmentation masks. To ensure precise alignment between image-mask pairs, we introduce Joint Cross-Attention (JCA), enabling a collaborative denoising paradigm by dynamic cross-conditioning between streams. This bidirectional interaction allows both representations to guide each other's generation, enhancing consistency between generated pairs. MedSegFactory unlocks on-demand generation of paired medical images and segmentation masks through user-defined prompts that specify the target labels, imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and pathological conditions, facilitating scalable and high-quality data generation. This new paradigm of medical image synthesis enables seamless integration into diverse medical imaging workflows, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments show that MedSegFactory generates data of superior quality and usability, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints.
Towards deployment-centric multimodal AI beyond vision and language
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Multimodal artificial intelligence (AI) integrates diverse types of data via machine learning to improve understanding, prediction, and decision-making across disciplines such as healthcare, science, and engineering. However, most multimodal AI advances focus on models for vision and language data, while their deployability remains a key challenge. We advocate a deployment-centric workflow that incorporates deployment constraints early to reduce the likelihood of undeployable solutions, complementing data-centric and model-centric approaches. We also emphasise deeper integration across multiple levels of multimodality and multidisciplinary collaboration to significantly broaden the research scope beyond vision and language. To facilitate this approach, we identify common multimodal-AI-specific challenges shared across disciplines and examine three real-world use cases: pandemic response, self-driving car design, and climate change adaptation, drawing expertise from healthcare, social science, engineering, science, sustainability, and finance. By fostering multidisciplinary dialogue and open research practices, our community can accelerate deployment-centric development for broad societal impact.
LL4G: Self-Supervised Dynamic Optimization for Graph-Based Personality Detection
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Graph-based personality detection constructs graph structures from textual data, particularly social media posts. Current methods often struggle with sparse or noisy data and rely on static graphs, limiting their ability to capture dynamic changes between nodes and relationships. This paper introduces LL4G, a self-supervised framework leveraging large language models (LLMs) to optimize graph neural networks (GNNs). LLMs extract rich semantic features to generate node representations and to infer explicit and implicit relationships. The graph structure adaptively adds nodes and edges based on input data, continuously optimizing itself. The GNN then uses these optimized representations for joint training on node reconstruction, edge prediction, and contrastive learning tasks. This integration of semantic and structural information generates robust personality profiles. Experimental results on Kaggle and Pandora datasets show LL4G outperforms state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge