Imran Razzak
CALM: Culturally Self-Aware Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Cultural awareness in language models is the capacity to understand and adapt to diverse cultural contexts. However, most existing approaches treat culture as static background knowledge, overlooking its dynamic and evolving nature. This limitation reduces their reliability in downstream tasks that demand genuine cultural sensitivity. In this work, we introduce CALM, a novel framework designed to endow language models with cultural self-awareness. CALM disentangles task semantics from explicit cultural concepts and latent cultural signals, shaping them into structured cultural clusters through contrastive learning. These clusters are then aligned via cross-attention to establish fine-grained interactions among related cultural features and are adaptively integrated through a Mixture-of-Experts mechanism along culture-specific dimensions. The resulting unified representation is fused with the model's original knowledge to construct a culturally grounded internal identity state, which is further enhanced through self-prompted reflective learning, enabling continual adaptation and self-correction. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple cross-cultural benchmark datasets demonstrate that CALM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
PRISM: A Personality-Driven Multi-Agent Framework for Social Media Simulation
Dec 22, 2025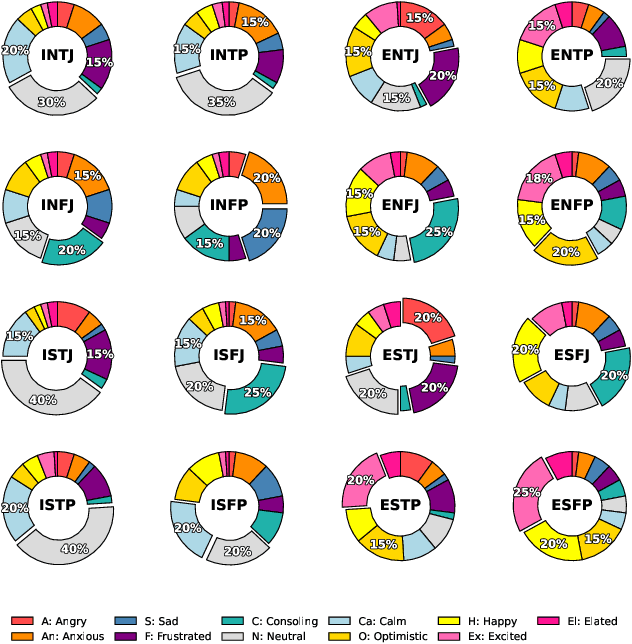
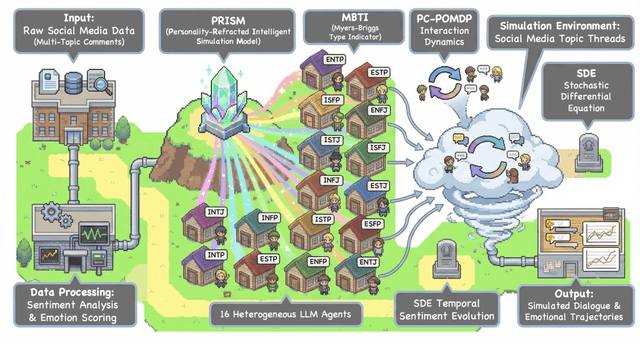
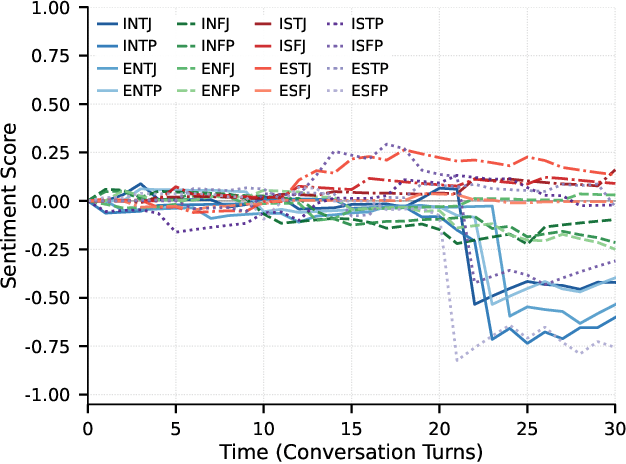

Abstract:Traditional agent-based models (ABMs) of opinion dynamics often fail to capture the psychological heterogeneity driving online polarization due to simplistic homogeneity assumptions. This limitation obscures the critical interplay between individual cognitive biases and information propagation, thereby hindering a mechanistic understanding of how ideological divides are amplified. To address this challenge, we introduce the Personality-Refracted Intelligent Simulation Model (PRISM), a hybrid framework coupling stochastic differential equations (SDE) for continuous emotional evolution with a personality-conditional partially observable Markov decision process (PC-POMDP) for discrete decision-making. In contrast to continuous trait approaches, PRISM assigns distinct Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) based cognitive policies to multimodal large language model (MLLM) agents, initialized via data-driven priors from large-scale social media datasets. PRISM achieves superior personality consistency aligned with human ground truth, significantly outperforming standard homogeneous and Big Five benchmarks. This framework effectively replicates emergent phenomena such as rational suppression and affective resonance, offering a robust tool for analyzing complex social media ecosystems.
QuAnTS: Question Answering on Time Series
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Text offers intuitive access to information. This can, in particular, complement the density of numerical time series, thereby allowing improved interactions with time series models to enhance accessibility and decision-making. While the creation of question-answering datasets and models has recently seen remarkable growth, most research focuses on question answering (QA) on vision and text, with time series receiving minute attention. To bridge this gap, we propose a challenging novel time series QA (TSQA) dataset, QuAnTS, for Question Answering on Time Series data. Specifically, we pose a wide variety of questions and answers about human motion in the form of tracked skeleton trajectories. We verify that the large-scale QuAnTS dataset is well-formed and comprehensive through extensive experiments. Thoroughly evaluating existing and newly proposed baselines then lays the groundwork for a deeper exploration of TSQA using QuAnTS. Additionally, we provide human performances as a key reference for gauging the practical usability of such models. We hope to encourage future research on interacting with time series models through text, enabling better decision-making and more transparent systems.
Robust Atypical Mitosis Classification with DenseNet121: Stain-Aware Augmentation and Hybrid Loss for Domain Generalization
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Atypical mitotic figures are important biomarkers of tumor aggressiveness in histopathology, yet reliable recognition remains challenging due to severe class imbalance and variability across imaging domains. We present a DenseNet-121-based framework tailored for atypical mitosis classification in the MIDOG 2025 (Track 2) setting. Our method integrates stain-aware augmentation (Macenko), geometric and intensity transformations, and imbalance-aware learning via weighted sampling with a hybrid objective combining class-weighted binary cross-entropy and focal loss. Trained end-to-end with AdamW and evaluated across multiple independent domains, the model demonstrates strong generalization under scanner and staining shifts, achieving balanced accuracy 85.0%, AUROC 0.927, sensitivity 89.2%, and specificity 80.9% on the official test set. These results indicate that combining DenseNet-121 with stain-aware augmentation and imbalance-adaptive objectives yields a robust, domain-generalizable framework for atypical mitosis classification suitable for real-world computational pathology workflows.
Hierarchical Sequence Iteration for Heterogeneous Question Answering
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) remains brittle on multi-step questions and heterogeneous evidence sources, trading accuracy against latency and token/tool budgets. This paper introducesHierarchical Sequence (HSEQ) Iteration for Heterogeneous Question Answering, a unified framework that (i) linearize documents, tables, and knowledge graphs into a reversible hierarchical sequence with lightweight structural tags, and (ii) perform structure-aware iteration to collect just-enough evidence before answer synthesis. A Head Agent provides guidance that leads retrieval, while an Iteration Agent selects and expands HSeq via structure-respecting actions (e.g., parent/child hops, table row/column neighbors, KG relations); Finally the head agent composes canonicalized evidence to genearte the final answer, with an optional refinement loop to resolve detected contradictions. Experiments on HotpotQA (text), HybridQA/TAT-QA (table+text), and MetaQA (KG) show consistent EM/F1 gains over strong single-pass, multi-hop, and agentic RAG baselines with high efficiency. Besides, HSEQ exhibits three key advantages: (1) a format-agnostic unification that enables a single policy to operate across text, tables, and KGs without per-dataset specialization; (2) guided, budget-aware iteration that reduces unnecessary hops, tool calls, and tokens while preserving accuracy; and (3) evidence canonicalization for reliable QA, improving answers consistency and auditability.
Phenome-Wide Multi-Omics Integration Uncovers Distinct Archetypes of Human Aging
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Aging is a highly complex and heterogeneous process that progresses at different rates across individuals, making biological age (BA) a more accurate indicator of physiological decline than chronological age. While previous studies have built aging clocks using single-omics data, they often fail to capture the full molecular complexity of human aging. In this work, we leveraged the Human Phenotype Project, a large-scale cohort of 12,000 adults aged 30--70 years, with extensive longitudinal profiling that includes clinical, behavioral, environmental, and multi-omics datasets -- spanning transcriptomics, lipidomics, metabolomics, and the microbiome. By employing advanced machine learning frameworks capable of modeling nonlinear biological dynamics, we developed and rigorously validated a multi-omics aging clock that robustly predicts diverse health outcomes and future disease risk. Unsupervised clustering of the integrated molecular profiles from multi-omics uncovered distinct biological subtypes of aging, revealing striking heterogeneity in aging trajectories and pinpointing pathway-specific alterations associated with different aging patterns. These findings demonstrate the power of multi-omics integration to decode the molecular landscape of aging and lay the groundwork for personalized healthspan monitoring and precision strategies to prevent age-related diseases.
Towards Robust Visual Continual Learning with Multi-Prototype Supervision
Sep 19, 2025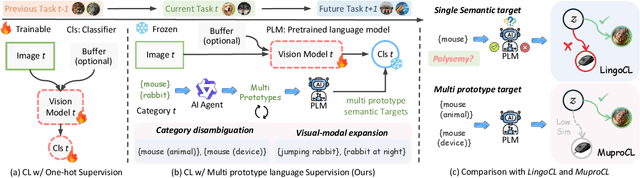
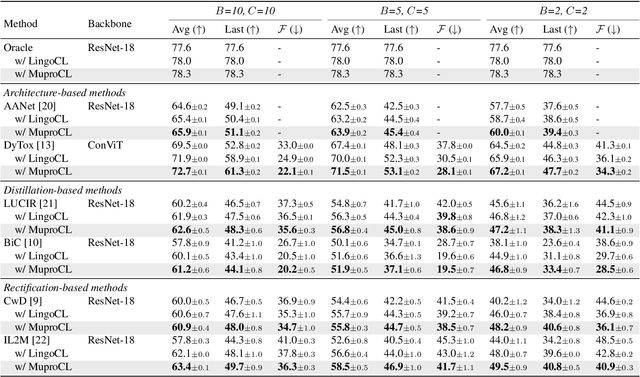
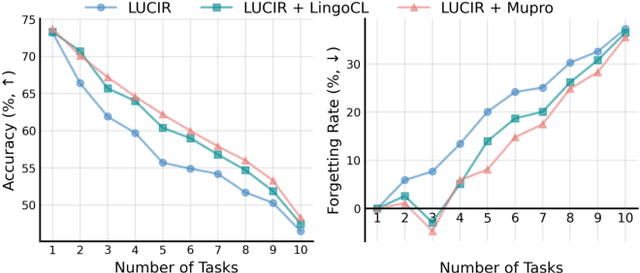
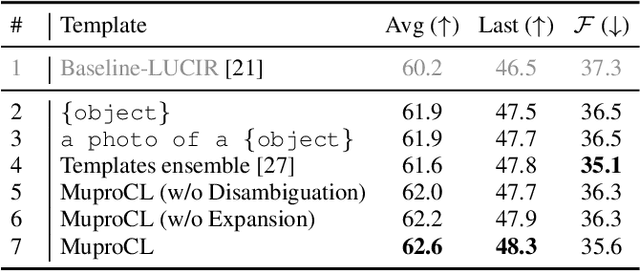
Abstract:Language-guided supervision, which utilizes a frozen semantic target from a Pretrained Language Model (PLM), has emerged as a promising paradigm for visual Continual Learning (CL). However, relying on a single target introduces two critical limitations: 1) semantic ambiguity, where a polysemous category name results in conflicting visual representations, and 2) intra-class visual diversity, where a single prototype fails to capture the rich variety of visual appearances within a class. To this end, we propose MuproCL, a novel framework that replaces the single target with multiple, context-aware prototypes. Specifically, we employ a lightweight LLM agent to perform category disambiguation and visual-modal expansion to generate a robust set of semantic prototypes. A LogSumExp aggregation mechanism allows the vision model to adaptively align with the most relevant prototype for a given image. Extensive experiments across various CL baselines demonstrate that MuproCL consistently enhances performance and robustness, establishing a more effective path for language-guided continual learning.
A Knowledge-driven Adaptive Collaboration of LLMs for Enhancing Medical Decision-making
Sep 18, 2025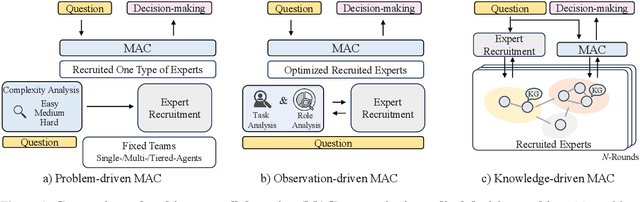
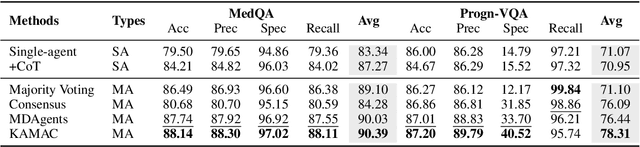
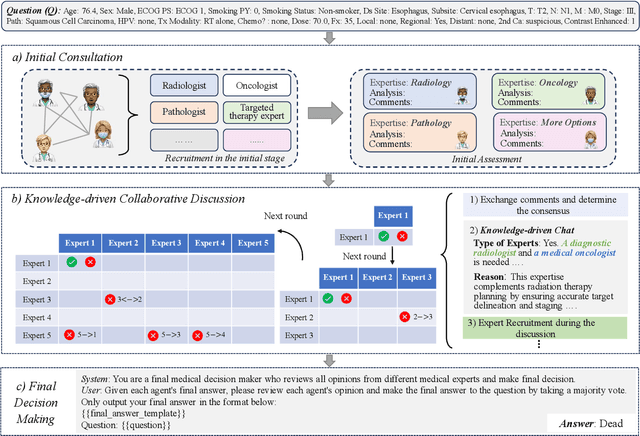
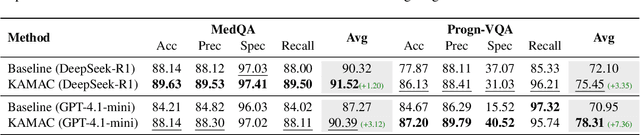
Abstract:Medical decision-making often involves integrating knowledge from multiple clinical specialties, typically achieved through multidisciplinary teams. Inspired by this collaborative process, recent work has leveraged large language models (LLMs) in multi-agent collaboration frameworks to emulate expert teamwork. While these approaches improve reasoning through agent interaction, they are limited by static, pre-assigned roles, which hinder adaptability and dynamic knowledge integration. To address these limitations, we propose KAMAC, a Knowledge-driven Adaptive Multi-Agent Collaboration framework that enables LLM agents to dynamically form and expand expert teams based on the evolving diagnostic context. KAMAC begins with one or more expert agents and then conducts a knowledge-driven discussion to identify and fill knowledge gaps by recruiting additional specialists as needed. This supports flexible, scalable collaboration in complex clinical scenarios, with decisions finalized through reviewing updated agent comments. Experiments on two real-world medical benchmarks demonstrate that KAMAC significantly outperforms both single-agent and advanced multi-agent methods, particularly in complex clinical scenarios (i.e., cancer prognosis) requiring dynamic, cross-specialty expertise. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/XiaoXiao-Woo/KAMAC.
Task Allocation for Autonomous Machines using Computational Intelligence and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Enabling multiple autonomous machines to perform reliably requires the development of efficient cooperative control algorithms. This paper presents a survey of algorithms that have been developed for controlling and coordinating autonomous machines in complex environments. We especially focus on task allocation methods using computational intelligence (CI) and deep reinforcement learning (RL). The advantages and disadvantages of the surveyed methods are analysed thoroughly. We also propose and discuss in detail various future research directions that shed light on how to improve existing algorithms or create new methods to enhance the employability and performance of autonomous machines in real-world applications. The findings indicate that CI and deep RL methods provide viable approaches to addressing complex task allocation problems in dynamic and uncertain environments. The recent development of deep RL has greatly contributed to the literature on controlling and coordinating autonomous machines, and it has become a growing trend in this area. It is envisaged that this paper will provide researchers and engineers with a comprehensive overview of progress in machine learning research related to autonomous machines. It also highlights underexplored areas, identifies emerging methodologies, and suggests new avenues for exploration in future research within this domain.
A Survey of Scientific Large Language Models: From Data Foundations to Agent Frontiers
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) are transforming how knowledge is represented, integrated, and applied in scientific research, yet their progress is shaped by the complex nature of scientific data. This survey presents a comprehensive, data-centric synthesis that reframes the development of Sci-LLMs as a co-evolution between models and their underlying data substrate. We formulate a unified taxonomy of scientific data and a hierarchical model of scientific knowledge, emphasizing the multimodal, cross-scale, and domain-specific challenges that differentiate scientific corpora from general natural language processing datasets. We systematically review recent Sci-LLMs, from general-purpose foundations to specialized models across diverse scientific disciplines, alongside an extensive analysis of over 270 pre-/post-training datasets, showing why Sci-LLMs pose distinct demands -- heterogeneous, multi-scale, uncertainty-laden corpora that require representations preserving domain invariance and enabling cross-modal reasoning. On evaluation, we examine over 190 benchmark datasets and trace a shift from static exams toward process- and discovery-oriented assessments with advanced evaluation protocols. These data-centric analyses highlight persistent issues in scientific data development and discuss emerging solutions involving semi-automated annotation pipelines and expert validation. Finally, we outline a paradigm shift toward closed-loop systems where autonomous agents based on Sci-LLMs actively experiment, validate, and contribute to a living, evolving knowledge base. Collectively, this work provides a roadmap for building trustworthy, continually evolving artificial intelligence (AI) systems that function as a true partner in accelerating scientific discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge