Armin Mustafa
SSLAM: Enhancing Self-Supervised Models with Audio Mixtures for Polyphonic Soundscapes
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised pre-trained audio networks have seen widespread adoption in real-world systems, particularly in multi-modal large language models. These networks are often employed in a frozen state, under the assumption that the SSL pre-training has sufficiently equipped them to handle real-world audio. However, a critical question remains: how well do these models actually perform in real-world conditions, where audio is typically polyphonic and complex, involving multiple overlapping sound sources? Current audio SSL methods are often benchmarked on datasets predominantly featuring monophonic audio, such as environmental sounds, and speech. As a result, the ability of SSL models to generalize to polyphonic audio, a common characteristic in natural scenarios, remains underexplored. This limitation raises concerns about the practical robustness of SSL models in more realistic audio settings. To address this gap, we introduce Self-Supervised Learning from Audio Mixtures (SSLAM), a novel direction in audio SSL research, designed to improve, designed to improve the model's ability to learn from polyphonic data while maintaining strong performance on monophonic data. We thoroughly evaluate SSLAM on standard audio SSL benchmark datasets which are predominantly monophonic and conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis against SOTA methods using a range of high-quality, publicly available polyphonic datasets. SSLAM not only improves model performance on polyphonic audio, but also maintains or exceeds performance on standard audio SSL benchmarks. Notably, it achieves up to a 3.9\% improvement on the AudioSet-2M (AS-2M), reaching a mean average precision (mAP) of 50.2. For polyphonic datasets, SSLAM sets new SOTA in both linear evaluation and fine-tuning regimes with performance improvements of up to 9.1\% (mAP).
PAL: Probing Audio Encoders via LLMs -- A Study of Information Transfer from Audio Encoders to LLMs
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:The integration of audio perception capabilities into Large Language Models (LLMs) has enabled significant advances in Audio-LLMs. Although application-focused developments, particularly in curating training data for specific capabilities e.g., audio reasoning, have progressed rapidly, the underlying mechanisms that govern efficient transfer of rich semantic representations from audio encoders to LLMs remain under-explored. We conceptualize effective audio-LLM interaction as the LLM's ability to proficiently probe the audio encoder representations to satisfy textual queries. This paper presents a systematic investigation on how architectural design choices can affect that. Beginning with a standard Pengi/LLaVA-style audio-LLM architecture, we propose and evaluate several modifications guided by hypotheses derived from mechanistic interpretability studies and LLM operational principles. Our experiments demonstrate that: (1) delaying audio integration until the LLM's initial layers establish textual context that enhances its ability to probe the audio representations for relevant information; (2) the LLM can proficiently probe audio representations exclusively through LLM layer's attention submodule, without requiring propagation to its Feed-Forward Network (FFN) submodule; (3) an efficiently integrated ensemble of diverse audio encoders provides richer, complementary representations, thereby broadening the LLM's capacity to probe a wider spectrum of audio information. All hypotheses are evaluated using an identical three-stage training curriculum on a dataset of 5.6 million audio-text pairs, ensuring controlled comparisons. Our final architecture, which incorporates all proposed modifications, achieves relative improvements from 10\% to 60\% over the baseline, validating our approach to optimizing cross-modal information transfer in audio-LLMs. Project page: https://ta012.github.io/PAL/
Joint Reconstruction of Spatially-Coherent and Realistic Clothed Humans and Objects from a Single Image
Feb 25, 2025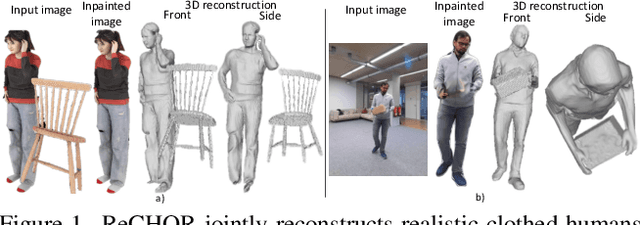
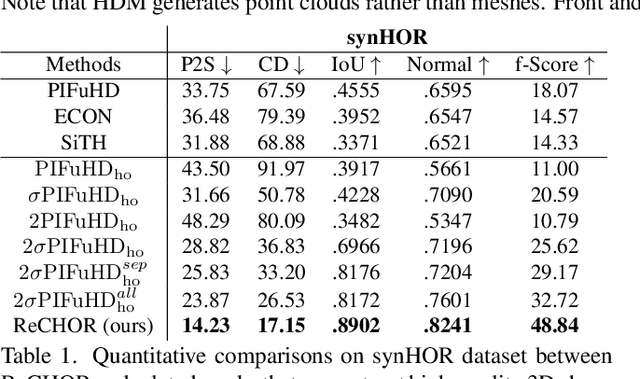
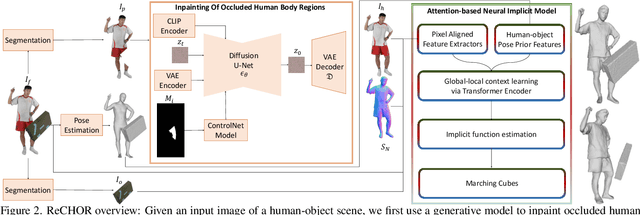
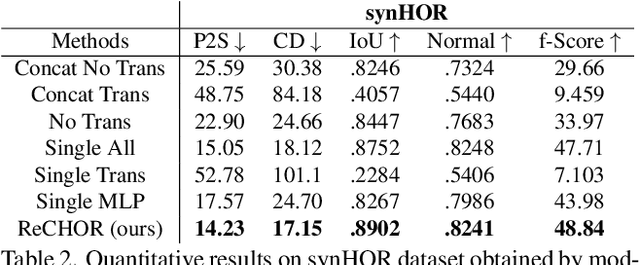
Abstract:Recent advances in human shape learning have focused on achieving accurate human reconstruction from single-view images. However, in the real world, humans share space with other objects. Reconstructing images with humans and objects is challenging due to the occlusions and lack of 3D spatial awareness, which leads to depth ambiguity in the reconstruction. Existing methods in monocular human-object reconstruction fail to capture intricate details of clothed human bodies and object surfaces due to their template-based nature. In this paper, we jointly reconstruct clothed humans and objects in a spatially coherent manner from single-view images, while addressing human-object occlusions. A novel attention-based neural implicit model is proposed that leverages image pixel alignment to retrieve high-quality details, and incorporates semantic features extracted from the human-object pose to enable 3D spatial awareness. A generative diffusion model is used to handle human-object occlusions. For training and evaluation, we introduce a synthetic dataset with rendered scenes of inter-occluded 3D human scans and diverse objects. Extensive evaluation on both synthetic and real datasets demonstrates the superior quality of proposed human-object reconstructions over competitive methods.
Deconstruct Complexity (DeComplex): A Novel Perspective on Tackling Dense Action Detection
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Dense action detection involves detecting multiple co-occurring actions in an untrimmed video while action classes are often ambiguous and represent overlapping concepts. To address this challenge task, we introduce a novel perspective inspired by how humans tackle complex tasks by breaking them into manageable sub-tasks. Instead of relying on a single network to address the entire problem, as in current approaches, we propose decomposing the problem into detecting key concepts present in action classes, specifically, detecting dense static concepts and detecting dense dynamic concepts, and assigning them to distinct, specialized networks. Furthermore, simultaneous actions in a video often exhibit interrelationships, and exploiting these relationships can improve performance. However, we argue that current networks fail to effectively learn these relationships due to their reliance on binary cross-entropy optimization, which treats each class independently. To address this limitation, we propose providing explicit supervision on co-occurring concepts during network optimization through a novel language-guided contrastive learning loss. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach over state-of-the-art methods, achieving substantial relative improvements of 23.4% and 2.5% mAP on the challenging benchmark datasets, Charades and MultiTHUMOS.
Efficient Audio-Visual Fusion for Video Classification
Nov 08, 2024
Abstract:We present Attend-Fusion, a novel and efficient approach for audio-visual fusion in video classification tasks. Our method addresses the challenge of exploiting both audio and visual modalities while maintaining a compact model architecture. Through extensive experiments on the YouTube-8M dataset, we demonstrate that our Attend-Fusion achieves competitive performance with significantly reduced model complexity compared to larger baseline models.
Boosting Camera Motion Control for Video Diffusion Transformers
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in diffusion models have significantly enhanced the quality of video generation. However, fine-grained control over camera pose remains a challenge. While U-Net-based models have shown promising results for camera control, transformer-based diffusion models (DiT)-the preferred architecture for large-scale video generation - suffer from severe degradation in camera motion accuracy. In this paper, we investigate the underlying causes of this issue and propose solutions tailored to DiT architectures. Our study reveals that camera control performance depends heavily on the choice of conditioning methods rather than camera pose representations that is commonly believed. To address the persistent motion degradation in DiT, we introduce Camera Motion Guidance (CMG), based on classifier-free guidance, which boosts camera control by over 400%. Additionally, we present a sparse camera control pipeline, significantly simplifying the process of specifying camera poses for long videos. Our method universally applies to both U-Net and DiT models, offering improved camera control for video generation tasks.
RenDetNet: Weakly-supervised Shadow Detection with Shadow Caster Verification
Aug 30, 2024
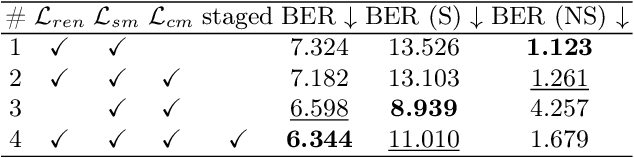

Abstract:Existing shadow detection models struggle to differentiate dark image areas from shadows. In this paper, we tackle this issue by verifying that all detected shadows are real, i.e. they have paired shadow casters. We perform this step in a physically-accurate manner by differentiably re-rendering the scene and observing the changes stemming from carving out estimated shadow casters. Thanks to this approach, the RenDetNet proposed in this paper is the first learning-based shadow detection model whose supervisory signals can be computed in a self-supervised manner. The developed system compares favourably against recent models trained on our data. As part of this publication, we release our code on github.
Attend-Fusion: Efficient Audio-Visual Fusion for Video Classification
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:Exploiting both audio and visual modalities for video classification is a challenging task, as the existing methods require large model architectures, leading to high computational complexity and resource requirements. Smaller architectures, on the other hand, struggle to achieve optimal performance. In this paper, we propose Attend-Fusion, an audio-visual (AV) fusion approach that introduces a compact model architecture specifically designed to capture intricate audio-visual relationships in video data. Through extensive experiments on the challenging YouTube-8M dataset, we demonstrate that Attend-Fusion achieves an F1 score of 75.64\% with only 72M parameters, which is comparable to the performance of larger baseline models such as Fully-Connected Late Fusion (75.96\% F1 score, 341M parameters). Attend-Fusion achieves similar performance to the larger baseline model while reducing the model size by nearly 80\%, highlighting its efficiency in terms of model complexity. Our work demonstrates that the Attend-Fusion model effectively combines audio and visual information for video classification, achieving competitive performance with significantly reduced model size. This approach opens new possibilities for deploying high-performance video understanding systems in resource-constrained environments across various applications.
Single-image coherent reconstruction of objects and humans
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Existing methods for reconstructing objects and humans from a monocular image suffer from severe mesh collisions and performance limitations for interacting occluding objects. This paper introduces a method to obtain a globally consistent 3D reconstruction of interacting objects and people from a single image. Our contributions include: 1) an optimization framework, featuring a collision loss, tailored to handle human-object and human-human interactions, ensuring spatially coherent scene reconstruction; and 2) a novel technique to robustly estimate 6 degrees of freedom (DOF) poses, specifically for heavily occluded objects, exploiting image inpainting. Notably, our proposed method operates effectively on images from real-world scenarios, without necessitating scene or object-level 3D supervision. Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluation against existing methods demonstrates a significant reduction in collisions in the final reconstructions of scenes with multiple interacting humans and objects and a more coherent scene reconstruction.
NarrativeBridge: Enhancing Video Captioning with Causal-Temporal Narrative
Jun 10, 2024
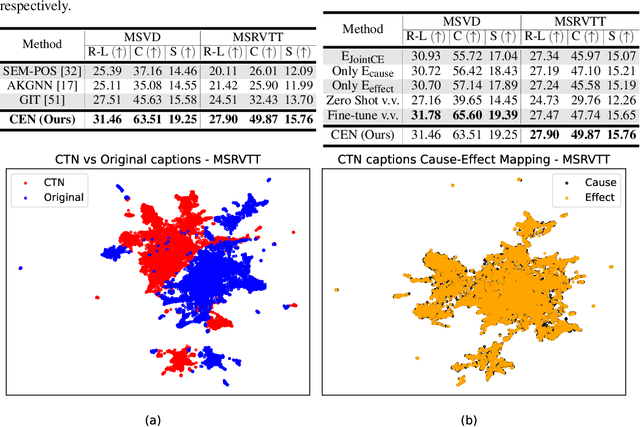
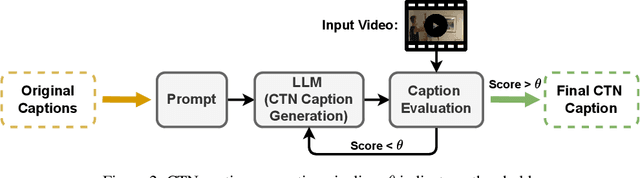
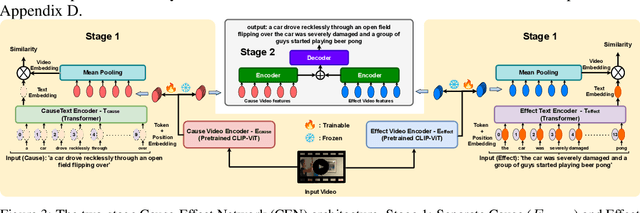
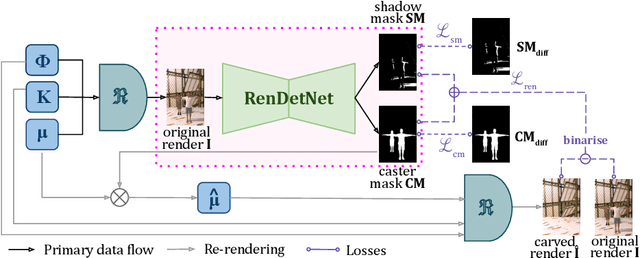
Abstract:Existing video captioning benchmarks and models lack coherent representations of causal-temporal narrative, which is sequences of events linked through cause and effect, unfolding over time and driven by characters or agents. This lack of narrative restricts models' ability to generate text descriptions that capture the causal and temporal dynamics inherent in video content. To address this gap, we propose NarrativeBridge, an approach comprising of: (1) a novel Causal-Temporal Narrative (CTN) captions benchmark generated using a large language model and few-shot prompting, explicitly encoding cause-effect temporal relationships in video descriptions, evaluated automatically to ensure caption quality and relevance; and (2) a dedicated Cause-Effect Network (CEN) architecture with separate encoders for capturing cause and effect dynamics independently, enabling effective learning and generation of captions with causal-temporal narrative. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CEN is more accurate in articulating the causal and temporal aspects of video content than the second best model (GIT): 17.88 and 17.44 CIDEr on the MSVD and MSR-VTT datasets, respectively. The proposed framework understands and generates nuanced text descriptions with intricate causal-temporal narrative structures present in videos, addressing a critical limitation in video captioning. For project details, visit https://narrativebridge.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge