Gelareh Mohammadi
for the Sydney Memory and Ageing Study and the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Flick: Few Labels Text Classification using K-Aware Intermediate Learning in Multi-Task Low-Resource Languages
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Training deep learning networks with minimal supervision has gained significant research attention due to its potential to reduce reliance on extensive labelled data. While self-training methods have proven effective in semi-supervised learning, they remain vulnerable to errors from noisy pseudo labels. Moreover, most recent approaches to the few-label classification problem are either designed for resource-rich languages such as English or involve complex cascading models that are prone to overfitting. To address the persistent challenge of few-label text classification in truly low-resource linguistic contexts, where existing methods often struggle with noisy pseudo-labels and domain adaptation, we propose Flick. Unlike prior methods that rely on generic multi-cluster pseudo-labelling or complex cascading architectures, Flick leverages the fundamental insight that distilling high-confidence pseudo-labels from a broader set of initial clusters can dramatically improve pseudo-label quality, particularly for linguistically diverse, low-resource settings. Flick introduces a novel pseudo-label refinement component, a departure from traditional pseudo-labelling strategies by identifying and leveraging top-performing pseudo-label clusters. This component specifically learns to distil highly reliable pseudo-labels from an initial broad set by focusing on single-cluster cohesion and leveraging an adaptive top-k selection mechanism. This targeted refinement process is crucial for mitigating the propagation of errors inherent in low-resource data, allowing for robust fine-tuning of pre-trained language models with only a handful of true labels. We demonstrate Flick's efficacy across 14 diverse datasets, encompassing challenging low-resource languages such as Arabic, Urdu, and Setswana, alongside English, showcasing its superior performance and adaptability.
Exploring Emotions in Multi-componential Space using Interactive VR Games
Apr 04, 2024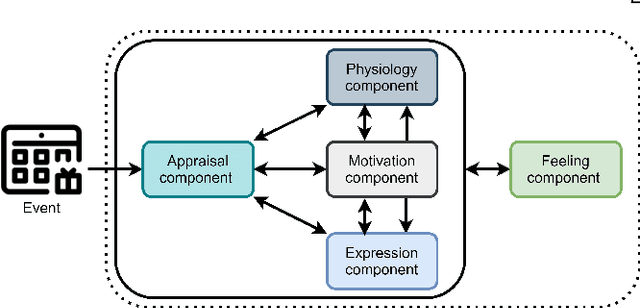
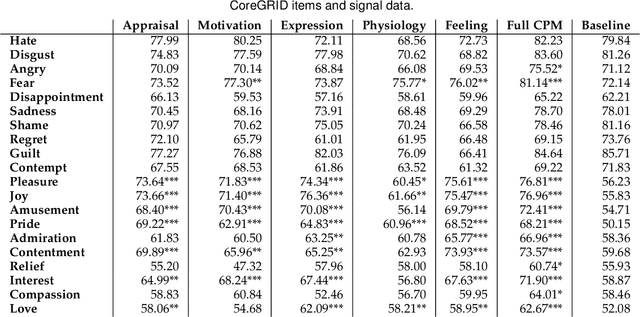
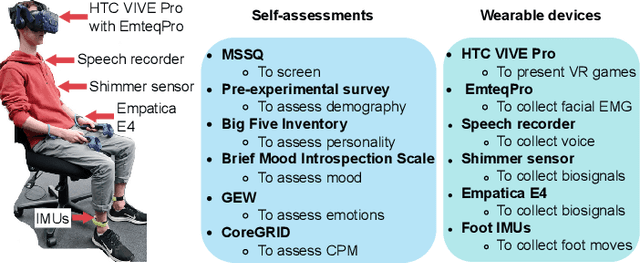
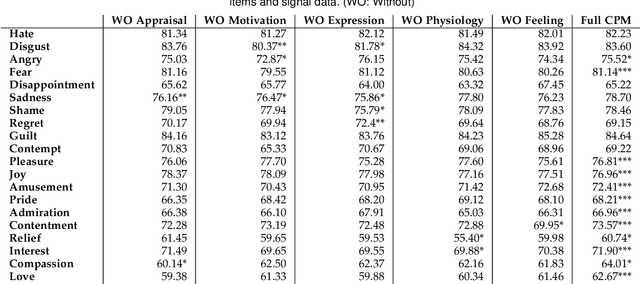
Abstract:Emotion understanding is a complex process that involves multiple components. The ability to recognise emotions not only leads to new context awareness methods but also enhances system interaction's effectiveness by perceiving and expressing emotions. Despite the attention to discrete and dimensional models, neuroscientific evidence supports those emotions as being complex and multi-faceted. One framework that resonated well with such findings is the Component Process Model (CPM), a theory that considers the complexity of emotions with five interconnected components: appraisal, expression, motivation, physiology and feeling. However, the relationship between CPM and discrete emotions has not yet been fully explored. Therefore, to better understand emotions underlying processes, we operationalised a data-driven approach using interactive Virtual Reality (VR) games and collected multimodal measures (self-reports, physiological and facial signals) from 39 participants. We used Machine Learning (ML) methods to identify the unique contributions of each component to emotion differentiation. Our results showed the role of different components in emotion differentiation, with the model including all components demonstrating the most significant contribution. Moreover, we found that at least five dimensions are needed to represent the variation of emotions in our dataset. These findings also have implications for using VR environments in emotion research and highlight the role of physiological signals in emotion recognition within such environments.
Speech-Gesture GAN: Gesture Generation for Robots and Embodied Agents
Sep 17, 2023Abstract:Embodied agents, in the form of virtual agents or social robots, are rapidly becoming more widespread. In human-human interactions, humans use nonverbal behaviours to convey their attitudes, feelings, and intentions. Therefore, this capability is also required for embodied agents in order to enhance the quality and effectiveness of their interactions with humans. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that can generate sequences of joint angles from the speech text and speech audio utterances. Based on a conditional Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), our proposed neural network model learns the relationships between the co-speech gestures and both semantic and acoustic features from the speech input. In order to train our neural network model, we employ a public dataset containing co-speech gestures with corresponding speech audio utterances, which were captured from a single male native English speaker. The results from both objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate the efficacy of our gesture-generation framework for Robots and Embodied Agents.
2CET-GAN: Pixel-Level GAN Model for Human Facial Expression Transfer
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:Recent studies have used GAN to transfer expressions between human faces. However, existing models have many flaws: relying on emotion labels, lacking continuous expressions, and failing to capture the expression details. To address these limitations, we propose a novel CycleGAN- and InfoGAN-based network called 2 Cycles Expression Transfer GAN (2CET-GAN), which can learn continuous expression transfer without using emotion labels. The experiment shows our network can generate diverse and high-quality expressions and can generalize to unknown identities. To the best of our knowledge, we are among the first to successfully use an unsupervised approach to disentangle expression representation from identities at the pixel level.
Temporal Pattern Mining for Analysis of Longitudinal Clinical Data: Identifying Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease
Sep 11, 2022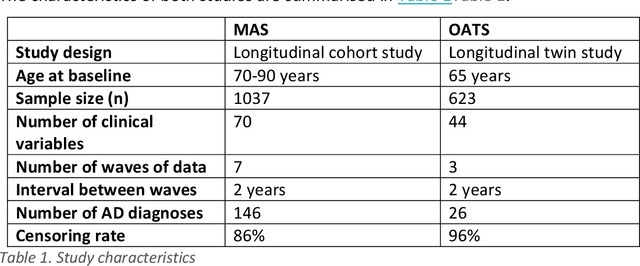
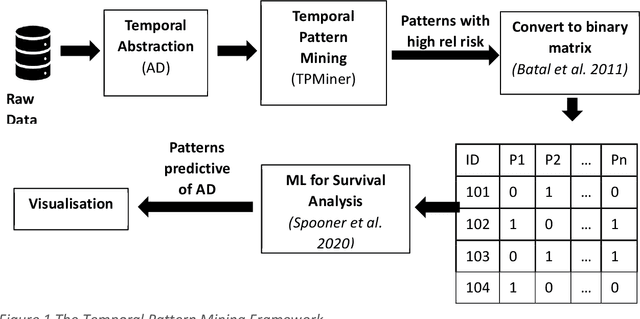

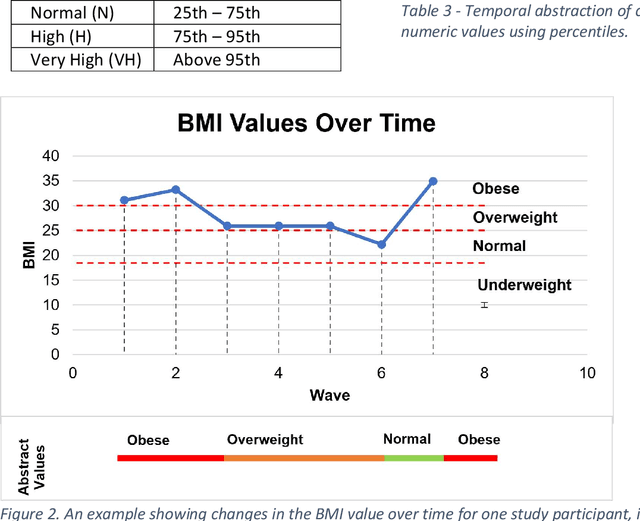
Abstract:A novel framework is proposed for handling the complex task of modelling and analysis of longitudinal, multivariate, heterogeneous clinical data. This method uses temporal abstraction to convert the data into a more appropriate form for modelling, temporal pattern mining, to discover patterns in the complex, longitudinal data and machine learning models of survival analysis to select the discovered patterns. The method is applied to a real-world study of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has no cure. The patterns discovered were predictive of AD in survival analysis models with a Concordance index of up to 0.8. This is the first work that performs survival analysis of AD data using temporal data collections for AD. A visualisation module also provides a clear picture of the discovered patterns for ease of interpretability.
Ensemble feature selection with clustering for analysis of high-dimensional, correlated clinical data in the search for Alzheimer's disease biomarkers
Jul 06, 2022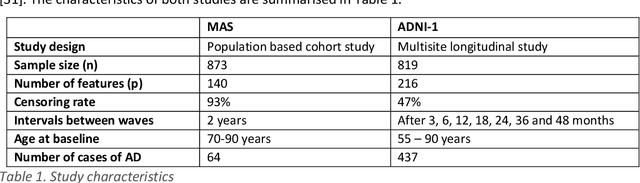
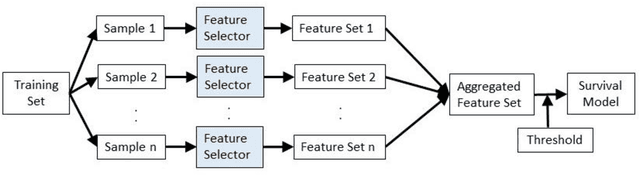
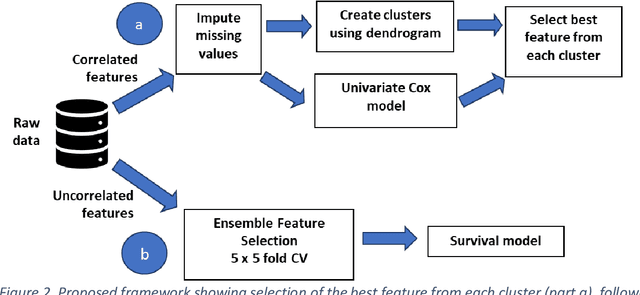
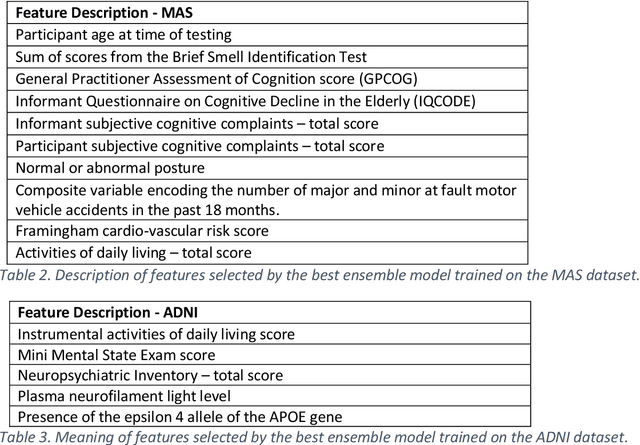
Abstract:Healthcare datasets often contain groups of highly correlated features, such as features from the same biological system. When feature selection is applied to these datasets to identify the most important features, the biases inherent in some multivariate feature selectors due to correlated features make it difficult for these methods to distinguish between the important and irrelevant features and the results of the feature selection process can be unstable. Feature selection ensembles, which aggregate the results of multiple individual base feature selectors, have been investigated as a means of stabilising feature selection results, but do not address the problem of correlated features. We present a novel framework to create feature selection ensembles from multivariate feature selectors while taking into account the biases produced by groups of correlated features, using agglomerative hierarchical clustering in a pre-processing step. These methods were applied to two real-world datasets from studies of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has no cure and is not yet fully understood. Our results show a marked improvement in the stability of features selected over the models without clustering, and the features selected by these models are in keeping with the findings in the AD literature.
Ensemble feature selection with data-driven thresholding for Alzheimer's disease biomarker discovery
Jul 05, 2022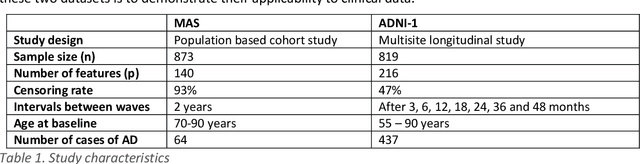

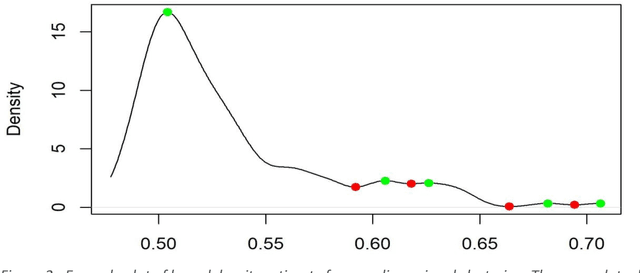
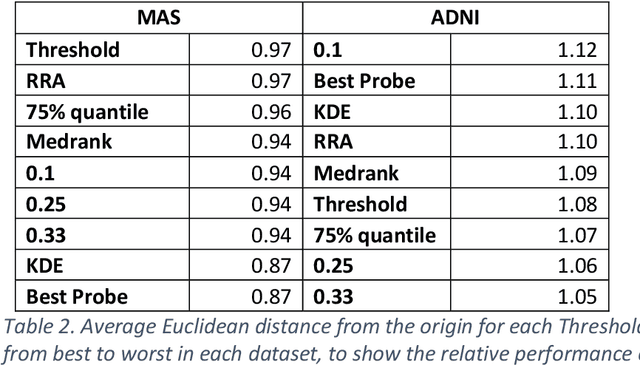
Abstract:Healthcare datasets present many challenges to both machine learning and statistics as their data are typically heterogeneous, censored, high-dimensional and have missing information. Feature selection is often used to identify the important features but can produce unstable results when applied to high-dimensional data, selecting a different set of features on each iteration. The stability of feature selection can be improved with the use of feature selection ensembles, which aggregate the results of multiple base feature selectors. A threshold must be applied to the final aggregated feature set to separate the relevant features from the redundant ones. A fixed threshold, which is typically applied, offers no guarantee that the final set of selected features contains only relevant features. This work develops several data-driven thresholds to automatically identify the relevant features in an ensemble feature selector and evaluates their predictive accuracy and stability. To demonstrate the applicability of these methods to clinical data, they are applied to data from two real-world Alzheimer's disease (AD) studies. AD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease with no known cure, that begins at least 2-3 decades before overt symptoms appear, presenting an opportunity for researchers to identify early biomarkers that might identify patients at risk of developing AD. Features identified by applying these methods to both datasets reflect current findings in the AD literature.
Video Generative Adversarial Networks: A Review
Nov 04, 2020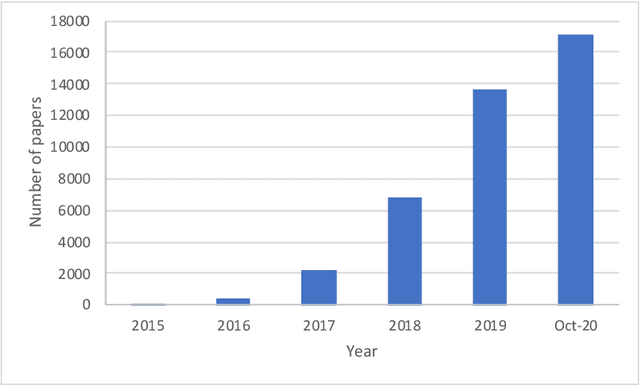
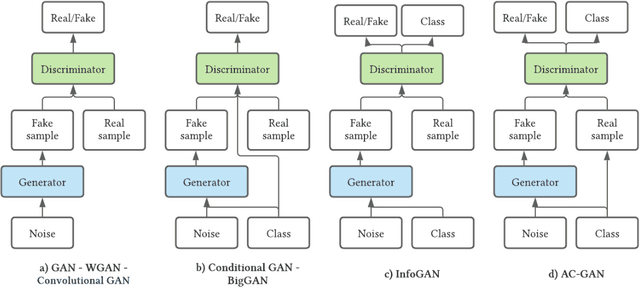
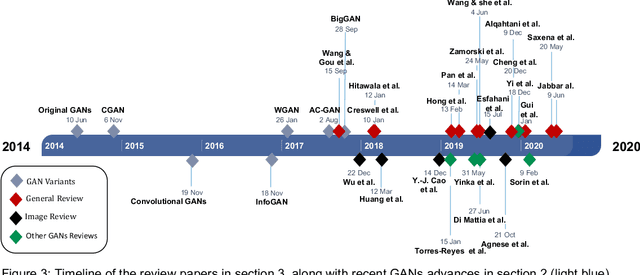
Abstract:With the increasing interest in the content creation field in multiple sectors such as media, education, and entertainment, there is an increasing trend in the papers that uses AI algorithms to generate content such as images, videos, audio, and text. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in one of the promising models that synthesizes data samples that are similar to real data samples. While the variations of GANs models, in general, have been covered to some extent in several survey papers, to the best of our knowledge, this is among the first survey papers that reviews the state-of-the-art video GANs models. This paper first categorized GANs review papers into general GANs review papers, image GANs review papers, and special field GANs review papers such as anomaly detection, medical imaging, or cybersecurity. The paper then summarizes the main improvements in GANs frameworks that are not initially developed for the video domain but have been adopted in multiple video GANs variations. Then, a comprehensive review of video GANs models is provided under two main divisions according to the presence or non-presence of a condition. The conditional models then further grouped according to the type of condition into audio, text, video, and image. The paper is concluded by highlighting the main challenges and limitations of the current video GANs models. A comprehensive list of datasets, applied loss functions, and evaluation metrics is provided in the supplementary material.
A Multi-Componential Approach to Emotion Recognition and the Effect of Personality
Oct 22, 2020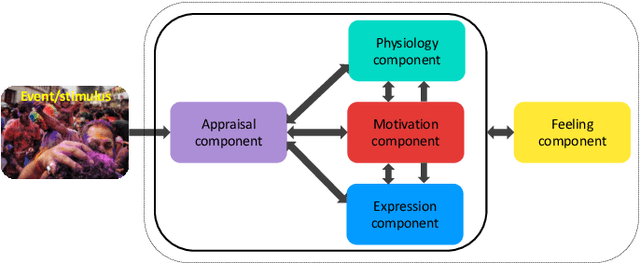
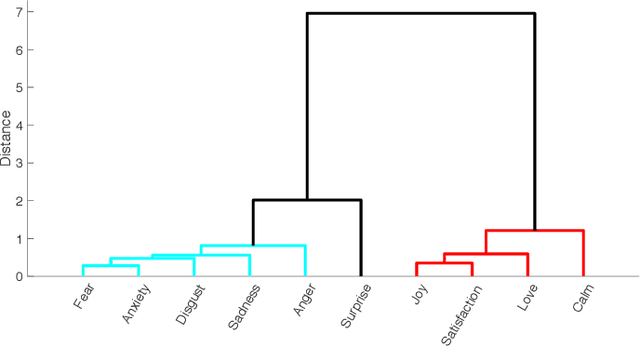
Abstract:Emotions are an inseparable part of human nature affecting our behavior in response to the outside world. Although most empirical studies have been dominated by two theoretical models including discrete categories of emotion and dichotomous dimensions, results from neuroscience approaches suggest a multi-processes mechanism underpinning emotional experience with a large overlap across different emotions. While these findings are consistent with the influential theories of emotion in psychology that emphasize a role for multiple component processes to generate emotion episodes, few studies have systematically investigated the relationship between discrete emotions and a full componential view. This paper applies a componential framework with a data-driven approach to characterize emotional experiences evoked during movie watching. The results suggest that differences between various emotions can be captured by a few (at least 6) latent dimensions, each defined by features associated with component processes, including appraisal, expression, physiology, motivation, and feeling. In addition, the link between discrete emotions and component model is explored and results show that a componential model with a limited number of descriptors is still able to predict the level of experienced discrete emotion(s) to a satisfactory level. Finally, as appraisals may vary according to individual dispositions and biases, we also study the relationship between personality traits and emotions in our computational framework and show that the role of personality on discrete emotion differences can be better justified using the component model.
* 13 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge