Temporal Pattern Mining for Analysis of Longitudinal Clinical Data: Identifying Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2022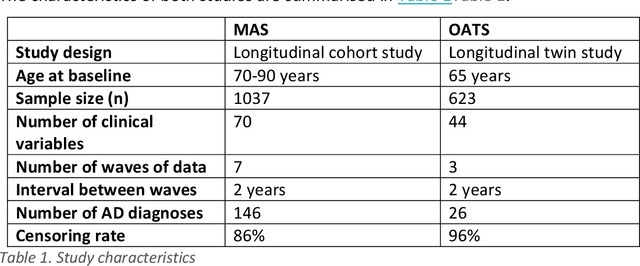
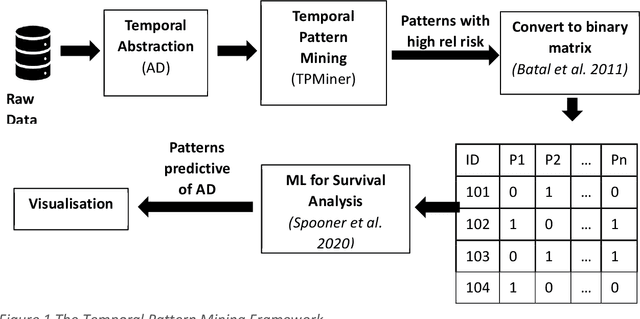

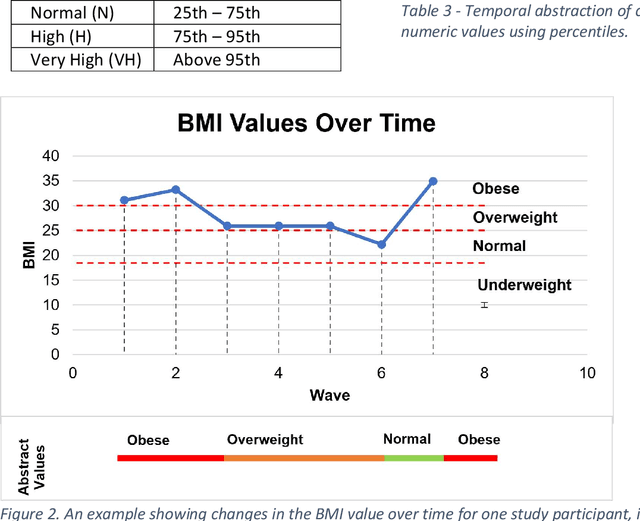
A novel framework is proposed for handling the complex task of modelling and analysis of longitudinal, multivariate, heterogeneous clinical data. This method uses temporal abstraction to convert the data into a more appropriate form for modelling, temporal pattern mining, to discover patterns in the complex, longitudinal data and machine learning models of survival analysis to select the discovered patterns. The method is applied to a real-world study of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has no cure. The patterns discovered were predictive of AD in survival analysis models with a Concordance index of up to 0.8. This is the first work that performs survival analysis of AD data using temporal data collections for AD. A visualisation module also provides a clear picture of the discovered patterns for ease of interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge