Zhihao Shuai
Spatial-Temporal Perception with Causal Inference for Naturalistic Driving Action Recognition
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Naturalistic driving action recognition is essential for vehicle cabin monitoring systems. However, the complexity of real-world backgrounds presents significant challenges for this task, and previous approaches have struggled with practical implementation due to their limited ability to observe subtle behavioral differences and effectively learn inter-frame features from video. In this paper, we propose a novel Spatial-Temporal Perception (STP) architecture that emphasizes both temporal information and spatial relationships between key objects, incorporating a causal decoder to perform behavior recognition and temporal action localization. Without requiring multimodal input, STP directly extracts temporal and spatial distance features from RGB video clips. Subsequently, these dual features are jointly encoded by maximizing the expected likelihood across all possible permutations of the factorization order. By integrating temporal and spatial features at different scales, STP can perceive subtle behavioral changes in challenging scenarios. Additionally, we introduce a causal-aware module to explore relationships between video frame features, significantly enhancing detection efficiency and performance. We validate the effectiveness of our approach using two publicly available driver distraction detection benchmarks. The results demonstrate that our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance.
PEPL: Precision-Enhanced Pseudo-Labeling for Fine-Grained Image Classification in Semi-Supervised Learning
Sep 05, 2024
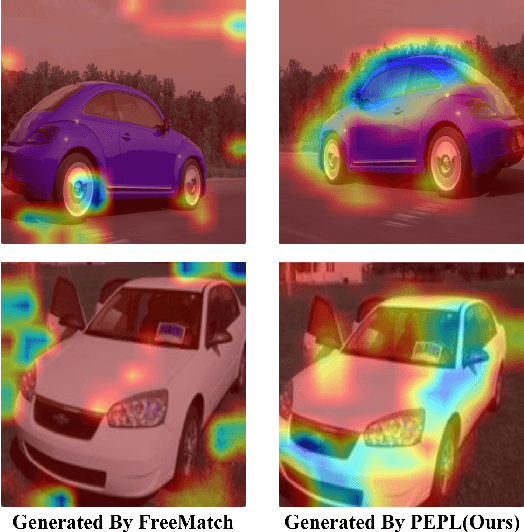



Abstract:Fine-grained image classification has witnessed significant advancements with the advent of deep learning and computer vision technologies. However, the scarcity of detailed annotations remains a major challenge, especially in scenarios where obtaining high-quality labeled data is costly or time-consuming. To address this limitation, we introduce Precision-Enhanced Pseudo-Labeling(PEPL) approach specifically designed for fine-grained image classification within a semi-supervised learning framework. Our method leverages the abundance of unlabeled data by generating high-quality pseudo-labels that are progressively refined through two key phases: initial pseudo-label generation and semantic-mixed pseudo-label generation. These phases utilize Class Activation Maps (CAMs) to accurately estimate the semantic content and generate refined labels that capture the essential details necessary for fine-grained classification. By focusing on semantic-level information, our approach effectively addresses the limitations of standard data augmentation and image-mixing techniques in preserving critical fine-grained features. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets, demonstrating significant improvements over existing semi-supervised strategies, with notable boosts in accuracy and robustness.Our code has been open sourced at https://github.com/TianSuya/SemiFG.
DiffSeg: A Segmentation Model for Skin Lesions Based on Diffusion Difference
Apr 25, 2024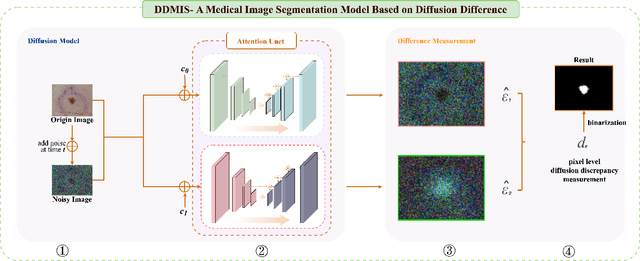
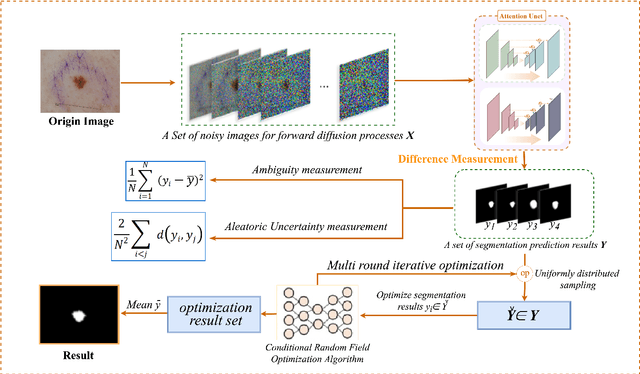
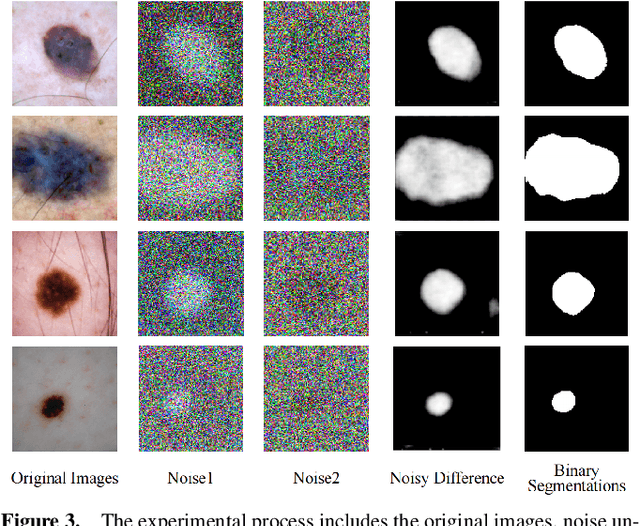
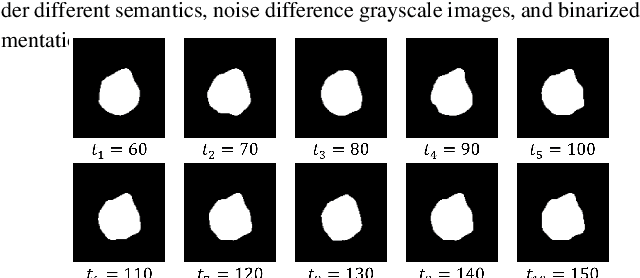
Abstract:Weakly supervised medical image segmentation (MIS) using generative models is crucial for clinical diagnosis. However, the accuracy of the segmentation results is often limited by insufficient supervision and the complex nature of medical imaging. Existing models also only provide a single outcome, which does not allow for the measurement of uncertainty. In this paper, we introduce DiffSeg, a segmentation model for skin lesions based on diffusion difference which exploits diffusion model principles to ex-tract noise-based features from images with diverse semantic information. By discerning difference between these noise features, the model identifies diseased areas. Moreover, its multi-output capability mimics doctors' annotation behavior, facilitating the visualization of segmentation result consistency and ambiguity. Additionally, it quantifies output uncertainty using Generalized Energy Distance (GED), aiding interpretability and decision-making for physicians. Finally, the model integrates outputs through the Dense Conditional Random Field (DenseCRF) algorithm to refine the segmentation boundaries by considering inter-pixel correlations, which improves the accuracy and optimizes the segmentation results. We demonstrate the effectiveness of DiffSeg on the ISIC 2018 Challenge dataset, outperforming state-of-the-art U-Net-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge