Samarth Agrawal
NEAR$^2$: A Nested Embedding Approach to Efficient Product Retrieval and Ranking
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:E-commerce information retrieval (IR) systems struggle to simultaneously achieve high accuracy in interpreting complex user queries and maintain efficient processing of vast product catalogs. The dual challenge lies in precisely matching user intent with relevant products while managing the computational demands of real-time search across massive inventories. In this paper, we propose a Nested Embedding Approach to product Retrieval and Ranking, called NEAR$^2$, which can achieve up to $12$ times efficiency in embedding size at inference time while introducing no extra cost in training and improving performance in accuracy for various encoder-based Transformer models. We validate our approach using different loss functions for the retrieval and ranking task, including multiple negative ranking loss and online contrastive loss, on four different test sets with various IR challenges such as short and implicit queries. Our approach achieves an improved performance over a smaller embedding dimension, compared to any existing models.
Centrality-aware Product Retrieval and Ranking
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of improving user experience on e-commerce platforms by enhancing product ranking relevant to users' search queries. Ambiguity and complexity of user queries often lead to a mismatch between the user's intent and retrieved product titles or documents. Recent approaches have proposed the use of Transformer-based models, which need millions of annotated query-title pairs during the pre-training stage, and this data often does not take user intent into account. To tackle this, we curate samples from existing datasets at eBay, manually annotated with buyer-centric relevance scores and centrality scores, which reflect how well the product title matches the users' intent. We introduce a User-intent Centrality Optimization (UCO) approach for existing models, which optimises for the user intent in semantic product search. To that end, we propose a dual-loss based optimisation to handle hard negatives, i.e., product titles that are semantically relevant but do not reflect the user's intent. Our contributions include curating challenging evaluation sets and implementing UCO, resulting in significant product ranking efficiency improvements observed for different evaluation metrics. Our work aims to ensure that the most buyer-centric titles for a query are ranked higher, thereby, enhancing the user experience on e-commerce platforms.
Expect the unexpected: Harnessing Sentence Completion for Sarcasm Detection
Jul 19, 2017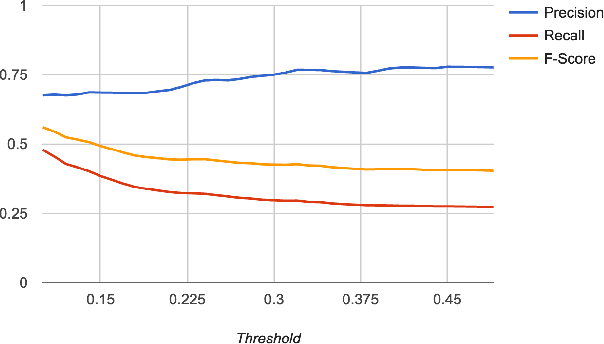
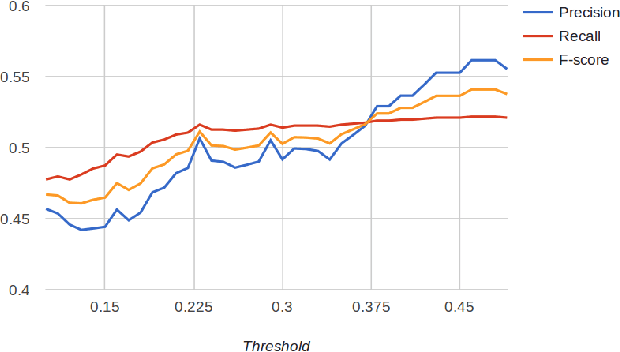
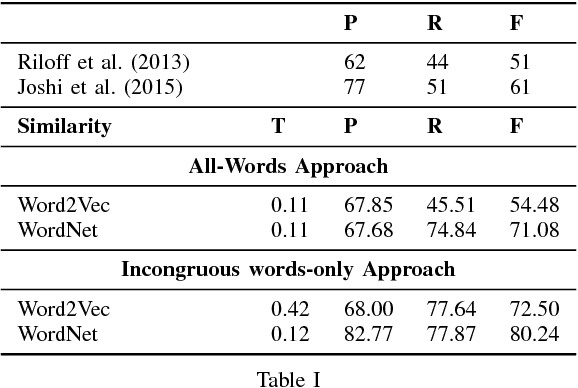
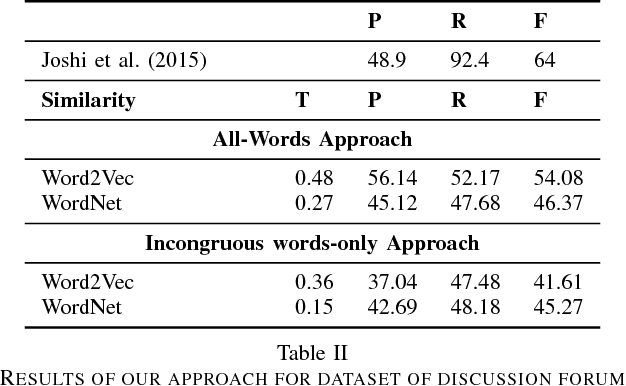
Abstract:The trigram `I love being' is expected to be followed by positive words such as `happy'. In a sarcastic sentence, however, the word `ignored' may be observed. The expected and the observed words are, thus, incongruous. We model sarcasm detection as the task of detecting incongruity between an observed and an expected word. In order to obtain the expected word, we use Context2Vec, a sentence completion library based on Bidirectional LSTM. However, since the exact word where such an incongruity occurs may not be known in advance, we present two approaches: an All-words approach (which consults sentence completion for every content word) and an Incongruous words-only approach (which consults sentence completion for the 50% most incongruous content words). The approaches outperform reported values for tweets but not for discussion forum posts. This is likely to be because of redundant consultation of sentence completion for discussion forum posts. Therefore, we consider an oracle case where the exact incongruous word is manually labeled in a corpus reported in past work. In this case, the performance is higher than the all-words approach. This sets up the promise for using sentence completion for sarcasm detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge