Yuzhe Yang
Time-Annealed Perturbation Sampling: Diverse Generation for Diffusion Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Diffusion language models (Diffusion-LMs) introduce an explicit temporal dimension into text generation, yet how this structure can be leveraged to control generation diversity for exploring multiple valid semantic or reasoning paths remains underexplored. In this paper, we show that Diffusion-LMs, like diffusion models in image generation, exhibit a temporal division of labor: early denoising steps largely determine the global semantic structure, while later steps focus on local lexical refinement. Building on this insight, we propose Time-Annealed Perturbation Sampling (TAPS), a training-free inference strategy that encourages semantic branching early in the diffusion process while progressively reducing perturbations to preserve fluency and instruction adherence. TAPS is compatible with both non-autoregressive and semi-autoregressive Diffusion backbones, demonstrated on LLaDA and TraDo in our paper, and consistently improves output diversity across creative writing and reasoning benchmarks without compromising generation quality.
Towards a Science of Scaling Agent Systems
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Agents, language model-based systems that are capable of reasoning, planning, and acting are becoming the dominant paradigm for real-world AI applications. Despite this widespread adoption, the principles that determine their performance remain underexplored. We address this by deriving quantitative scaling principles for agent systems. We first formalize a definition for agentic evaluation and characterize scaling laws as the interplay between agent quantity, coordination structure, model capability, and task properties. We evaluate this across four benchmarks: Finance-Agent, BrowseComp-Plus, PlanCraft, and Workbench. With five canonical agent architectures (Single-Agent and four Multi-Agent Systems: Independent, Centralized, Decentralized, Hybrid), instantiated across three LLM families, we perform a controlled evaluation spanning 180 configurations. We derive a predictive model using coordination metrics, that achieves cross-validated R^2=0.524, enabling prediction on unseen task domains. We identify three effects: (1) a tool-coordination trade-off: under fixed computational budgets, tool-heavy tasks suffer disproportionately from multi-agent overhead. (2) a capability saturation: coordination yields diminishing or negative returns once single-agent baselines exceed ~45%. (3) topology-dependent error amplification: independent agents amplify errors 17.2x, while centralized coordination contains this to 4.4x. Centralized coordination improves performance by 80.8% on parallelizable tasks, while decentralized coordination excels on web navigation (+9.2% vs. +0.2%). Yet for sequential reasoning tasks, every multi-agent variants degraded performance by 39-70%. The framework predicts the optimal coordination strategy for 87% of held-out configurations. Out-of-sample validation on GPT-5.2, achieves MAE=0.071 and confirms four of five scaling principles generalize to unseen frontier models.
Reasoning Within the Mind: Dynamic Multimodal Interleaving in Latent Space
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced cross-modal understanding and reasoning by incorporating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning in the semantic space. Building upon this, recent studies extend the CoT mechanism to the visual modality, enabling models to integrate visual information during reasoning through external tools or explicit image generation. However, these methods remain dependent on explicit step-by-step reasoning, unstable perception-reasoning interaction and notable computational overhead. Inspired by human cognition, we posit that thinking unfolds not linearly but through the dynamic interleaving of reasoning and perception within the mind. Motivated by this perspective, we propose DMLR, a test-time Dynamic Multimodal Latent Reasoning framework that employs confidence-guided latent policy gradient optimization to refine latent think tokens for in-depth reasoning. Furthermore, a Dynamic Visual Injection Strategy is introduced, which retrieves the most relevant visual features at each latent think token and updates the set of best visual patches. The updated patches are then injected into latent think token to achieve dynamic visual-textual interleaving. Experiments across seven multimodal reasoning benchmarks and various model architectures demonstrate that DMLR significantly improves reasoning and perception performance while maintaining high inference efficiency.
SensorLM: Learning the Language of Wearable Sensors
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:We present SensorLM, a family of sensor-language foundation models that enable wearable sensor data understanding with natural language. Despite its pervasive nature, aligning and interpreting sensor data with language remains challenging due to the lack of paired, richly annotated sensor-text descriptions in uncurated, real-world wearable data. We introduce a hierarchical caption generation pipeline designed to capture statistical, structural, and semantic information from sensor data. This approach enabled the curation of the largest sensor-language dataset to date, comprising over 59.7 million hours of data from more than 103,000 people. Furthermore, SensorLM extends prominent multimodal pretraining architectures (e.g., CLIP, CoCa) and recovers them as specific variants within a generic architecture. Extensive experiments on real-world tasks in human activity analysis and healthcare verify the superior performance of SensorLM over state-of-the-art in zero-shot recognition, few-shot learning, and cross-modal retrieval. SensorLM also demonstrates intriguing capabilities including scaling behaviors, label efficiency, sensor captioning, and zero-shot generalization to unseen tasks.
RADAR: Benchmarking Language Models on Imperfect Tabular Data
Jun 09, 2025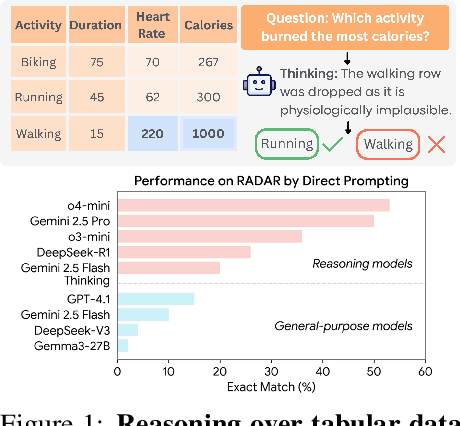
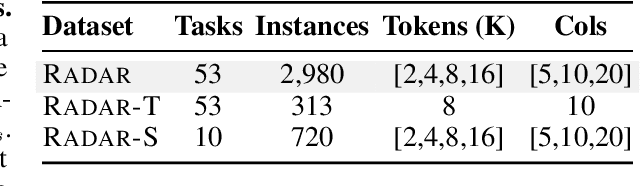
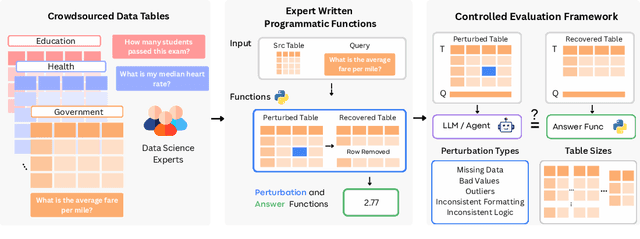
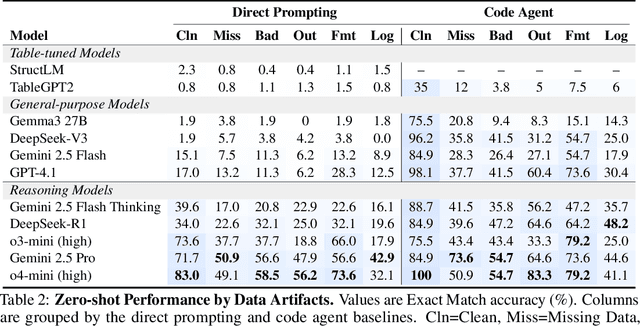
Abstract:Language models (LMs) are increasingly being deployed to perform autonomous data analyses. However, their data awareness -- the ability to recognize, reason over, and appropriately handle data artifacts such as missing values, outliers, and logical inconsistencies -- remains underexplored. These artifacts are especially common in real-world tabular data and, if mishandled, can significantly compromise the validity of analytical conclusions. To address this gap, we present RADAR, a benchmark for systematically evaluating data-aware reasoning on tabular data. We develop a framework to simulate data artifacts via programmatic perturbations to enable targeted evaluation of model behavior. RADAR comprises 2980 table query pairs, grounded in real-world data spanning 9 domains and 5 data artifact types. In addition to evaluating artifact handling, RADAR systematically varies table size to study how reasoning performance holds when increasing table size. Our evaluation reveals that, despite decent performance on tables without data artifacts, frontier models degrade significantly when data artifacts are introduced, exposing critical gaps in their capacity for robust, data-aware analysis. Designed to be flexible and extensible, RADAR supports diverse perturbation types and controllable table sizes, offering a valuable resource for advancing tabular reasoning.
LSM-2: Learning from Incomplete Wearable Sensor Data
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models, a cornerstone of recent advancements in machine learning, have predominantly thrived on complete and well-structured data. Wearable sensor data frequently suffers from significant missingness, posing a substantial challenge for self-supervised learning (SSL) models that typically assume complete data inputs. This paper introduces the second generation of Large Sensor Model (LSM-2) with Adaptive and Inherited Masking (AIM), a novel SSL approach that learns robust representations directly from incomplete data without requiring explicit imputation. AIM's core novelty lies in its use of learnable mask tokens to model both existing ("inherited") and artificially introduced missingness, enabling it to robustly handle fragmented real-world data during inference. Pre-trained on an extensive dataset of 40M hours of day-long multimodal sensor data, our LSM-2 with AIM achieves the best performance across a diverse range of tasks, including classification, regression and generative modeling. Furthermore, LSM-2 with AIM exhibits superior scaling performance, and critically, maintains high performance even under targeted missingness scenarios, reflecting clinically coherent patterns, such as the diagnostic value of nighttime biosignals for hypertension prediction. This makes AIM a more reliable choice for real-world wearable data applications.
Feature Extraction and Steering for Enhanced Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Language Models
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate the ability to solve reasoning and mathematical problems using the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) technique. Expanding CoT length, as seen in models such as DeepSeek-R1, significantly enhances this reasoning for complex problems, but requires costly and high-quality long CoT data and fine-tuning. This work, inspired by the deep thinking paradigm of DeepSeek-R1, utilizes a steering technique to enhance the reasoning ability of an LLM without external datasets. Our method first employs Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) to extract interpretable features from vanilla CoT. These features are then used to steer the LLM's internal states during generation. Recognizing that many LLMs do not have corresponding pre-trained SAEs, we further introduce a novel SAE-free steering algorithm, which directly computes steering directions from the residual activations of an LLM, obviating the need for an explicit SAE. Experimental results demonstrate that both our SAE-based and subsequent SAE-free steering algorithms significantly enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
Political-LLM: Large Language Models in Political Science
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have been widely adopted in political science tasks such as election prediction, sentiment analysis, policy impact assessment, and misinformation detection. Meanwhile, the need to systematically understand how LLMs can further revolutionize the field also becomes urgent. In this work, we--a multidisciplinary team of researchers spanning computer science and political science--present the first principled framework termed Political-LLM to advance the comprehensive understanding of integrating LLMs into computational political science. Specifically, we first introduce a fundamental taxonomy classifying the existing explorations into two perspectives: political science and computational methodologies. In particular, from the political science perspective, we highlight the role of LLMs in automating predictive and generative tasks, simulating behavior dynamics, and improving causal inference through tools like counterfactual generation; from a computational perspective, we introduce advancements in data preparation, fine-tuning, and evaluation methods for LLMs that are tailored to political contexts. We identify key challenges and future directions, emphasizing the development of domain-specific datasets, addressing issues of bias and fairness, incorporating human expertise, and redefining evaluation criteria to align with the unique requirements of computational political science. Political-LLM seeks to serve as a guidebook for researchers to foster an informed, ethical, and impactful use of Artificial Intelligence in political science. Our online resource is available at: http://political-llm.org/.
FedDTPT: Federated Discrete and Transferable Prompt Tuning for Black-Box Large Language Models
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced the field of natural language processing (NLP). By fine-tuning LLMs with data from specific scenarios, these foundation models can better adapt to various downstream tasks. However, the fine-tuning process poses privacy leakage risks, particularly in centralized data processing scenarios. To address user privacy concerns, federated learning (FL) has been introduced to mitigate the risks associated with centralized data collection from multiple sources. Nevertheless, the privacy of LLMs themselves is equally critical, as potential malicious attacks challenge their security, an issue that has received limited attention in current research. Consequently, establishing a trusted multi-party model fine-tuning environment is essential. Additionally, the local deployment of large LLMs incurs significant storage costs and high computational demands. To address these challenges, we propose for the first time a federated discrete and transferable prompt tuning, namely FedDTPT, for black-box large language models. In the client optimization phase, we adopt a token-level discrete prompt optimization method that leverages a feedback loop based on prediction accuracy to drive gradient-free prompt optimization through the MLM API. For server optimization, we employ an attention mechanism based on semantic similarity to filter all local prompt tokens, along with an embedding distance elbow detection and DBSCAN clustering strategy to enhance the filtering process. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to state-of-the-art methods, our approach achieves higher accuracy, reduced communication overhead, and robustness to non-iid data in a black-box setting. Moreover, the optimized prompts are transferable.
Meta-Learning for Speeding Up Large Model Inference in Decentralized Environments
Oct 28, 2024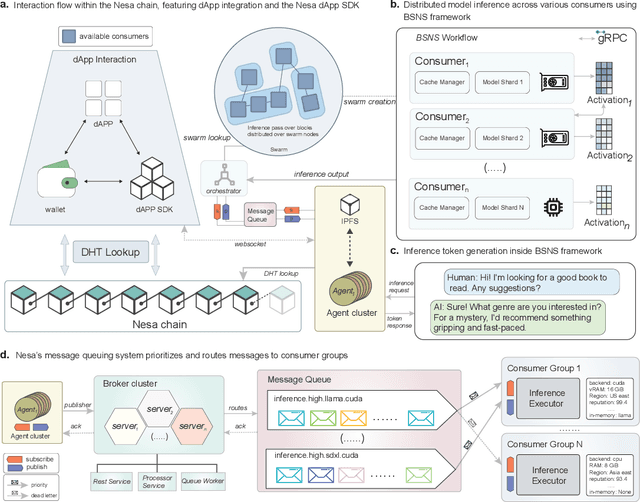
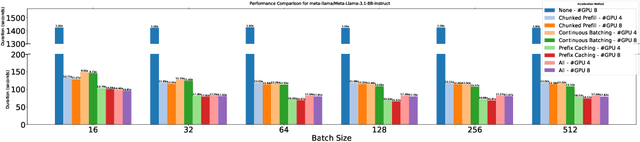
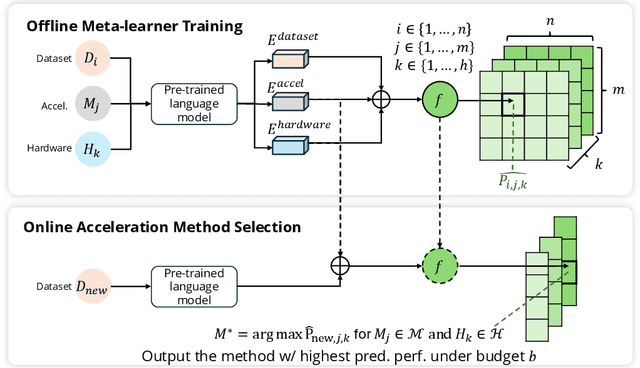
Abstract:The deployment of large-scale models, such as large language models (LLMs) and sophisticated image generation systems, incurs substantial costs due to their computational demands. To mitigate these costs and address challenges related to scalability and data security, there is a growing shift towards decentralized systems for deploying such models. In these decentralized environments, efficient inference acceleration becomes crucial to manage computational resources effectively and enhance system responsiveness. In this work, we address the challenge of selecting optimal acceleration methods in decentralized systems by introducing a meta-learning-based framework. This framework automates the selection process by learning from historical performance data of various acceleration techniques across different tasks. Unlike traditional methods that rely on random selection or expert intuition, our approach systematically identifies the best acceleration strategies based on the specific characteristics of each task. We demonstrate that our meta-learning framework not only streamlines the decision-making process but also consistently outperforms conventional methods in terms of efficiency and performance. Our results highlight the potential of meta-learning to revolutionize inference acceleration in decentralized AI systems, offering a path towards more democratic and economically feasible artificial intelligence solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge