Yizhu Jiao
Rethinking the Reranker: Boundary-Aware Evidence Selection for Robust Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems remain brittle under realistic retrieval noise, even when the required evidence appears in the top-K results. A key reason is that retrievers and rerankers optimize solely for relevance, often selecting either trivial, answer-revealing passages or evidence that lacks the critical information required to answer the question, without considering whether the evidence is suitable for the generator. We propose BAR-RAG, which reframes the reranker as a boundary-aware evidence selector that targets the generator's Goldilocks Zone -- evidence that is neither trivially easy nor fundamentally unanswerable for the generator, but is challenging yet sufficient for inference and thus provides the strongest learning signal. BAR-RAG trains the selector with reinforcement learning using generator feedback, and adopts a two-stage pipeline that fine-tunes the generator under the induced evidence distribution to mitigate the distribution mismatch between training and inference. Experiments on knowledge-intensive question answering benchmarks show that BAR-RAG consistently improves end-to-end performance under noisy retrieval, achieving an average gain of 10.3 percent over strong RAG and reranking baselines while substantially improving robustness. Code is publicly avaliable at https://github.com/GasolSun36/BAR-RAG.
Synergistic Weak-Strong Collaboration by Aligning Preferences
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Current Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in general reasoning yet struggle with specialized tasks requiring proprietary or domain-specific knowledge. Fine-tuning large models for every niche application is often infeasible due to black-box constraints and high computational overhead. To address this, we propose a collaborative framework that pairs a specialized weak model with a general strong model. The weak model, tailored to specific domains, produces initial drafts and background information, while the strong model leverages its advanced reasoning to refine these drafts, extending LLMs' capabilities to critical yet specialized tasks. To optimize this collaboration, we introduce a collaborative feedback to fine-tunes the weak model, which quantifies the influence of the weak model's contributions in the collaboration procedure and establishes preference pairs to guide preference tuning of the weak model. We validate our framework through experiments on three domains. We find that the collaboration significantly outperforms each model alone by leveraging complementary strengths. Moreover, aligning the weak model with the collaborative preference further enhances overall performance.
A Comprehensive Analysis on LLM-based Node Classification Algorithms
Feb 02, 2025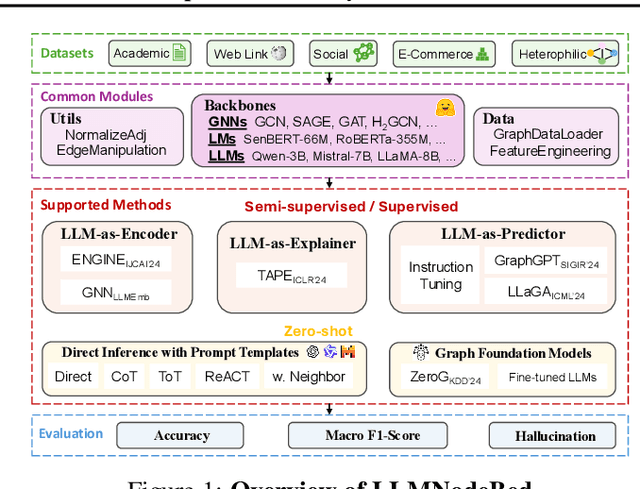
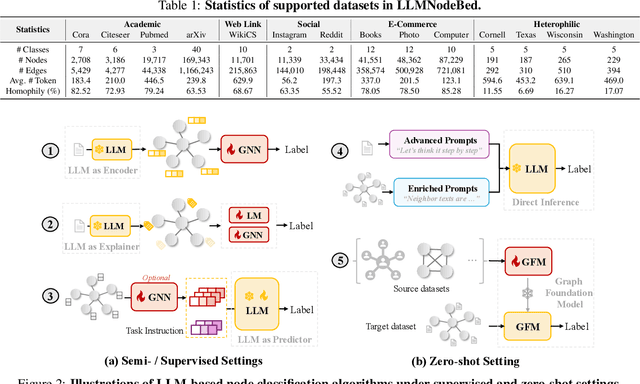
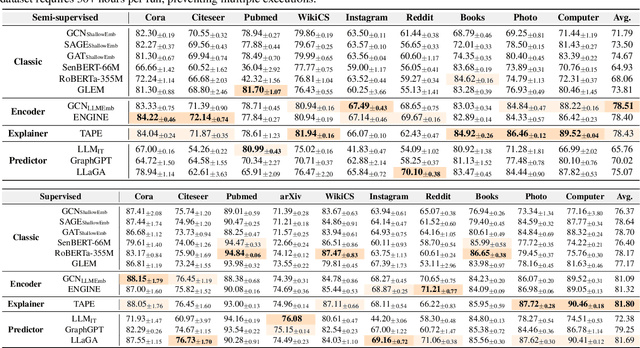
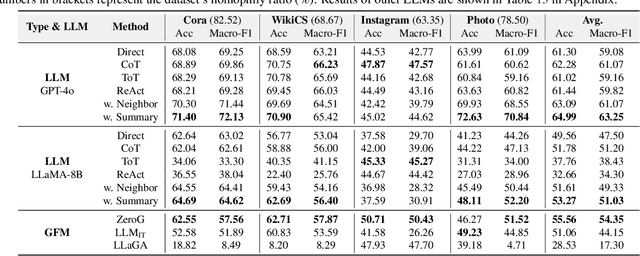
Abstract:Node classification is a fundamental task in graph analysis, with broad applications across various fields. Recent breakthroughs in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled LLM-based approaches for this task. Although many studies demonstrate the impressive performance of LLM-based methods, the lack of clear design guidelines may hinder their practical application. In this work, we aim to establish such guidelines through a fair and systematic comparison of these algorithms. As a first step, we developed LLMNodeBed, a comprehensive codebase and testbed for node classification using LLMs. It includes ten datasets, eight LLM-based algorithms, and three learning paradigms, and is designed for easy extension with new methods and datasets. Subsequently, we conducted extensive experiments, training and evaluating over 2,200 models, to determine the key settings (e.g., learning paradigms and homophily) and components (e.g., model size) that affect performance. Our findings uncover eight insights, e.g., (1) LLM-based methods can significantly outperform traditional methods in a semi-supervised setting, while the advantage is marginal in a supervised setting; (2) Graph Foundation Models can beat open-source LLMs but still fall short of strong LLMs like GPT-4o in a zero-shot setting. We hope that the release of LLMNodeBed, along with our insights, will facilitate reproducible research and inspire future studies in this field. Codes and datasets are released at \href{https://llmnodebed.github.io/}{https://llmnodebed.github.io/}.
Investigating Instruction Tuning Large Language Models on Graphs
Aug 10, 2024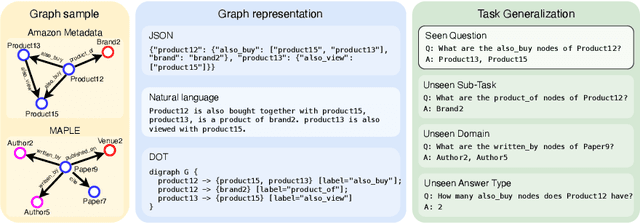
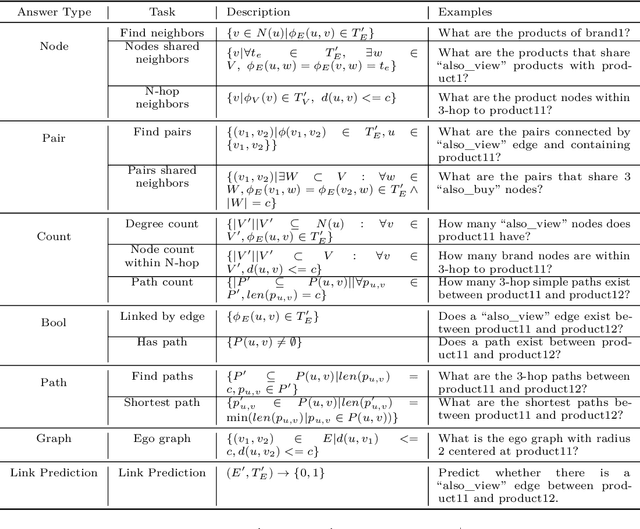

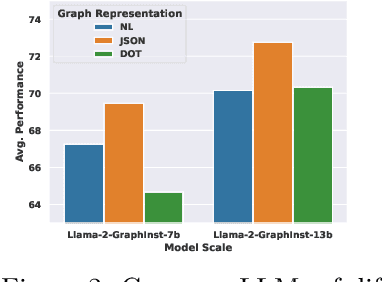
Abstract:Inspired by the recent advancements of Large Language Models (LLMs) in NLP tasks, there's growing interest in applying LLMs to graph-related tasks. This study delves into the capabilities of instruction-following LLMs for engaging with real-world graphs, aiming to offer empirical insights into how LLMs can effectively interact with graphs and generalize across graph tasks. We begin by constructing a dataset designed for instruction tuning, which comprises a diverse collection of 79 graph-related tasks from academic and e-commerce domains, featuring 44,240 training instances and 18,960 test samples. Utilizing this benchmark, our initial investigation focuses on identifying the optimal graph representation that serves as a conduit for LLMs to understand complex graph structures. Our findings indicate that JSON format for graph representation consistently outperforms natural language and code formats across various LLMs and graph types. Furthermore, we examine the key factors that influence the generalization abilities of instruction-tuned LLMs by evaluating their performance on both in-domain and out-of-domain graph tasks.
Unsupervised Episode Detection for Large-Scale News Events
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Episodic structures are inherently interpretable and adaptable to evolving large-scale key events. However, state-of-the-art automatic event detection methods overlook event episodes and, therefore, struggle with these crucial characteristics. This paper introduces a novel task, episode detection, aimed at identifying episodes from a news corpus containing key event articles. An episode describes a cohesive cluster of core entities (e.g., "protesters", "police") performing actions at a specific time and location. Furthermore, an episode is a significant part of a larger group of episodes under a particular key event. Automatically detecting episodes is challenging because, unlike key events and atomic actions, we cannot rely on explicit mentions of times and locations to distinguish between episodes or use semantic similarity to merge inconsistent episode co-references. To address these challenges, we introduce EpiMine, an unsupervised episode detection framework that (1) automatically identifies the most salient, key-event-relevant terms and segments, (2) determines candidate episodes in an article based on natural episodic partitions estimated through shifts in discriminative term combinations, and (3) refines and forms final episode clusters using large language model-based reasoning on the candidate episodes. We construct three diverse, real-world event datasets annotated at the episode level. EpiMine outperforms all baselines on these datasets by an average 59.2% increase across all metrics.
Establishing Knowledge Preference in Language Models
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:Language models are known to encode a great amount of factual knowledge through pretraining. However, such knowledge might be insufficient to cater to user requests, requiring the model to integrate external knowledge sources and adhere to user-provided specifications. When answering questions about ongoing events, the model should use recent news articles to update its response; when asked to provide recommendations, the model should prioritize user specifications over retrieved product reviews; when some facts are edited in the model, the updated facts should override all prior knowledge learned by the model even if they are conflicting. In all of the cases above, the model faces a decision between its own parametric knowledge, (retrieved) contextual knowledge, and user instruction knowledge. In this paper, we (1) unify such settings into the problem of knowledge preference and define a three-level preference hierarchy over these knowledge sources; (2) compile a collection of existing datasets IfQA, MQuAKE, and MRQA covering a combination of settings (with/without user specifications, with/without context documents) to systematically evaluate how well models obey the intended knowledge preference; and (3) propose a dataset synthesis method that composes diverse question-answer pairs with user assumptions and related context to directly fine-tune LMs for instilling the hierarchy of knowledge. We demonstrate that a 7B model, fine-tuned on only a few thousand examples automatically generated by our proposed method, effectively achieves superior performance (more than 18% improvement across all evaluation benchmarks) in adhering to the desired knowledge preference hierarchy.
MMLongBench-Doc: Benchmarking Long-context Document Understanding with Visualizations
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:Understanding documents with rich layouts and multi-modal components is a long-standing and practical task. Recent Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have made remarkable strides in various tasks, particularly in single-page document understanding (DU). However, their abilities on long-context DU remain an open problem. This work presents MMLongBench-Doc, a long-context, multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,062 expert-annotated questions. Distinct from previous datasets, it is constructed upon 130 lengthy PDF-formatted documents with an average of 49.4 pages and 20,971 textual tokens. Towards comprehensive evaluation, answers to these questions rely on pieces of evidence from (1) different sources (text, image, chart, table, and layout structure) and (2) various locations (i.e. page number). Moreover, 33.2% of the questions are cross-page questions requiring evidence across multiple pages. 22.8% of the questions are designed to be unanswerable for detecting potential hallucinations. Experiments on 14 LVLMs demonstrate that long-context DU greatly challenges current models. Notably, the best-performing model, GPT-4o, achieves an F1 score of only 42.7%, while the second-best, GPT-4V, scores 31.4%. Furthermore, 12 LVLMs (all except GPT-4o and GPT-4V) even present worse performance than their LLM counterparts which are fed with lossy-parsed OCR documents. These results validate the necessity of future research toward more capable long-context LVLMs. Project Page: https://mayubo2333.github.io/MMLongBench-Doc
Multi-LoRA Composition for Image Generation
Feb 26, 2024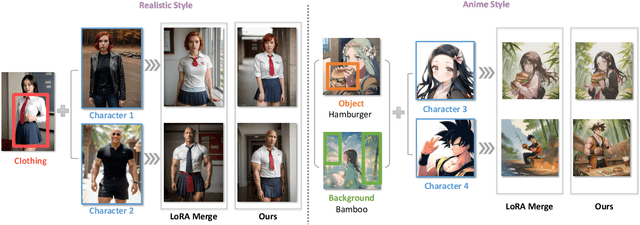
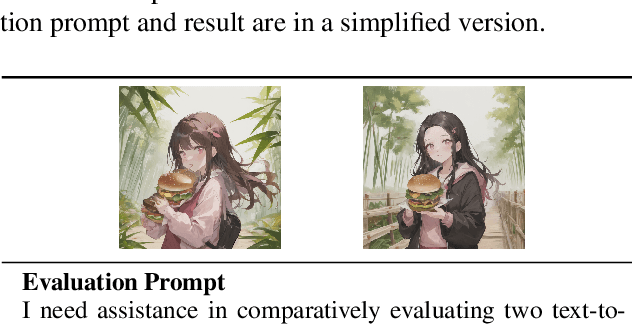
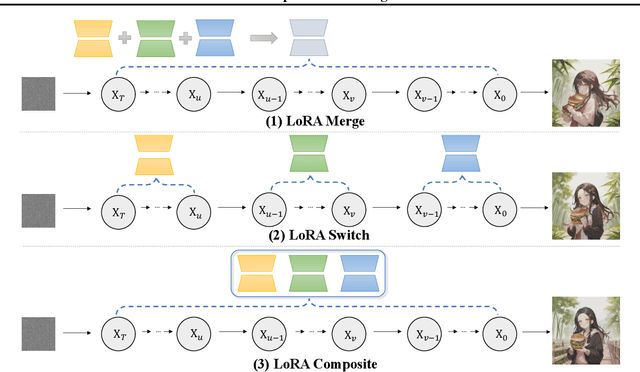
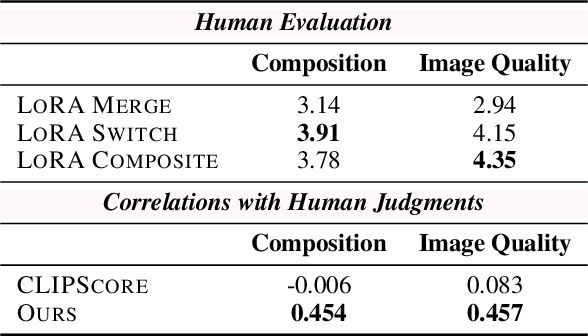
Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is extensively utilized in text-to-image models for the accurate rendition of specific elements like distinct characters or unique styles in generated images. Nonetheless, existing methods face challenges in effectively composing multiple LoRAs, especially as the number of LoRAs to be integrated grows, thus hindering the creation of complex imagery. In this paper, we study multi-LoRA composition through a decoding-centric perspective. We present two training-free methods: LoRA Switch, which alternates between different LoRAs at each denoising step, and LoRA Composite, which simultaneously incorporates all LoRAs to guide more cohesive image synthesis. To evaluate the proposed approaches, we establish ComposLoRA, a new comprehensive testbed as part of this research. It features a diverse range of LoRA categories with 480 composition sets. Utilizing an evaluation framework based on GPT-4V, our findings demonstrate a clear improvement in performance with our methods over the prevalent baseline, particularly evident when increasing the number of LoRAs in a composition.
Instruct and Extract: Instruction Tuning for On-Demand Information Extraction
Oct 24, 2023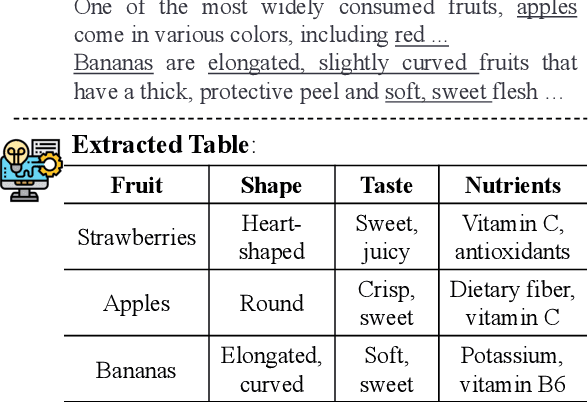
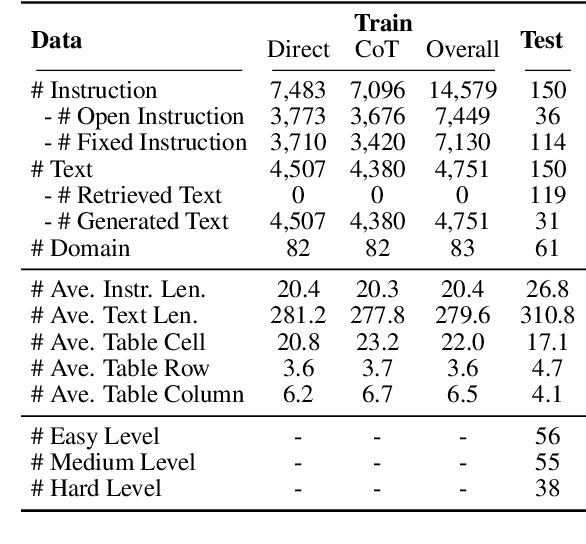
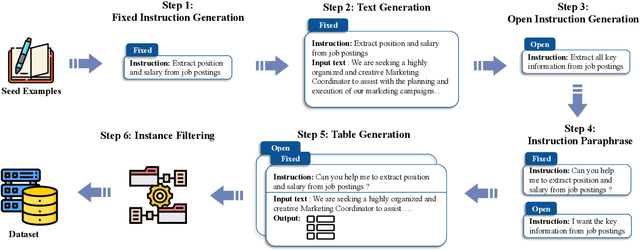
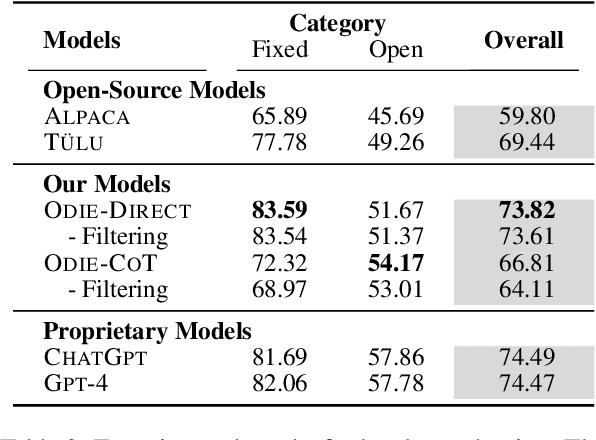
Abstract:Large language models with instruction-following capabilities open the door to a wider group of users. However, when it comes to information extraction - a classic task in natural language processing - most task-specific systems cannot align well with long-tail ad hoc extraction use cases for non-expert users. To address this, we propose a novel paradigm, termed On-Demand Information Extraction, to fulfill the personalized demands of real-world users. Our task aims to follow the instructions to extract the desired content from the associated text and present it in a structured tabular format. The table headers can either be user-specified or inferred contextually by the model. To facilitate research in this emerging area, we present a benchmark named InstructIE, inclusive of both automatically generated training data, as well as the human-annotated test set. Building on InstructIE, we further develop an On-Demand Information Extractor, ODIE. Comprehensive evaluations on our benchmark reveal that ODIE substantially outperforms the existing open-source models of similar size. Our code and dataset are released on https://github.com/yzjiao/On-Demand-IE.
The Shifted and The Overlooked: A Task-oriented Investigation of User-GPT Interactions
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:Recent progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) has produced models that exhibit remarkable performance across a variety of NLP tasks. However, it remains unclear whether the existing focus of NLP research accurately captures the genuine requirements of human users. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the divergence between current NLP research and the needs of real-world NLP applications via a large-scale collection of user-GPT conversations. We analyze a large-scale collection of real user queries to GPT. We compare these queries against existing NLP benchmark tasks and identify a significant gap between the tasks that users frequently request from LLMs and the tasks that are commonly studied in academic research. For example, we find that tasks such as ``design'' and ``planning'' are prevalent in user interactions but are largely neglected or different from traditional NLP benchmarks. We investigate these overlooked tasks, dissect the practical challenges they pose, and provide insights toward a roadmap to make LLMs better aligned with user needs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge