Sha Li
Virginia Tech
RAG without Forgetting: Continual Query-Infused Key Memory
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems commonly improve robustness via query-time adaptations such as query expansion and iterative retrieval. While effective, these approaches are inherently stateless: adaptations are recomputed for each query and discarded thereafter, precluding cumulative learning and repeatedly incurring inference-time cost. Index-side approaches like key expansion introduce persistence but rely on offline preprocessing or heuristic updates that are weakly aligned with downstream task utility, leading to semantic drift and noise accumulation. We propose Evolving Retrieval Memory (ERM), a training-free framework that transforms transient query-time gains into persistent retrieval improvements. ERM updates the retrieval index through correctness-gated feedback, selectively attributes atomic expansion signals to the document keys they benefit, and progressively evolves keys via stable, norm-bounded updates. We show that query and key expansion are theoretically equivalent under standard similarity functions and prove convergence of ERM's selective updates, amortizing optimal query expansion into a stable index with zero inference-time overhead. Experiments on BEIR and BRIGHT across 13 domains demonstrate consistent gains in retrieval and generation, particularly on reasoning-intensive tasks, at native retrieval speed.
Agentic Conversational Search with Contextualized Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become a popular interface for human-AI interaction, supporting information seeking and task assistance through natural, multi-turn dialogue. To respond to users within multi-turn dialogues, the context-dependent user intent evolves across interactions, requiring contextual interpretation, query reformulation, and dynamic coordination between retrieval and generation. Existing studies usually follow static rewrite, retrieve, and generate pipelines, which optimize different procedures separately and overlook the mixed-initiative action optimization simultaneously. Although the recent developments in deep search agents demonstrate the effectiveness in jointly optimizing retrieval and generation via reasoning, these approaches focus on single-turn scenarios, which might lack the ability to handle multi-turn interactions. We introduce a conversational agent that interleaves search and reasoning across turns, enabling exploratory and adaptive behaviors learned through reinforcement learning (RL) training with tailored rewards towards evolving user goals. The experimental results across four widely used conversational benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods by surpassing several existing strong baselines.
How Do Large Language Models Learn Concepts During Continual Pre-Training?
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Human beings primarily understand the world through concepts (e.g., dog), abstract mental representations that structure perception, reasoning, and learning. However, how large language models (LLMs) acquire, retain, and forget such concepts during continual pretraining remains poorly understood. In this work, we study how individual concepts are acquired and forgotten, as well as how multiple concepts interact through interference and synergy. We link these behavioral dynamics to LLMs' internal Concept Circuits, computational subgraphs associated with specific concepts, and incorporate Graph Metrics to characterize circuit structure. Our analysis reveals: (1) LLMs concept circuits provide a non-trivial, statistically significant signal of concept learning and forgetting; (2) Concept circuits exhibit a stage-wise temporal pattern during continual pretraining, with an early increase followed by gradual decrease and stabilization; (3) concepts with larger learning gains tend to exhibit greater forgetting under subsequent training; (4) semantically similar concepts induce stronger interference than weakly related ones; (5) conceptual knowledge differs in their transferability, with some significantly facilitating the learning of others. Together, our findings offer a circuit-level view of concept learning dynamics and inform the design of more interpretable and robust concept-aware training strategies for LLMs.
Exploring LLMs for Scientific Information Extraction Using The SciEx Framework
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly touted as powerful tools for automating scientific information extraction. However, existing methods and tools often struggle with the realities of scientific literature: long-context documents, multi-modal content, and reconciling varied and inconsistent fine-grained information across multiple publications into standardized formats. These challenges are further compounded when the desired data schema or extraction ontology changes rapidly, making it difficult to re-architect or fine-tune existing systems. We present SciEx, a modular and composable framework that decouples key components including PDF parsing, multi-modal retrieval, extraction, and aggregation. This design streamlines on-demand data extraction while enabling extensibility and flexible integration of new models, prompting strategies, and reasoning mechanisms. We evaluate SciEx on datasets spanning three scientific topics for its ability to extract fine-grained information accurately and consistently. Our findings provide practical insights into both the strengths and limitations of current LLM-based pipelines.
WebCoach: Self-Evolving Web Agents with Cross-Session Memory Guidance
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Multimodal LLM-powered agents have recently demonstrated impressive capabilities in web navigation, enabling agents to complete complex browsing tasks across diverse domains. However, current agents struggle with repetitive errors and lack the ability to learn from past experiences across sessions, limiting their long-term robustness and sample efficiency. We introduce WebCoach, a model-agnostic self-evolving framework that equips web browsing agents with persistent cross-session memory, enabling improved long-term planning, reflection, and continual learning without retraining. WebCoach consists of three key components: (1) a WebCondenser, which standardizes raw navigation logs into concise summaries; (2) an External Memory Store, which organizes complete trajectories as episodic experiences; and (3) a Coach, which retrieves relevant experiences based on similarity and recency, and decides whether to inject task-specific advice into the agent via runtime hooks. This design empowers web agents to access long-term memory beyond their native context window, improving robustness in complex browsing tasks. Moreover, WebCoach achieves self-evolution by continuously curating episodic memory from new navigation trajectories, enabling agents to improve over time without retraining. Evaluations on the WebVoyager benchmark demonstrate that WebCoach consistently improves the performance of browser-use agents across three different LLM backbones. With a 38B model, it increases task success rates from 47% to 61% while reducing or maintaining the average number of steps. Notably, smaller base models with WebCoach achieve performance comparable to the same web agent using GPT-4o.
FanChuan: A Multilingual and Graph-Structured Benchmark For Parody Detection and Analysis
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Parody is an emerging phenomenon on social media, where individuals imitate a role or position opposite to their own, often for humor, provocation, or controversy. Detecting and analyzing parody can be challenging and is often reliant on context, yet it plays a crucial role in understanding cultural values, promoting subcultures, and enhancing self-expression. However, the study of parody is hindered by limited available data and deficient diversity in current datasets. To bridge this gap, we built seven parody datasets from both English and Chinese corpora, with 14,755 annotated users and 21,210 annotated comments in total. To provide sufficient context information, we also collect replies and construct user-interaction graphs to provide richer contextual information, which is lacking in existing datasets. With these datasets, we test traditional methods and Large Language Models (LLMs) on three key tasks: (1) parody detection, (2) comment sentiment analysis with parody, and (3) user sentiment analysis with parody. Our extensive experiments reveal that parody-related tasks still remain challenging for all models, and contextual information plays a critical role. Interestingly, we find that, in certain scenarios, traditional sentence embedding methods combined with simple classifiers can outperform advanced LLMs, i.e. DeepSeek-R1 and GPT-o3, highlighting parody as a significant challenge for LLMs.
The Law of Knowledge Overshadowing: Towards Understanding, Predicting, and Preventing LLM Hallucination
Feb 22, 2025



Abstract:Hallucination is a persistent challenge in large language models (LLMs), where even with rigorous quality control, models often generate distorted facts. This paradox, in which error generation continues despite high-quality training data, calls for a deeper understanding of the underlying LLM mechanisms. To address it, we propose a novel concept: knowledge overshadowing, where model's dominant knowledge can obscure less prominent knowledge during text generation, causing the model to fabricate inaccurate details. Building on this idea, we introduce a novel framework to quantify factual hallucinations by modeling knowledge overshadowing. Central to our approach is the log-linear law, which predicts that the rate of factual hallucination increases linearly with the logarithmic scale of (1) Knowledge Popularity, (2) Knowledge Length, and (3) Model Size. The law provides a means to preemptively quantify hallucinations, offering foresight into their occurrence even before model training or inference. Built on overshadowing effect, we propose a new decoding strategy CoDa, to mitigate hallucinations, which notably enhance model factuality on Overshadow (27.9%), MemoTrap (13.1%) and NQ-Swap (18.3%). Our findings not only deepen understandings of the underlying mechanisms behind hallucinations but also provide actionable insights for developing more predictable and controllable language models.
Oreo: A Plug-in Context Reconstructor to Enhance Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Despite the remarkable capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in various NLP tasks, they remain vulnerable to hallucinations due to their limited parametric knowledge and lack of domain-specific expertise. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses this challenge by incorporating external document retrieval to augment the knowledge base of LLMs. In this approach, RAG retrieves document chunks from an external corpus in response to a query, which are then used as context for the downstream language model to generate an answer. However, these retrieved knowledge sources often include irrelevant or erroneous information, undermining the effectiveness of RAG in downstream tasks. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a compact, efficient, and pluggable module designed to refine external knowledge sources before feeding them to the generator. The module reconstructs retrieved content by extracting the most relevant and supportive information and reorganising it into a concise, query-specific format. Through a three-stage training paradigm - comprising supervised fine-tuning, contrastive multi-task learning, and reinforcement learning-based alignment - it prioritises critical knowledge and aligns it with the generator's preferences. This method enables LLMs to produce outputs that are more accurate, reliable, and contextually appropriate.
SyncMind: Measuring Agent Out-of-Sync Recovery in Collaborative Software Engineering
Feb 10, 2025
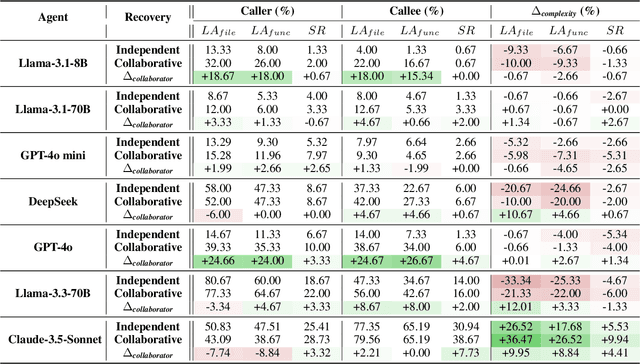


Abstract:Software engineering (SE) is increasingly collaborative, with developers working together on shared complex codebases. Effective collaboration in shared environments requires participants -- whether humans or AI agents -- to stay on the same page as their environment evolves. When a collaborator's understanding diverges from the current state -- what we term the out-of-sync challenge -- the collaborator's actions may fail, leading to integration issues. In this work, we introduce SyncMind, a framework that systematically defines the out-of-sync problem faced by large language model (LLM) agents in collaborative software engineering (CSE). Based on SyncMind, we create SyncBench, a benchmark featuring 24,332 instances of agent out-of-sync scenarios in real-world CSE derived from 21 popular GitHub repositories with executable verification tests. Experiments on SyncBench uncover critical insights into existing LLM agents' capabilities and limitations. Besides substantial performance gaps among agents (from Llama-3.1 agent <= 3.33% to Claude-3.5-Sonnet >= 28.18%), their consistently low collaboration willingness (<= 4.86%) suggests fundamental limitations of existing LLM in CSE. However, when collaboration occurs, it positively correlates with out-of-sync recovery success. Minimal performance differences in agents' resource-aware out-of-sync recoveries further reveal their significant lack of resource awareness and adaptability, shedding light on future resource-efficient collaborative systems. Code and data are openly available on our project website: https://xhguo7.github.io/SyncMind/.
Schema-Guided Culture-Aware Complex Event Simulation with Multi-Agent Role-Play
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:Complex news events, such as natural disasters and socio-political conflicts, require swift responses from the government and society. Relying on historical events to project the future is insufficient as such events are sparse and do not cover all possible conditions and nuanced situations. Simulation of these complex events can help better prepare and reduce the negative impact. We develop a controllable complex news event simulator guided by both the event schema representing domain knowledge about the scenario and user-provided assumptions representing case-specific conditions. As event dynamics depend on the fine-grained social and cultural context, we further introduce a geo-diverse commonsense and cultural norm-aware knowledge enhancement component. To enhance the coherence of the simulation, apart from the global timeline of events, we take an agent-based approach to simulate the individual character states, plans, and actions. By incorporating the schema and cultural norms, our generated simulations achieve much higher coherence and appropriateness and are received favorably by participants from a humanitarian assistance organization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge