Zixuan Huang
Heterogeneous Agent Collaborative Reinforcement Learning
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:We introduce Heterogeneous Agent Collaborative Reinforcement Learning (HACRL), a new learning paradigm that addresses the inefficiencies of isolated on-policy optimization. HACRL enables collaborative optimization with independent execution: heterogeneous agents share verified rollouts during training to mutually improve, while operating independently at inference time. Unlike LLM-based multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), HACRL does not require coordinated deployment, and unlike on-/off-policy distillation, it enables bidirectional mutual learning among heterogeneous agents rather than one-directional teacher-to-student transfer. Building on this paradigm, we propose HACPO, a collaborative RL algorithm that enables principled rollout sharing to maximize sample utilization and cross-agent knowledge transfer. To mitigate capability discrepancies and policy distribution shifts, HACPO introduces four tailored mechanisms with theoretical guarantees on unbiased advantage estimation and optimization correctness. Extensive experiments across diverse heterogeneous model combinations and reasoning benchmarks show that HACPO consistently improves all participating agents, outperforming GSPO by an average of 3.3\% while using only half the rollout cost.
Vinedresser3D: Agentic Text-guided 3D Editing
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Text-guided 3D editing aims to modify existing 3D assets using natural-language instructions. Current methods struggle to jointly understand complex prompts, automatically localize edits in 3D, and preserve unedited content. We introduce Vinedresser3D, an agentic framework for high-quality text-guided 3D editing that operates directly in the latent space of a native 3D generative model. Given a 3D asset and an editing prompt, Vinedresser3D uses a multimodal large language model to infer rich descriptions of the original asset, identify the edit region and edit type (addition, modification, deletion), and generate decomposed structural and appearance-level text guidance. The agent then selects an informative view and applies an image editing model to obtain visual guidance. Finally, an inversion-based rectified-flow inpainting pipeline with an interleaved sampling module performs editing in the 3D latent space, enforcing prompt alignment while maintaining 3D coherence and unedited regions. Experiments on diverse 3D edits demonstrate that Vinedresser3D outperforms prior baselines in both automatic metrics and human preference studies, while enabling precise, coherent, and mask-free 3D editing.
UniARM: Towards a Unified Autoregressive Reward Model for Multi-Objective Test-Time Alignment
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Multi-objective alignment aims to align LLM responses with multiple human preference objectives. Among existing methods, guiding the generation of frozen LLMs through autoregressive reward models (ARMs) to accomplish multi-objective test-time alignment is a low-cost solution. However, these methods typically rely on independent parameters for each preference objective, either by training ARMs independently across preference dimensions, which neglects interactions among preference features, or by training a single ARM with separate feature extraction modules for each preference, which can cause feature entanglement. Both strategies can result in misalignment between generated outputs and user preferences. To address this limitation, we propose Preference-Modulated \& Shared Low-Rank Adaptation (MoSLoRA) for ARM training, which first extracts shared features via a preference-agnostic module and then applies affine transformations to shared features via a preference modulation module conditioned on mixed preference vectors. This design mitigates feature entanglement and enables precise control over preference trade-offs during inference. Building on this, we introduce the Unified Autoregressive Reward Model (UniARM), a novel framework for multi-objective test-time alignment. UniARM jointly models all preference dimensions in a single parameter space, eliminating the need for independent parameters for each preference objective. es on larger-scale LLMs, enhancing its practical usability.
Does Your Reasoning Model Implicitly Know When to Stop Thinking?
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in large reasoning models (LRMs) have greatly improved their capabilities on complex reasoning tasks through Long Chains of Thought (CoTs). However, this approach often results in substantial redundancy, impairing computational efficiency and causing significant delays in real-time applications. Recent studies show that longer reasoning chains are frequently uncorrelated with correctness and can even be detrimental to accuracy. In a further in-depth analysis of this phenomenon, we surprisingly uncover and empirically verify that LRMs implicitly know the appropriate time to stop thinking, while this capability is obscured by current sampling paradigms. Motivated by this, we introduce SAGE (Self-Aware Guided Efficient Reasoning), a novel sampling paradigm that unleashes this efficient reasoning potential. Furthermore, integrating SAGE as mixed sampling into group-based reinforcement learning (SAGE-RL) enables SAGE-RL to effectively incorporate SAGE-discovered efficient reasoning patterns into standard pass@1 inference, markedly enhancing both the reasoning accuracy and efficiency of LRMs across multiple challenging mathematical benchmarks.
Weak-Driven Learning: How Weak Agents make Strong Agents Stronger
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:As post-training optimization becomes central to improving large language models, we observe a persistent saturation bottleneck: once models grow highly confident, further training yields diminishing returns. While existing methods continue to reinforce target predictions, we find that informative supervision signals remain latent in models' own historical weak states. Motivated by this observation, we propose WMSS (Weak Agents Can Make Strong Agents Stronger), a post-training paradigm that leverages weak checkpoints to guide continued optimization. By identifying recoverable learning gaps via entropy dynamics and reinforcing them through compensatory learning, WMSS enables strong agents to improve beyond conventional post-training saturation. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and code generation datasets show that agents trained with our approach achieve effective performance improvements, while incurring zero additional inference cost.
Real-Time Aligned Reward Model beyond Semantics
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is a pivotal technique for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences, yet it is susceptible to reward overoptimization, in which policy models overfit to the reward model, exploit spurious reward patterns instead of faithfully capturing human intent. Prior mitigations primarily relies on surface semantic information and fails to efficiently address the misalignment between the reward model (RM) and the policy model caused by continuous policy distribution shifts. This inevitably leads to an increasing reward discrepancy, exacerbating reward overoptimization. To address these limitations, we introduce R2M (Real-Time Aligned Reward Model), a novel lightweight RLHF framework. R2M goes beyond vanilla reward models that solely depend on the semantic representations of a pretrained LLM. Instead, it leverages the evolving hidden states of the policy (namely policy feedback) to align with the real-time distribution shift of the policy during the RL process. This work points to a promising new direction for improving the performance of reward models through real-time utilization of feedback from policy models.
Codebook Design for Limited Feedback in Near-Field XL-MIMO Systems
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we study efficient codebook design for limited feedback in extremely large-scale multiple-input-multiple-output (XL-MIMO) frequency division duplexing (FDD) systems. It is worth noting that existing codebook designs for XL-MIMO, such as polar-domain codebook, have not well taken into account user (location) distribution in practice, thereby incurring excessive feedback overhead. To address this issue, we propose in this paper a novel and efficient feedback codebook tailored to user distribution. To this end, we first consider a typical scenario where users are uniformly distributed within a specific polar-region, based on which a sum-rate maximization problem is formulated to jointly optimize angle-range samples and bit allocation among angle/range feedback. This problem is challenging to solve due to the lack of a closed-form expression for the received power in terms of angle and range samples. By leveraging a Voronoi partitioning approach, we show that uniform angle sampling is optimal for received power maximization. For more challenging range sampling design, we obtain a tight lower-bound on the received power and show that geometric sampling, where the ratio between adjacent samples is constant, can maximize the lower bound and thus serves as a high-quality suboptimal solution. We then extend the proposed framework to accommodate more general non-uniform user distribution via an alternating sampling method. Furthermore, theoretical analysis reveals that as the array size increases, the optimal allocation of feedback bits increasingly favors range samples at the expense of angle samples. Finally, numerical results validate the superior rate performance and robustness of the proposed codebook design under various system setups, achieving significant gains over benchmark schemes, including the widely used polar-domain codebook.
Semantic Radio Access Networks: Architecture, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Radio Access Network (RAN) is a bridge between user devices and the core network in mobile communication systems, responsible for the transmission and reception of wireless signals and air interface management. In recent years, Semantic Communication (SemCom) has represented a transformative communication paradigm that prioritizes meaning-level transmission over conventional bit-level delivery, thus providing improved spectrum efficiency, anti-interference ability in complex environments, flexible resource allocation, and enhanced user experience for RAN. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive reviews on the integration of SemCom into RAN. Motivated by this, we systematically explore recent advancements in Semantic RAN (SemRAN). We begin by introducing the fundamentals of RAN and SemCom, identifying the limitations of conventional RAN, and outlining the overall architecture of SemRAN. Subsequently, we review representative techniques of SemRAN across physical layer, data link layer, network layer, and security plane. Furthermore, we envision future services and applications enabled by SemRAN, alongside its current standardization progress. Finally, we conclude by identifying critical research challenges and outlining forward-looking directions to guide subsequent investigations in this burgeoning field.
How Much 3D Do Video Foundation Models Encode?
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Videos are continuous 2D projections of 3D worlds. After training on large video data, will global 3D understanding naturally emerge? We study this by quantifying the 3D understanding of existing Video Foundation Models (VidFMs) pretrained on vast video data. We propose the first model-agnostic framework that measures the 3D awareness of various VidFMs by estimating multiple 3D properties from their features via shallow read-outs. Our study presents meaningful findings regarding the 3D awareness of VidFMs on multiple axes. In particular, we show that state-of-the-art video generation models exhibit a strong understanding of 3D objects and scenes, despite not being trained on any 3D data. Such understanding can even surpass that of large expert models specifically trained for 3D tasks. Our findings, together with the 3D benchmarking of major VidFMs, provide valuable observations for building scalable 3D models.
Design of A Low-Latency and Parallelizable SVD Dataflow Architecture on FPGA
Nov 18, 2025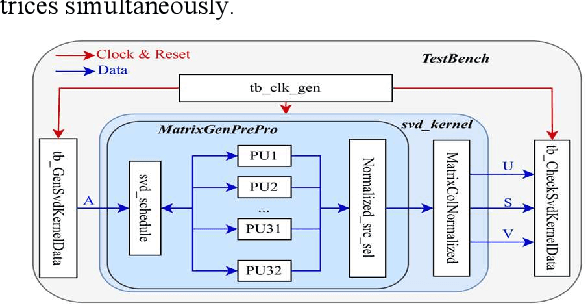
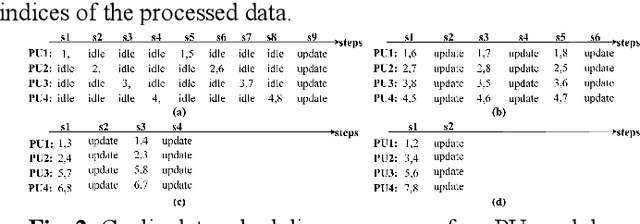
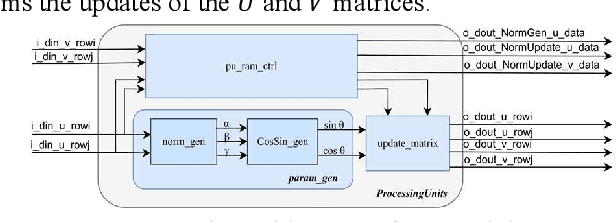
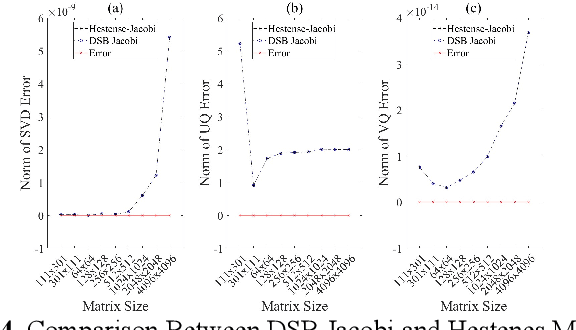
Abstract:Singular value decomposition (SVD) is widely used for dimensionality reduction and noise suppression, and it plays a pivotal role in numerous scientific and engineering applications. As the dimensions of the matrix grow rapidly, the computational cost increases significantly, posing a serious challenge to the efficiency of data analysis and signal processing systems,especially in time-sensitive scenarios with large-scale datasets. Although various dedicated hardware architectures have been proposed to accelerate the computation of intensive SVD, many of these designs suffer from limited scalability and high consumption of on-chip memory resources. Moreover, they typically overlook the computational and data transfer challenges associated with SVD, enabling them unsuitable for real-time processing of large-scale data stream matrices in embedded systems. In this express, we propose a Data Stream-Based SVD processing algorithm (DSB Jacobi), which significantly reduces on-chip BRAM usage while improving computational speed, offering a practical solution for real-time SVD computation of large-scale data streams. Compared with previous works, our experimental results indicate that the proposed method reduces on-chip RAM consumption by 41.5 percent and improves computational efficiency by 23 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge