Zhichao Hu
refer to the report for detailed contributions
TAGRPO: Boosting GRPO on Image-to-Video Generation with Direct Trajectory Alignment
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the efficacy of integrating Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) into flow matching models, particularly for text-to-image and text-to-video generation. However, we find that directly applying these techniques to image-to-video (I2V) models often fails to yield consistent reward improvements. To address this limitation, we present TAGRPO, a robust post-training framework for I2V models inspired by contrastive learning. Our approach is grounded in the observation that rollout videos generated from identical initial noise provide superior guidance for optimization. Leveraging this insight, we propose a novel GRPO loss applied to intermediate latents, encouraging direct alignment with high-reward trajectories while maximizing distance from low-reward counterparts. Furthermore, we introduce a memory bank for rollout videos to enhance diversity and reduce computational overhead. Despite its simplicity, TAGRPO achieves significant improvements over DanceGRPO in I2V generation.
UltraLogic: Enhancing LLM Reasoning through Large-Scale Data Synthesis and Bipolar Float Reward
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in natural language processing , complex general-purpose reasoning requiring multi-step logic, planning, and verification remains a critical bottleneck. Although Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has succeeded in specific domains , the field lacks large-scale, high-quality, and difficulty-calibrated data for general reasoning. To address this, we propose UltraLogic, a framework that decouples the logical core of a problem from its natural language expression through a Code-based Solving methodology to automate high-quality data production. The framework comprises hundreds of unique task types and an automated calibration pipeline across ten difficulty levels. Furthermore, to mitigate binary reward sparsity and the Non-negative Reward Trap, we introduce the Bipolar Float Reward (BFR) mechanism, utilizing graded penalties to effectively distinguish perfect responses from those with logical flaws. Our experiments demonstrate that task diversity is the primary driver for reasoning enhancement , and that BFR, combined with a difficulty matching strategy, significantly improves training efficiency, guiding models toward global logical optima.
EternalMath: A Living Benchmark of Frontier Mathematics that Evolves with Human Discovery
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Current evaluations of mathematical reasoning in large language models (LLMs) are dominated by static benchmarks, either derived from competition-style problems or curated through costly expert effort, resulting in limited coverage of research-level mathematics and rapid performance saturation. We propose a fully automated, theorem-grounded pipeline for evaluating frontier mathematical reasoning, which directly transforms recent peer-reviewed mathematical literature into executable and verifiable reasoning tasks. The pipeline identifies constructive or quantitative results, instantiates them into parameterized problem templates, and generates deterministic solutions through execution-based verification, enabling scalable, reproducible, and continuously updatable evaluation without reliance on large-scale expert authoring. By design, this approach supports temporal extensibility, intrinsic correctness checking, and domain-specific customization across mathematical subfields. Applying this pipeline yields \textbf{EternalMath}, an evolving evaluation suite derived from contemporary research papers. Experiments with state-of-the-art LLMs reveal substantial performance gaps, indicating that mathematical reasoning at the research frontier remains far from saturated and underscoring the need for evaluation methodologies that evolve in step with human mathematical discovery.
HY-Motion 1.0: Scaling Flow Matching Models for Text-To-Motion Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We present HY-Motion 1.0, a series of state-of-the-art, large-scale, motion generation models capable of generating 3D human motions from textual descriptions. HY-Motion 1.0 represents the first successful attempt to scale up Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based flow matching models to the billion-parameter scale within the motion generation domain, delivering instruction-following capabilities that significantly outperform current open-source benchmarks. Uniquely, we introduce a comprehensive, full-stage training paradigm -- including large-scale pretraining on over 3,000 hours of motion data, high-quality fine-tuning on 400 hours of curated data, and reinforcement learning from both human feedback and reward models -- to ensure precise alignment with the text instruction and high motion quality. This framework is supported by our meticulous data processing pipeline, which performs rigorous motion cleaning and captioning. Consequently, our model achieves the most extensive coverage, spanning over 200 motion categories across 6 major classes. We release HY-Motion 1.0 to the open-source community to foster future research and accelerate the transition of 3D human motion generation models towards commercial maturity.
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
FanChuan: A Multilingual and Graph-Structured Benchmark For Parody Detection and Analysis
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Parody is an emerging phenomenon on social media, where individuals imitate a role or position opposite to their own, often for humor, provocation, or controversy. Detecting and analyzing parody can be challenging and is often reliant on context, yet it plays a crucial role in understanding cultural values, promoting subcultures, and enhancing self-expression. However, the study of parody is hindered by limited available data and deficient diversity in current datasets. To bridge this gap, we built seven parody datasets from both English and Chinese corpora, with 14,755 annotated users and 21,210 annotated comments in total. To provide sufficient context information, we also collect replies and construct user-interaction graphs to provide richer contextual information, which is lacking in existing datasets. With these datasets, we test traditional methods and Large Language Models (LLMs) on three key tasks: (1) parody detection, (2) comment sentiment analysis with parody, and (3) user sentiment analysis with parody. Our extensive experiments reveal that parody-related tasks still remain challenging for all models, and contextual information plays a critical role. Interestingly, we find that, in certain scenarios, traditional sentence embedding methods combined with simple classifiers can outperform advanced LLMs, i.e. DeepSeek-R1 and GPT-o3, highlighting parody as a significant challenge for LLMs.
Hunyuan3D 2.0: Scaling Diffusion Models for High Resolution Textured 3D Assets Generation
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:We present Hunyuan3D 2.0, an advanced large-scale 3D synthesis system for generating high-resolution textured 3D assets. This system includes two foundation components: a large-scale shape generation model -- Hunyuan3D-DiT, and a large-scale texture synthesis model -- Hunyuan3D-Paint. The shape generative model, built on a scalable flow-based diffusion transformer, aims to create geometry that properly aligns with a given condition image, laying a solid foundation for downstream applications. The texture synthesis model, benefiting from strong geometric and diffusion priors, produces high-resolution and vibrant texture maps for either generated or hand-crafted meshes. Furthermore, we build Hunyuan3D-Studio -- a versatile, user-friendly production platform that simplifies the re-creation process of 3D assets. It allows both professional and amateur users to manipulate or even animate their meshes efficiently. We systematically evaluate our models, showing that Hunyuan3D 2.0 outperforms previous state-of-the-art models, including the open-source models and closed-source models in geometry details, condition alignment, texture quality, and etc. Hunyuan3D 2.0 is publicly released in order to fill the gaps in the open-source 3D community for large-scale foundation generative models. The code and pre-trained weights of our models are available at: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan3D-2
Hunyuan-Large: An Open-Source MoE Model with 52 Billion Activated Parameters by Tencent
Nov 05, 2024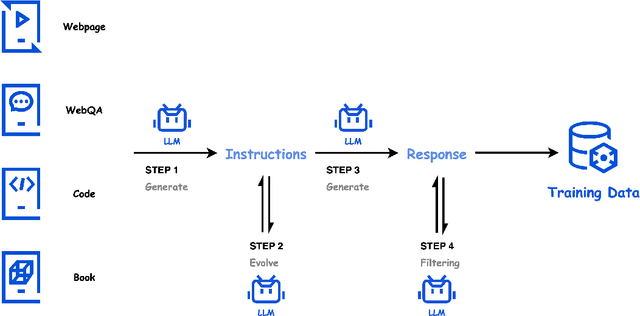
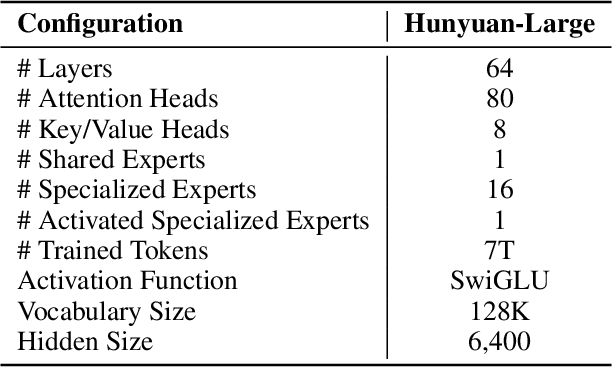
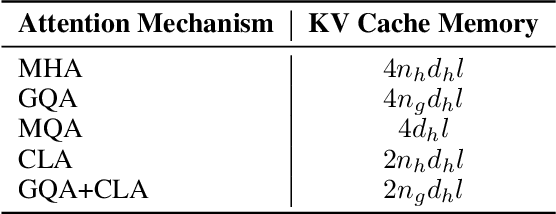
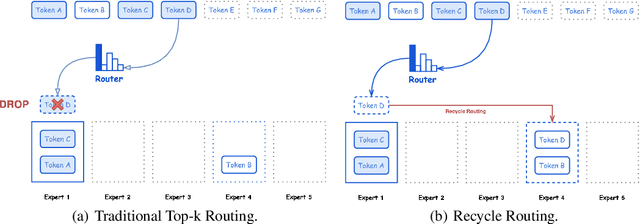
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Hunyuan-Large, which is currently the largest open-source Transformer-based mixture of experts model, with a total of 389 billion parameters and 52 billion activation parameters, capable of handling up to 256K tokens. We conduct a thorough evaluation of Hunyuan-Large's superior performance across various benchmarks including language understanding and generation, logical reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, coding, long-context, and aggregated tasks, where it outperforms LLama3.1-70B and exhibits comparable performance when compared to the significantly larger LLama3.1-405B model. Key practice of Hunyuan-Large include large-scale synthetic data that is orders larger than in previous literature, a mixed expert routing strategy, a key-value cache compression technique, and an expert-specific learning rate strategy. Additionally, we also investigate the scaling laws and learning rate schedule of mixture of experts models, providing valuable insights and guidances for future model development and optimization. The code and checkpoints of Hunyuan-Large are released to facilitate future innovations and applications. Codes: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan-Large Models: https://huggingface.co/tencent/Tencent-Hunyuan-Large
IDGen: Item Discrimination Induced Prompt Generation for LLM Evaluation
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) grow increasingly adept at managing complex tasks, the evaluation set must keep pace with these advancements to ensure it remains sufficiently discriminative. Item Discrimination (ID) theory, which is widely used in educational assessment, measures the ability of individual test items to differentiate between high and low performers. Inspired by this theory, we propose an ID-induced prompt synthesis framework for evaluating LLMs to ensure the evaluation set can continually update and refine according to model abilities. Our data synthesis framework prioritizes both breadth and specificity. It can generate prompts that comprehensively evaluate the capabilities of LLMs while revealing meaningful performance differences between models, allowing for effective discrimination of their relative strengths and weaknesses across various tasks and domains. To produce high-quality data, we incorporate a self-correct mechanism into our generalization framework, and develop two models to predict prompt discrimination and difficulty score to facilitate our data synthesis framework, contributing valuable tools to evaluation data synthesis research. We apply our generated data to evaluate five SOTA models. Our data achieves an average score of 51.92, accompanied by a variance of 10.06. By contrast, previous works (i.e., SELF-INSTRUCT and WizardLM) obtain an average score exceeding 67, with a variance below 3.2. The results demonstrate that the data generated by our framework is more challenging and discriminative compared to previous works. We will release a dataset of over 3,000 carefully crafted prompts to facilitate evaluation research of LLMs.
Hunyuan-DiT: A Powerful Multi-Resolution Diffusion Transformer with Fine-Grained Chinese Understanding
May 14, 2024



Abstract:We present Hunyuan-DiT, a text-to-image diffusion transformer with fine-grained understanding of both English and Chinese. To construct Hunyuan-DiT, we carefully design the transformer structure, text encoder, and positional encoding. We also build from scratch a whole data pipeline to update and evaluate data for iterative model optimization. For fine-grained language understanding, we train a Multimodal Large Language Model to refine the captions of the images. Finally, Hunyuan-DiT can perform multi-turn multimodal dialogue with users, generating and refining images according to the context. Through our holistic human evaluation protocol with more than 50 professional human evaluators, Hunyuan-DiT sets a new state-of-the-art in Chinese-to-image generation compared with other open-source models. Code and pretrained models are publicly available at github.com/Tencent/HunyuanDiT
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge