Reid Swanson
Getting Reliable Annotations for Sarcasm in Online Dialogues
Sep 04, 2017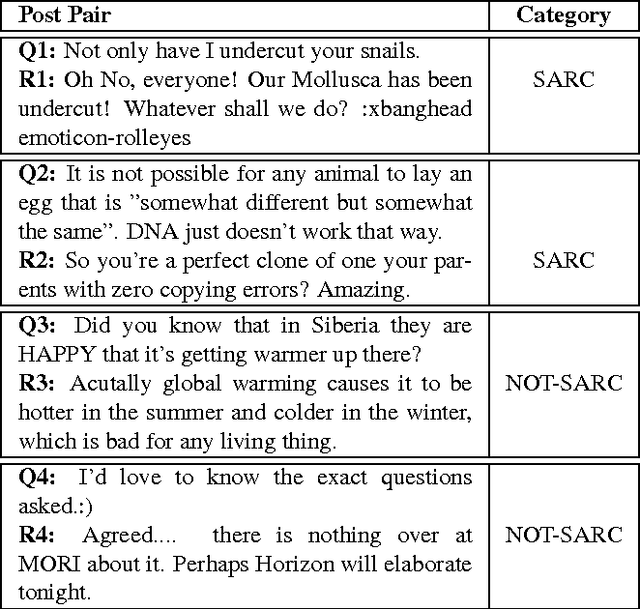
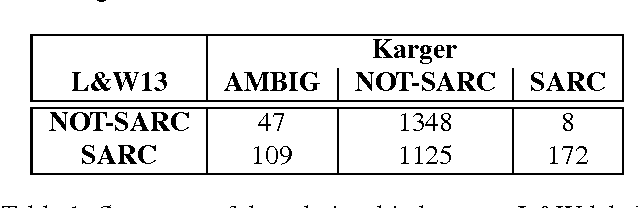
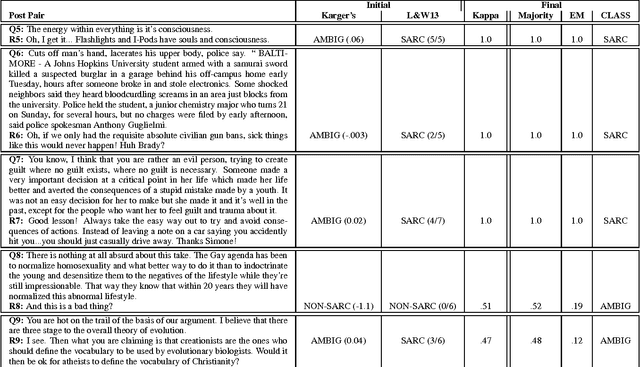
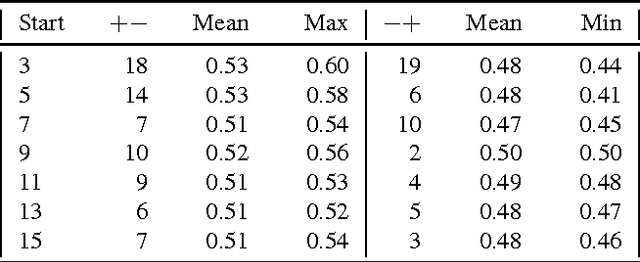
Abstract:The language used in online forums differs in many ways from that of traditional language resources such as news. One difference is the use and frequency of nonliteral, subjective dialogue acts such as sarcasm. Whether the aim is to develop a theory of sarcasm in dialogue, or engineer automatic methods for reliably detecting sarcasm, a major challenge is simply the difficulty of getting enough reliably labelled examples. In this paper we describe our work on methods for achieving highly reliable sarcasm annotations from untrained annotators on Mechanical Turk. We explore the use of a number of common statistical reliability measures, such as Kappa, Karger's, Majority Class, and EM. We show that more sophisticated measures do not appear to yield better results for our data than simple measures such as assuming that the correct label is the one that a majority of Turkers apply.
Unsupervised Induction of Contingent Event Pairs from Film Scenes
Aug 30, 2017
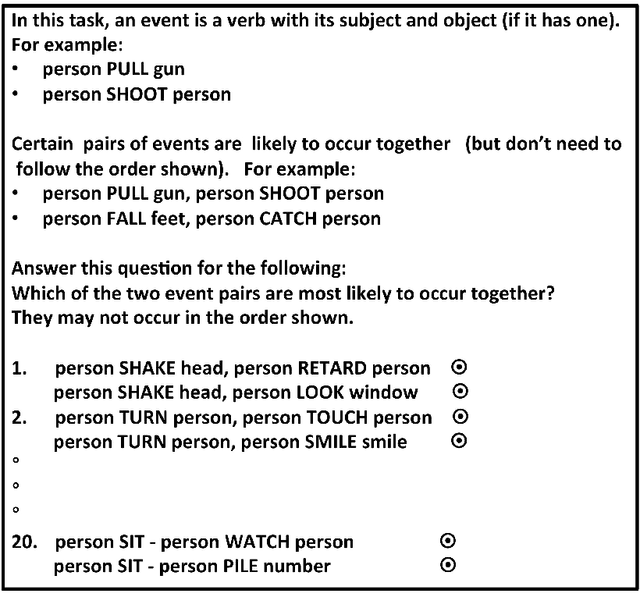

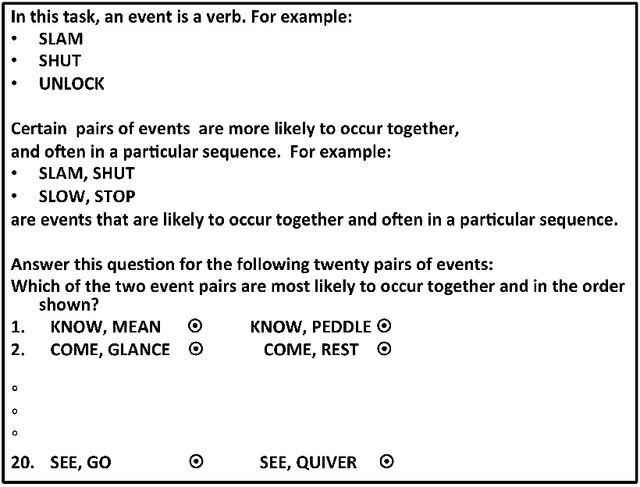
Abstract:Human engagement in narrative is partially driven by reasoning about discourse relations between narrative events, and the expectations about what is likely to happen next that results from such reasoning. Researchers in NLP have tackled modeling such expectations from a range of perspectives, including treating it as the inference of the contingent discourse relation, or as a type of common-sense causal reasoning. Our approach is to model likelihood between events by drawing on several of these lines of previous work. We implement and evaluate different unsupervised methods for learning event pairs that are likely to be contingent on one another. We refine event pairs that we learn from a corpus of film scene descriptions utilizing web search counts, and evaluate our results by collecting human judgments of contingency. Our results indicate that the use of web search counts increases the average accuracy of our best method to 85.64% over a baseline of 50%, as compared to an average accuracy of 75.15% without web search.
An Adaptation of Topic Modeling to Sentences
Jul 20, 2016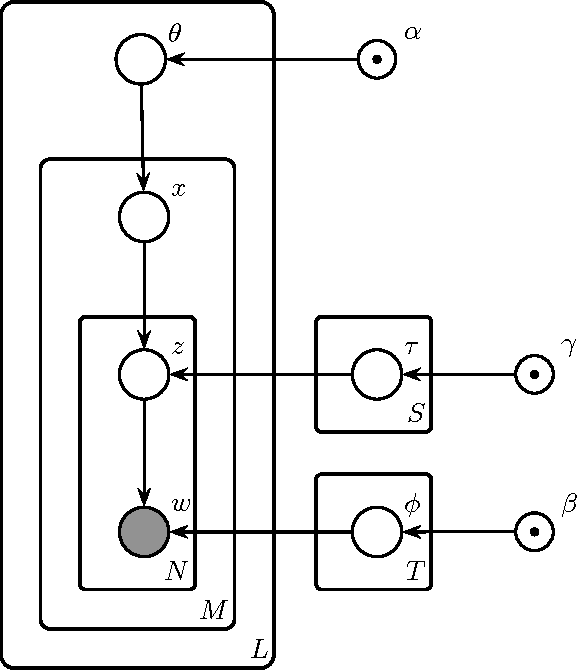
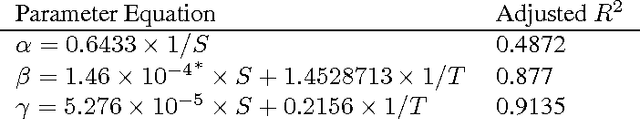
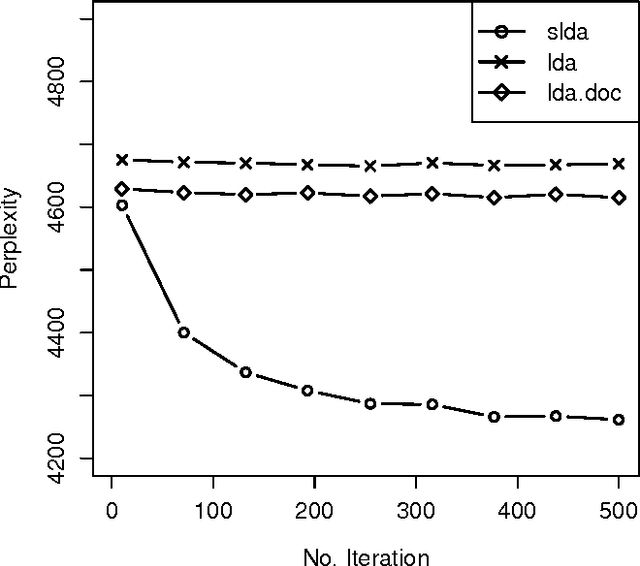
Abstract:Advances in topic modeling have yielded effective methods for characterizing the latent semantics of textual data. However, applying standard topic modeling approaches to sentence-level tasks introduces a number of challenges. In this paper, we adapt the approach of latent-Dirichlet allocation to include an additional layer for incorporating information about the sentence boundaries in documents. We show that the addition of this minimal information of document structure improves the perplexity results of a trained model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge