Ruey-Cheng Chen
BAMBINO-LM: (Bilingual-)Human-Inspired Continual Pretraining of BabyLM
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Children from bilingual backgrounds benefit from interactions with parents and teachers to re-acquire their heritage language. In this paper, we investigate how this insight from behavioral study can be incorporated into the learning of small-scale language models. We introduce BAMBINO-LM, a continual pretraining strategy for BabyLM that uses a novel combination of alternation and PPO-based perplexity reward induced from a parent Italian model. Upon evaluation on zero-shot classification tasks for English and Italian, BAMBINO-LM improves the Italian language capability of a BabyLM baseline. Our ablation analysis demonstrates that employing both the alternation strategy and PPO-based modeling is key to this effectiveness gain. We also show that, as a side effect, the proposed method leads to similar degradation in L1 effectiveness as human children would have had in an equivalent learning scenario.
Incorporating Behavioral Hypotheses for Query Generation
Oct 06, 2020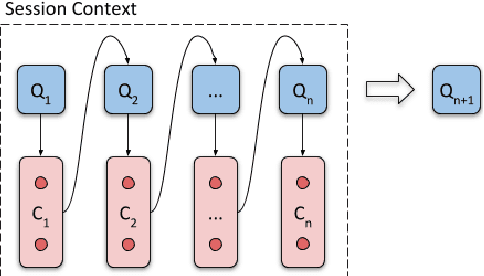
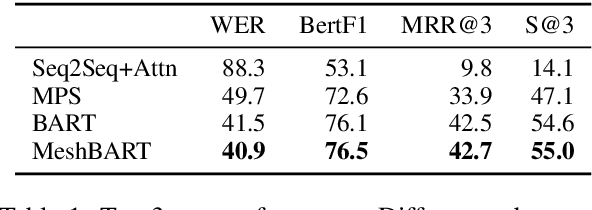
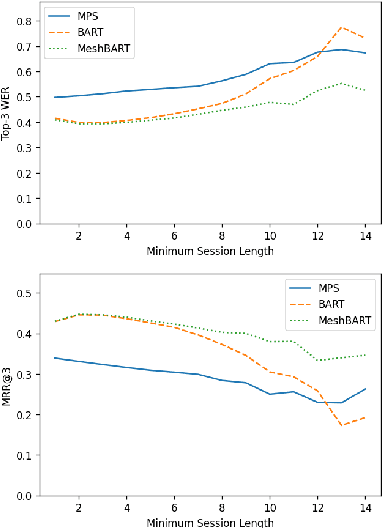

Abstract:Generative neural networks have been shown effective on query suggestion. Commonly posed as a conditional generation problem, the task aims to leverage earlier inputs from users in a search session to predict queries that they will likely issue at a later time. User inputs come in various forms such as querying and clicking, each of which can imply different semantic signals channeled through the corresponding behavioral patterns. This paper induces these behavioral biases as hypotheses for query generation, where a generic encoder-decoder Transformer framework is presented to aggregate arbitrary hypotheses of choice. Our experimental results show that the proposed approach leads to significant improvements on top-$k$ word error rate and Bert F1 Score compared to a recent BART model.
Incremental Learning for Fully Unsupervised Word Segmentation Using Penalized Likelihood and Model Selection
Sep 23, 2016



Abstract:We present a novel incremental learning approach for unsupervised word segmentation that combines features from probabilistic modeling and model selection. This includes super-additive penalties for addressing the cognitive burden imposed by long word formation, and new model selection criteria based on higher-order generative assumptions. Our approach is fully unsupervised; it relies on a small number of parameters that permits flexible modeling and a mechanism that automatically learns parameters from the data. Through experimentation, we show that this intricate design has led to top-tier performance in both phonemic and orthographic word segmentation.
An Adaptation of Topic Modeling to Sentences
Jul 20, 2016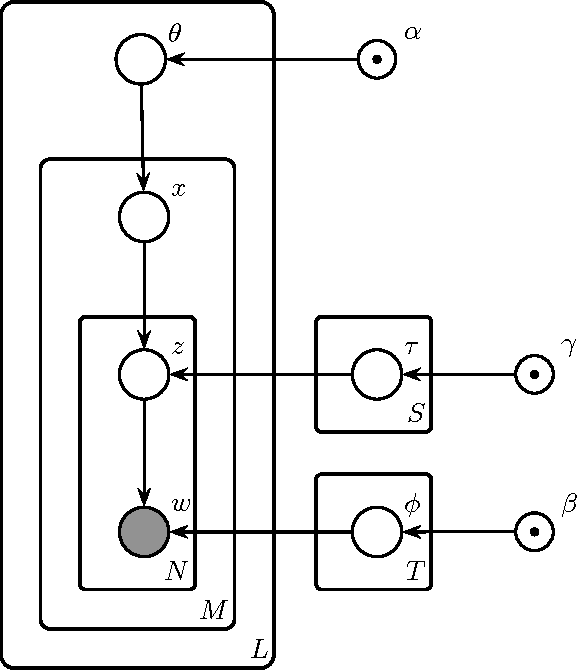
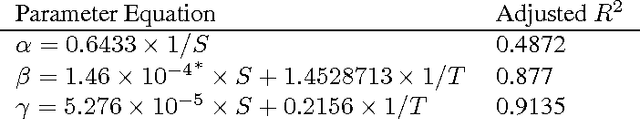
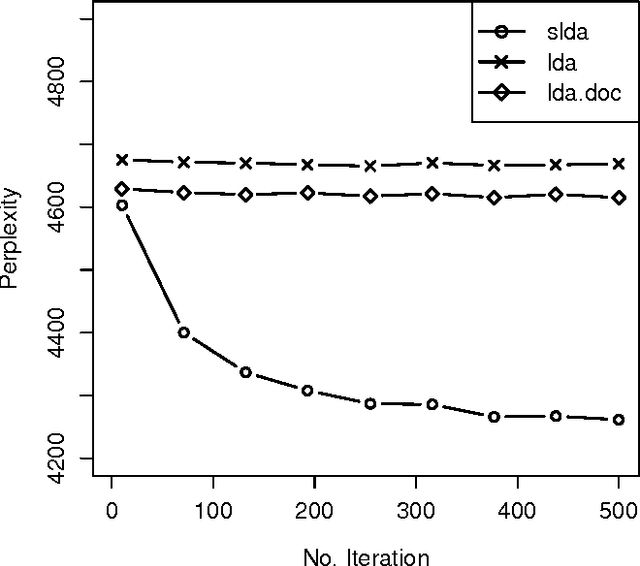
Abstract:Advances in topic modeling have yielded effective methods for characterizing the latent semantics of textual data. However, applying standard topic modeling approaches to sentence-level tasks introduces a number of challenges. In this paper, we adapt the approach of latent-Dirichlet allocation to include an additional layer for incorporating information about the sentence boundaries in documents. We show that the addition of this minimal information of document structure improves the perplexity results of a trained model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge