Zishan Xu
CoBA-RL: Capability-Oriented Budget Allocation for Reinforcement Learning in LLMs
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has emerged as a key approach for enhancing LLM reasoning.However, standard frameworks like Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) typically employ a uniform rollout budget, leading to resource inefficiency. Moreover, existing adaptive methods often rely on instance-level metrics, such as task pass rates, failing to capture the model's dynamic learning state. To address these limitations, we propose CoBA-RL, a reinforcement learning algorithm designed to adaptively allocate rollout budgets based on the model's evolving capability. Specifically, CoBA-RL utilizes a Capability-Oriented Value function to map tasks to their potential training gains and employs a heap-based greedy strategy to efficiently self-calibrate the distribution of computational resources to samples with high training value. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach effectively orchestrates the trade-off between exploration and exploitation, delivering consistent generalization improvements across multiple challenging benchmarks. These findings underscore that quantifying sample training value and optimizing budget allocation are pivotal for advancing LLM post-training efficiency.
EDIS: Diagnosing LLM Reasoning via Entropy Dynamics
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Entropy-based confidence signals are increasingly leveraged to improve reasoning in large language models (LLMs), yet existing approaches treat confidence as a static quantity -- typically aggregated over tokens. We show that the \emph{temporal evolution} of confidence during generation carries richer information than aggregate statistics alone. Analyzing token-level entropy trajectories, we identify characteristic patterns distinguishing correct from incorrect reasoning: erroneous solutions exhibit unstable dynamics, including burst spikes (sustained uncertainty growth) and peak-valley spikes (sharp rebounds following transient confidence). These patterns persist across models and training stages, suggesting they reflect intrinsic properties of reasoning failure rather than superficial noise. To formalize this observation, we introduce the Entropy Dynamics Instability Score (\textbf{EDIS}), a trajectory-level metric quantifying instability in entropy evolution. EDIS serves as an effective diagnostic signal for inference-time selection, substantially improving reasoning accuracy, and offers a promising direction for training-time sample curation. Our findings establish entropy dynamics as an underexplored yet informative lens for understanding and improving LLM reasoning.
ToolACE-MCP: Generalizing History-Aware Routing from MCP Tools to the Agent Web
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:With the rise of the Agent Web and Model Context Protocol (MCP), the agent ecosystem is evolving into an open collaborative network, exponentially increasing accessible tools. However, current architectures face severe scalability and generality bottlenecks. To address this, we propose ToolACE-MCP, a pipeline for training history-aware routers to empower precise navigation in large-scale ecosystems. By leveraging a dependency-rich candidate Graph to synthesize multi-turn trajectories, we effectively train routers with dynamic context understanding to create the plug-and-play Light Routing Agent. Experiments on the real-world benchmarks MCP-Universe and MCP-Mark demonstrate superior performance. Notably, ToolACE-MCP exhibits critical properties for the future Agent Web: it not only generalizes to multi-agent collaboration with minimal adaptation but also maintains exceptional robustness against noise and scales effectively to massive candidate spaces. These findings provide a strong empirical foundation for universal orchestration in open-ended ecosystems.
RealMem: Benchmarking LLMs in Real-World Memory-Driven Interaction
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) evolve from static dialogue interfaces to autonomous general agents, effective memory is paramount to ensuring long-term consistency. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on casual conversation or task-oriented dialogue, failing to capture **"long-term project-oriented"** interactions where agents must track evolving goals. To bridge this gap, we introduce **RealMem**, the first benchmark grounded in realistic project scenarios. RealMem comprises over 2,000 cross-session dialogues across eleven scenarios, utilizing natural user queries for evaluation. We propose a synthesis pipeline that integrates Project Foundation Construction, Multi-Agent Dialogue Generation, and Memory and Schedule Management to simulate the dynamic evolution of memory. Experiments reveal that current memory systems face significant challenges in managing the long-term project states and dynamic context dependencies inherent in real-world projects. Our code and datasets are available at [https://github.com/AvatarMemory/RealMemBench](https://github.com/AvatarMemory/RealMemBench).
Octopus: Agentic Multimodal Reasoning with Six-Capability Orchestration
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Existing multimodal reasoning models and frameworks suffer from fundamental architectural limitations: most lack the human-like ability to autonomously explore diverse reasoning pathways-whether in direct inference, tool-driven visual exploration, programmatic visual manipulation, or intrinsic visual imagination. Consequently, they struggle to adapt to dynamically changing capability requirements in real-world tasks. Meanwhile, humans exhibit a complementary set of thinking abilities when addressing such tasks, whereas existing methods typically cover only a subset of these dimensions. Inspired by this, we propose Octopus: Agentic Multimodal Reasoning with Six-Capability Orchestration, a new paradigm for multimodal agentic reasoning. We define six core capabilities essential for multimodal reasoning and organize a comprehensive evaluation benchmark, Octopus-Bench, accordingly. Octopus is capable of autonomously exploring during reasoning and dynamically selecting the most appropriate capability based on the current state. Experimental results show that Octopus achieves the best performance on the vast majority of tasks in Octopus-Bench, highlighting the crucial role of capability coordination in agentic multimodal reasoning.
Decoupling Continual Semantic Segmentation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Continual Semantic Segmentation (CSS) requires learning new classes without forgetting previously acquired knowledge, addressing the fundamental challenge of catastrophic forgetting in dense prediction tasks. However, existing CSS methods typically employ single-stage encoder-decoder architectures where segmentation masks and class labels are tightly coupled, leading to interference between old and new class learning and suboptimal retention-plasticity balance. We introduce DecoupleCSS, a novel two-stage framework for CSS. By decoupling class-aware detection from class-agnostic segmentation, DecoupleCSS enables more effective continual learning, preserving past knowledge while learning new classes. The first stage leverages pre-trained text and image encoders, adapted using LoRA, to encode class-specific information and generate location-aware prompts. In the second stage, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) is employed to produce precise segmentation masks, ensuring that segmentation knowledge is shared across both new and previous classes. This approach improves the balance between retention and adaptability in CSS, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of challenging tasks. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/euyis1019/Decoupling-Continual-Semantic-Segmentation.
RAISE: Reinforenced Adaptive Instruction Selection For Large Language Models
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:In the instruction fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs), it has become a consensus that a few high-quality instructions are superior to a large number of low-quality instructions. At present, many instruction selection methods have been proposed, but most of these methods select instruction based on heuristic quality metrics, and only consider data selection before training. These designs lead to insufficient optimization of instruction fine-tuning, and fixed heuristic indicators are often difficult to optimize for specific tasks. So we designed a dynamic, task-objective-driven instruction selection framework RAISE(Reinforenced Adaptive Instruction SElection), which incorporates the entire instruction fine-tuning process into optimization, selecting instruction at each step based on the expected impact of instruction on model performance improvement. Our approach is well interpretable and has strong task-specific optimization capabilities. By modeling dynamic instruction selection as a sequential decision-making process, we use RL to train our selection strategy. Extensive experiments and result analysis prove the superiority of our method compared with other instruction selection methods. Notably, RAISE achieves superior performance by updating only 1\% of the training steps compared to full-data training, demonstrating its efficiency and effectiveness.
Revisiting Classification Taxonomy for Grammatical Errors
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Grammatical error classification plays a crucial role in language learning systems, but existing classification taxonomies often lack rigorous validation, leading to inconsistencies and unreliable feedback. In this paper, we revisit previous classification taxonomies for grammatical errors by introducing a systematic and qualitative evaluation framework. Our approach examines four aspects of a taxonomy, i.e., exclusivity, coverage, balance, and usability. Then, we construct a high-quality grammatical error classification dataset annotated with multiple classification taxonomies and evaluate them grounding on our proposed evaluation framework. Our experiments reveal the drawbacks of existing taxonomies. Our contributions aim to improve the precision and effectiveness of error analysis, providing more understandable and actionable feedback for language learners.
DAST: Context-Aware Compression in LLMs via Dynamic Allocation of Soft Tokens
Feb 17, 2025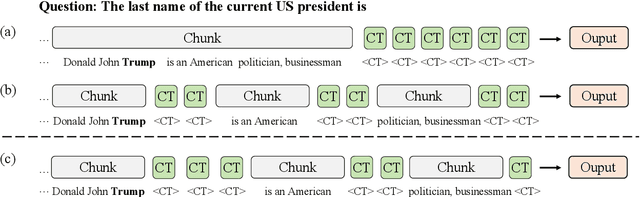
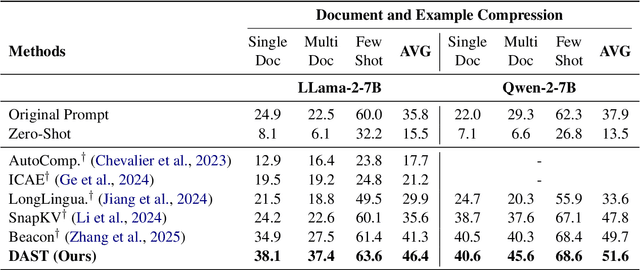
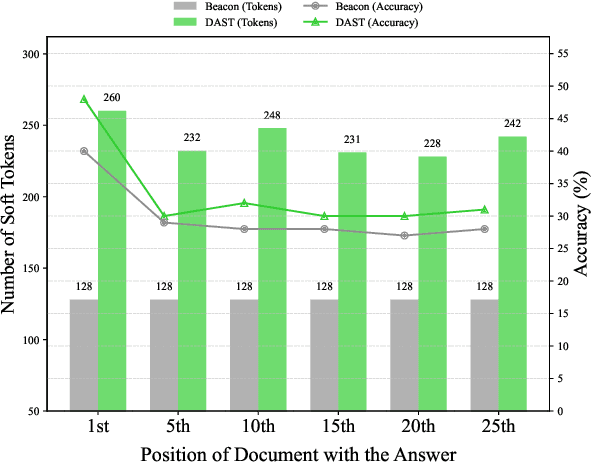
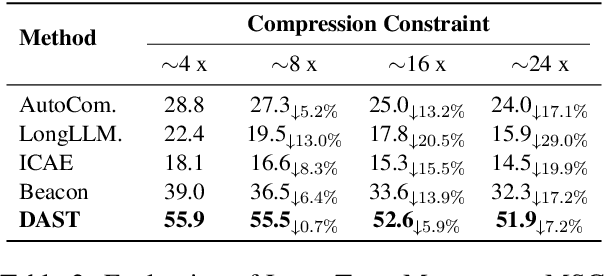
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) face computational inefficiencies and redundant processing when handling long context inputs, prompting a focus on compression techniques. While existing semantic vector-based compression methods achieve promising performance, these methods fail to account for the intrinsic information density variations between context chunks, instead allocating soft tokens uniformly across context chunks. This uniform distribution inevitably diminishes allocation to information-critical regions. To address this, we propose Dynamic Allocation of Soft Tokens (DAST), a simple yet effective method that leverages the LLM's intrinsic understanding of contextual relevance to guide compression. DAST combines perplexity-based local information with attention-driven global information to dynamically allocate soft tokens to the informative-rich chunks, enabling effective, context-aware compression. Experimental results across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that DAST surpasses state-of-the-art methods.
IDGen: Item Discrimination Induced Prompt Generation for LLM Evaluation
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) grow increasingly adept at managing complex tasks, the evaluation set must keep pace with these advancements to ensure it remains sufficiently discriminative. Item Discrimination (ID) theory, which is widely used in educational assessment, measures the ability of individual test items to differentiate between high and low performers. Inspired by this theory, we propose an ID-induced prompt synthesis framework for evaluating LLMs to ensure the evaluation set can continually update and refine according to model abilities. Our data synthesis framework prioritizes both breadth and specificity. It can generate prompts that comprehensively evaluate the capabilities of LLMs while revealing meaningful performance differences between models, allowing for effective discrimination of their relative strengths and weaknesses across various tasks and domains. To produce high-quality data, we incorporate a self-correct mechanism into our generalization framework, and develop two models to predict prompt discrimination and difficulty score to facilitate our data synthesis framework, contributing valuable tools to evaluation data synthesis research. We apply our generated data to evaluate five SOTA models. Our data achieves an average score of 51.92, accompanied by a variance of 10.06. By contrast, previous works (i.e., SELF-INSTRUCT and WizardLM) obtain an average score exceeding 67, with a variance below 3.2. The results demonstrate that the data generated by our framework is more challenging and discriminative compared to previous works. We will release a dataset of over 3,000 carefully crafted prompts to facilitate evaluation research of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge