Zhongli Li
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
A2R: An Asymmetric Two-Stage Reasoning Framework for Parallel Reasoning
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Recent Large Reasoning Models have achieved significant improvements in complex task-solving capabilities by allocating more computation at the inference stage with a "thinking longer" paradigm. Even as the foundational reasoning capabilities of models advance rapidly, the persistent gap between a model's performance in a single attempt and its latent potential, often revealed only across multiple solution paths, starkly highlights the disparity between its realized and inherent capabilities. To address this, we present A2R, an Asymmetric Two-Stage Reasoning framework designed to explicitly bridge the gap between a model's potential and its actual performance. In this framework, an "explorer" model first generates potential solutions in parallel through repeated sampling. Subsequently,a "synthesizer" model integrates these references for a more refined, second stage of reasoning. This two-stage process allows computation to be scaled orthogonally to existing sequential methods. Our work makes two key innovations: First, we present A2R as a plug-and-play parallel reasoning framework that explicitly enhances a model's capabilities on complex questions. For example, using our framework, the Qwen3-8B-distill model achieves a 75% performance improvement compared to its self-consistency baseline. Second, through a systematic analysis of the explorer and synthesizer roles, we identify an effective asymmetric scaling paradigm. This insight leads to A2R-Efficient, a "small-to-big" variant that combines a Qwen3-4B explorer with a Qwen3-8B synthesizer. This configuration surpasses the average performance of a monolithic Qwen3-32B model at a nearly 30% lower cost. Collectively, these results show that A2R is not only a performance-boosting framework but also an efficient and practical solution for real-world applications.
Towards Real-World Writing Assistance: A Chinese Character Checking Benchmark with Faked and Misspelled Characters
Nov 19, 2023



Abstract:Writing assistance is an application closely related to human life and is also a fundamental Natural Language Processing (NLP) research field. Its aim is to improve the correctness and quality of input texts, with character checking being crucial in detecting and correcting wrong characters. From the perspective of the real world where handwriting occupies the vast majority, characters that humans get wrong include faked characters (i.e., untrue characters created due to writing errors) and misspelled characters (i.e., true characters used incorrectly due to spelling errors). However, existing datasets and related studies only focus on misspelled characters mainly caused by phonological or visual confusion, thereby ignoring faked characters which are more common and difficult. To break through this dilemma, we present Visual-C$^3$, a human-annotated Visual Chinese Character Checking dataset with faked and misspelled Chinese characters. To the best of our knowledge, Visual-C$^3$ is the first real-world visual and the largest human-crafted dataset for the Chinese character checking scenario. Additionally, we also propose and evaluate novel baseline methods on Visual-C$^3$. Extensive empirical results and analyses show that Visual-C$^3$ is high-quality yet challenging. The Visual-C$^3$ dataset and the baseline methods will be publicly available to facilitate further research in the community.
Instance Segmentation for Chinese Character Stroke Extraction, Datasets and Benchmarks
Oct 25, 2022



Abstract:Stroke is the basic element of Chinese character and stroke extraction has been an important and long-standing endeavor. Existing stroke extraction methods are often handcrafted and highly depend on domain expertise due to the limited training data. Moreover, there are no standardized benchmarks to provide a fair comparison between different stroke extraction methods, which, we believe, is a major impediment to the development of Chinese character stroke understanding and related tasks. In this work, we present the first public available Chinese Character Stroke Extraction (CCSE) benchmark, with two new large-scale datasets: Kaiti CCSE (CCSE-Kai) and Handwritten CCSE (CCSE-HW). With the large-scale datasets, we hope to leverage the representation power of deep models such as CNNs to solve the stroke extraction task, which, however, remains an open question. To this end, we turn the stroke extraction problem into a stroke instance segmentation problem. Using the proposed datasets to train a stroke instance segmentation model, we surpass previous methods by a large margin. Moreover, the models trained with the proposed datasets benefit the downstream font generation and handwritten aesthetic assessment tasks. We hope these benchmark results can facilitate further research. The source code and datasets are publicly available at: https://github.com/lizhaoliu-Lec/CCSE.
Linguistic Rules-Based Corpus Generation for Native Chinese Grammatical Error Correction
Oct 19, 2022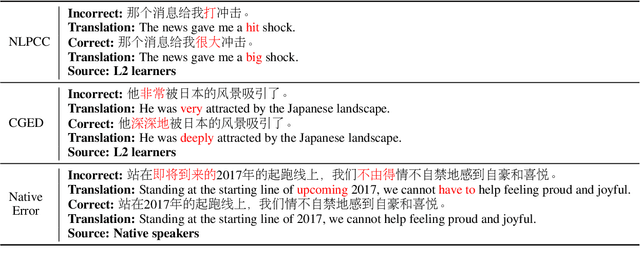
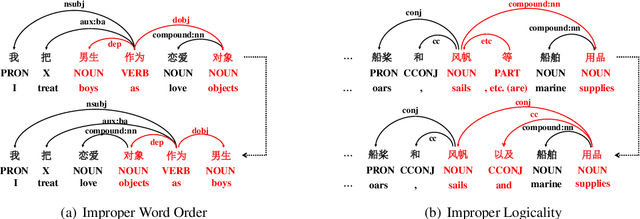
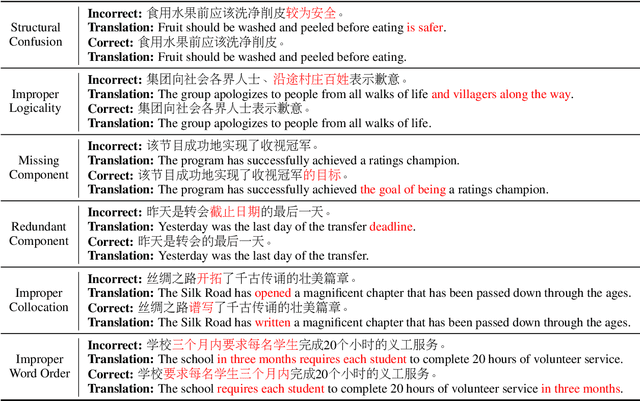
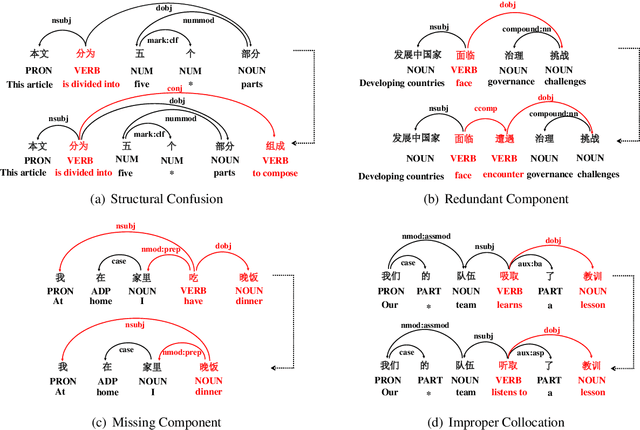
Abstract:Chinese Grammatical Error Correction (CGEC) is both a challenging NLP task and a common application in human daily life. Recently, many data-driven approaches are proposed for the development of CGEC research. However, there are two major limitations in the CGEC field: First, the lack of high-quality annotated training corpora prevents the performance of existing CGEC models from being significantly improved. Second, the grammatical errors in widely used test sets are not made by native Chinese speakers, resulting in a significant gap between the CGEC models and the real application. In this paper, we propose a linguistic rules-based approach to construct large-scale CGEC training corpora with automatically generated grammatical errors. Additionally, we present a challenging CGEC benchmark derived entirely from errors made by native Chinese speakers in real-world scenarios. Extensive experiments and detailed analyses not only demonstrate that the training data constructed by our method effectively improves the performance of CGEC models, but also reflect that our benchmark is an excellent resource for further development of the CGEC field.
Learning from the Dictionary: Heterogeneous Knowledge Guided Fine-tuning for Chinese Spell Checking
Oct 19, 2022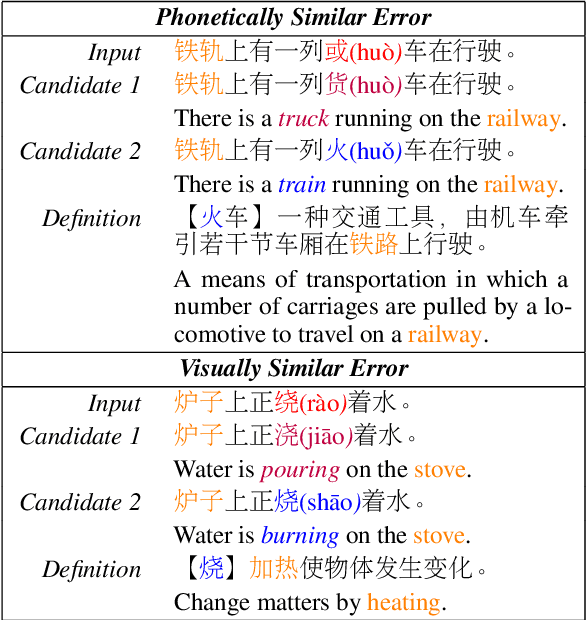
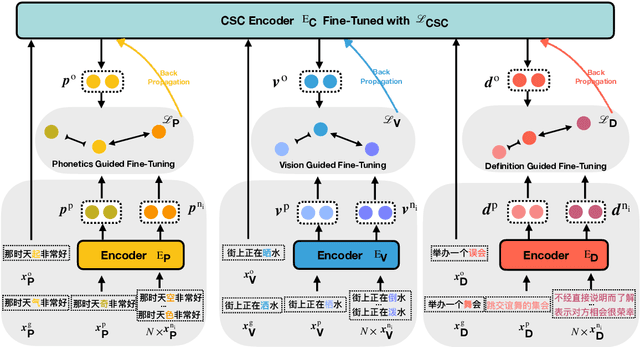
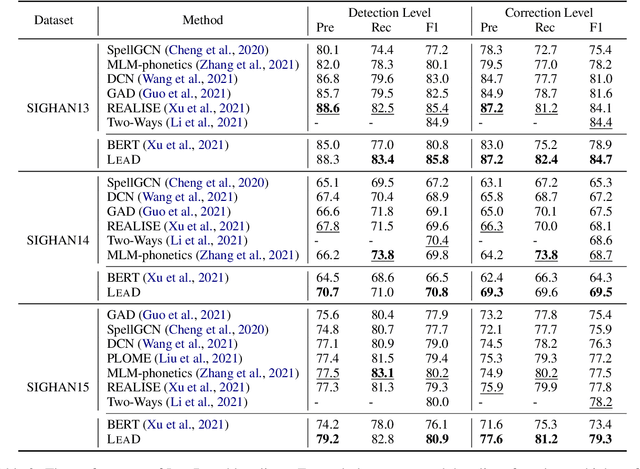
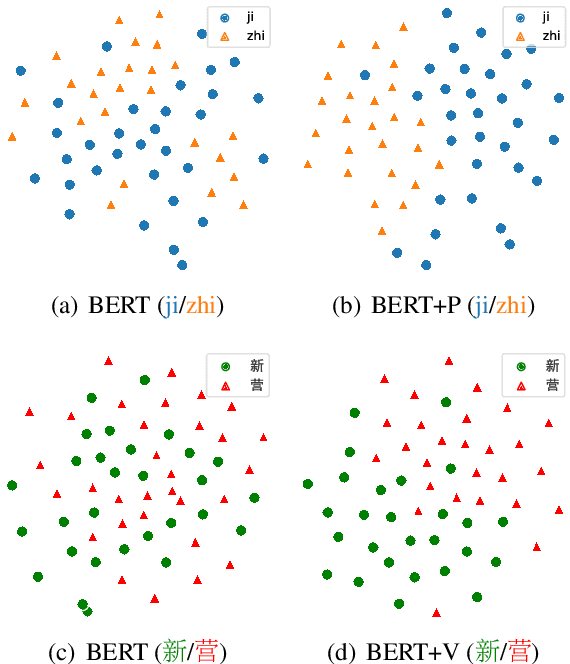
Abstract:Chinese Spell Checking (CSC) aims to detect and correct Chinese spelling errors. Recent researches start from the pretrained knowledge of language models and take multimodal information into CSC models to improve the performance. However, they overlook the rich knowledge in the dictionary, the reference book where one can learn how one character should be pronounced, written, and used. In this paper, we propose the LEAD framework, which renders the CSC model to learn heterogeneous knowledge from the dictionary in terms of phonetics, vision, and meaning. LEAD first constructs positive and negative samples according to the knowledge of character phonetics, glyphs, and definitions in the dictionary. Then a unified contrastive learning-based training scheme is employed to refine the representations of the CSC models. Extensive experiments and detailed analyses on the SIGHAN benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods.
AiM: Taking Answers in Mind to Correct Chinese Cloze Tests in Educational Applications
Aug 26, 2022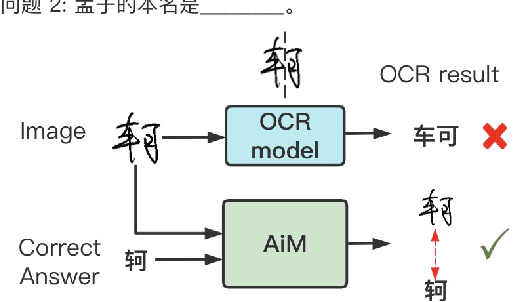
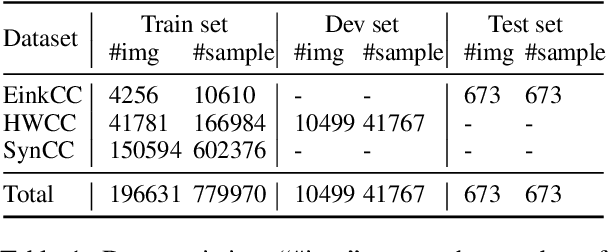
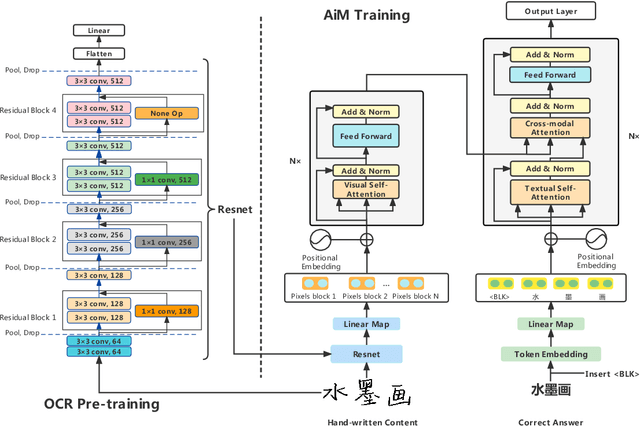
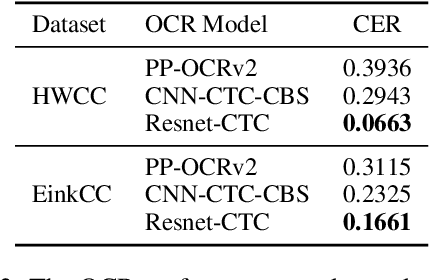
Abstract:To automatically correct handwritten assignments, the traditional approach is to use an OCR model to recognize characters and compare them to answers. The OCR model easily gets confused on recognizing handwritten Chinese characters, and the textual information of the answers is missing during the model inference. However, teachers always have these answers in mind to review and correct assignments. In this paper, we focus on the Chinese cloze tests correction and propose a multimodal approach (named AiM). The encoded representations of answers interact with the visual information of students' handwriting. Instead of predicting 'right' or 'wrong', we perform the sequence labeling on the answer text to infer which answer character differs from the handwritten content in a fine-grained way. We take samples of OCR datasets as the positive samples for this task, and develop a negative sample augmentation method to scale up the training data. Experimental results show that AiM outperforms OCR-based methods by a large margin. Extensive studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our multimodal approach.
Type-Driven Multi-Turn Corrections for Grammatical Error Correction
Mar 17, 2022
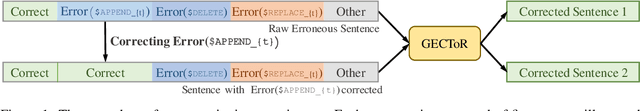
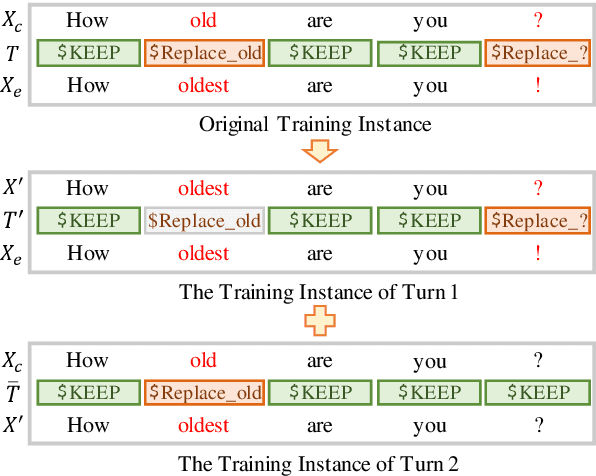
Abstract:Grammatical Error Correction (GEC) aims to automatically detect and correct grammatical errors. In this aspect, dominant models are trained by one-iteration learning while performing multiple iterations of corrections during inference. Previous studies mainly focus on the data augmentation approach to combat the exposure bias, which suffers from two drawbacks. First, they simply mix additionally-constructed training instances and original ones to train models, which fails to help models be explicitly aware of the procedure of gradual corrections. Second, they ignore the interdependence between different types of corrections. In this paper, we propose a Type-Driven Multi-Turn Corrections approach for GEC. Using this approach, from each training instance, we additionally construct multiple training instances, each of which involves the correction of a specific type of errors. Then, we use these additionally-constructed training instances and the original one to train the model in turn. Experimental results and in-depth analysis show that our approach significantly benefits the model training. Particularly, our enhanced model achieves state-of-the-art single-model performance on English GEC benchmarks. We release our code at Github.
The Past Mistake is the Future Wisdom: Error-driven Contrastive Probability Optimization for Chinese Spell Checking
Mar 02, 2022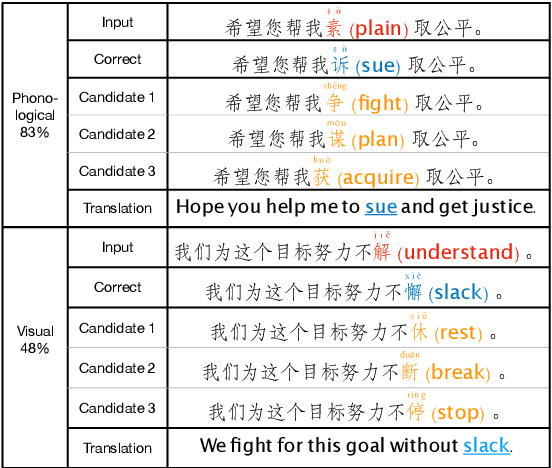



Abstract:Chinese Spell Checking (CSC) aims to detect and correct Chinese spelling errors, which are mainly caused by the phonological or visual similarity. Recently, pre-trained language models (PLMs) promote the progress of CSC task. However, there exists a gap between the learned knowledge of PLMs and the goal of CSC task. PLMs focus on the semantics in text and tend to correct the erroneous characters to semantically proper or commonly used ones, but these aren't the ground-truth corrections. To address this issue, we propose an Error-driven COntrastive Probability Optimization (ECOPO) framework for CSC task. ECOPO refines the knowledge representations of PLMs, and guides the model to avoid predicting these common characters through an error-driven way. Particularly, ECOPO is model-agnostic and it can be combined with existing CSC methods to achieve better performance. Extensive experiments and detailed analyses on SIGHAN datasets demonstrate that ECOPO is simple yet effective.
Seeking Patterns, Not just Memorizing Procedures: Contrastive Learning for Solving Math Word Problems
Oct 16, 2021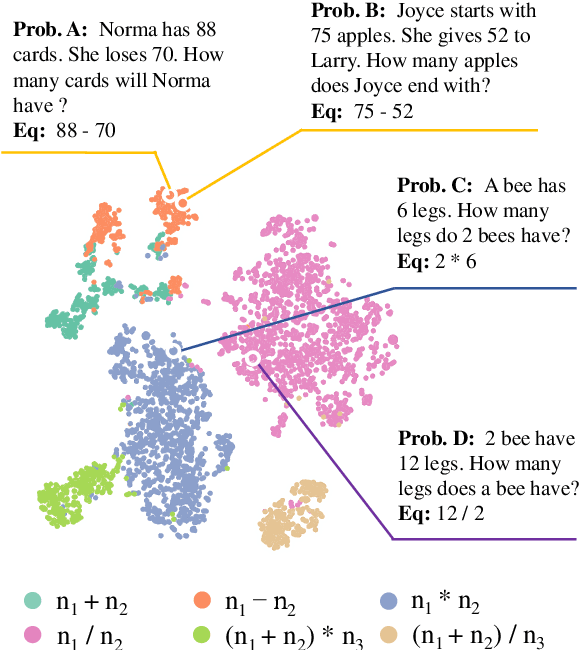
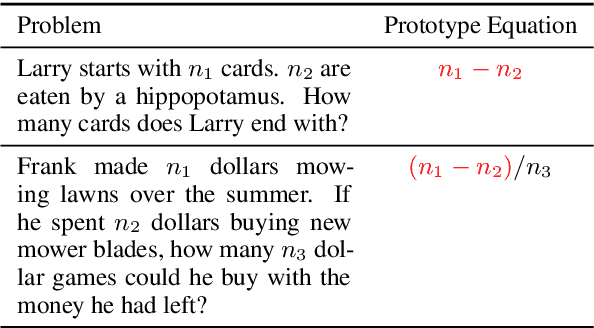
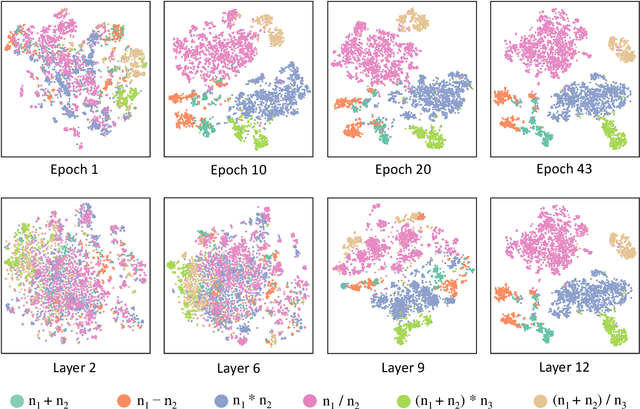
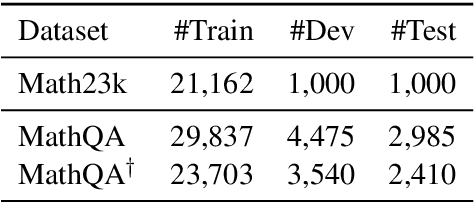
Abstract:Math Word Problem (MWP) solving needs to discover the quantitative relationships over natural language narratives. Recent work shows that existing models memorize procedures from context and rely on shallow heuristics to solve MWPs. In this paper, we look at this issue and argue that the cause is a lack of overall understanding of MWP patterns. We first investigate how a neural network understands patterns only from semantics, and observe that, if the prototype equations are the same, most problems get closer representations and those representations apart from them or close to other prototypes tend to produce wrong solutions. Inspired by it, we propose a contrastive learning approach, where the neural network perceives the divergence of patterns. We collect contrastive examples by converting the prototype equation into a tree and seeking similar tree structures. The solving model is trained with an auxiliary objective on the collected examples, resulting in the representations of problems with similar prototypes being pulled closer. We conduct experiments on the Chinese dataset Math23k and the English dataset MathQA. Our method greatly improves the performance in monolingual and multilingual settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge