Ding Zhang
It's all In the (Exponential) Family: An Equivalence between Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Control Variates for Sketching Algorithms
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Maximum likelihood estimators (MLE) and control variate estimators (CVE) have been used in conjunction with known information across sketching algorithms and applications in machine learning. We prove that under certain conditions in an exponential family, an optimal CVE will achieve the same asymptotic variance as the MLE, giving an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm for the MLE. Experiments show the EM algorithm is faster and numerically stable compared to other root finding algorithms for the MLE for the bivariate Normal distribution, and we expect this to hold across distributions satisfying these conditions. We show how the EM algorithm leads to reproducibility for algorithms using MLE / CVE, and demonstrate how the EM algorithm leads to finding the MLE when the CV weights are known.
It's all the (Exponential) Family: An Equivalence between Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Control Variates for Sketching Algorithms
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Maximum likelihood estimators (MLE) and control variate estimators (CVE) have been used in conjunction with known information across sketching algorithms and applications in machine learning. We prove that under certain conditions in an exponential family, an optimal CVE will achieve the same asymptotic variance as the MLE, giving an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm for the MLE. Experiments show the EM algorithm is faster and numerically stable compared to other root finding algorithms for the MLE for the bivariate Normal distribution, and we expect this to hold across distributions satisfying these conditions. We show how the EM algorithm leads to reproducibility for algorithms using MLE / CVE, and demonstrate how the EM algorithm leads to finding the MLE when the CV weights are known.
Loss-Aware Curriculum Learning for Chinese Grammatical Error Correction
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:Chinese grammatical error correction (CGEC) aims to detect and correct errors in the input Chinese sentences. Recently, Pre-trained Language Models (PLMS) have been employed to improve the performance. However, current approaches ignore that correction difficulty varies across different instances and treat these samples equally, enhancing the challenge of model learning. To address this problem, we propose a multi-granularity Curriculum Learning (CL) framework. Specifically, we first calculate the correction difficulty of these samples and feed them into the model from easy to hard batch by batch. Then Instance-Level CL is employed to help the model optimize in the appropriate direction automatically by regulating the loss function. Extensive experimental results and comprehensive analyses of various datasets prove the effectiveness of our method.
Efficient and Robust Continual Graph Learning for Graph Classification in Biology
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Graph classification is essential for understanding complex biological systems, where molecular structures and interactions are naturally represented as graphs. Traditional graph neural networks (GNNs) perform well on static tasks but struggle in dynamic settings due to catastrophic forgetting. We present Perturbed and Sparsified Continual Graph Learning (PSCGL), a robust and efficient continual graph learning framework for graph data classification, specifically targeting biological datasets. We introduce a perturbed sampling strategy to identify critical data points that contribute to model learning and a motif-based graph sparsification technique to reduce storage needs while maintaining performance. Additionally, our PSCGL framework inherently defends against graph backdoor attacks, which is crucial for applications in sensitive biological contexts. Extensive experiments on biological datasets demonstrate that PSCGL not only retains knowledge across tasks but also enhances the efficiency and robustness of graph classification models in biology.
Online Learning for Adaptive Probing and Scheduling in Dense WLANs
Dec 27, 2022Abstract:Existing solutions to network scheduling typically assume that the instantaneous link rates are completely known before a scheduling decision is made or consider a bandit setting where the accurate link quality is discovered only after it has been used for data transmission. In practice, the decision maker can obtain (relatively accurate) channel information, e.g., through beamforming in mmWave networks, right before data transmission. However, frequent beamforming incurs a formidable overhead in densely deployed mmWave WLANs. In this paper, we consider the important problem of throughput optimization with joint link probing and scheduling. The problem is challenging even when the link rate distributions are pre-known (the offline setting) due to the necessity of balancing the information gains from probing and the cost of reducing the data transmission opportunity. We develop an approximation algorithm with guaranteed performance when the probing decision is non-adaptive, and a dynamic programming based solution for the more challenging adaptive setting. We further extend our solutions to the online setting with unknown link rate distributions and develop a contextual-bandit based algorithm and derive its regret bound. Numerical results using data traces collected from real-world mmWave deployments demonstrate the efficiency of our solutions.
Linguistic Rules-Based Corpus Generation for Native Chinese Grammatical Error Correction
Oct 19, 2022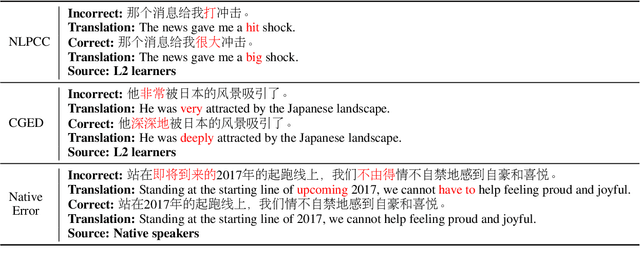
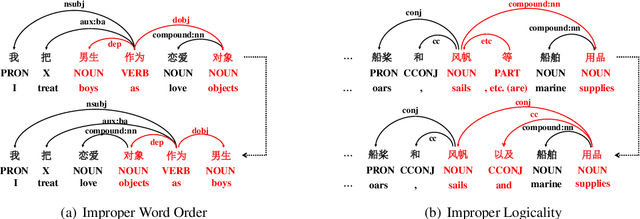
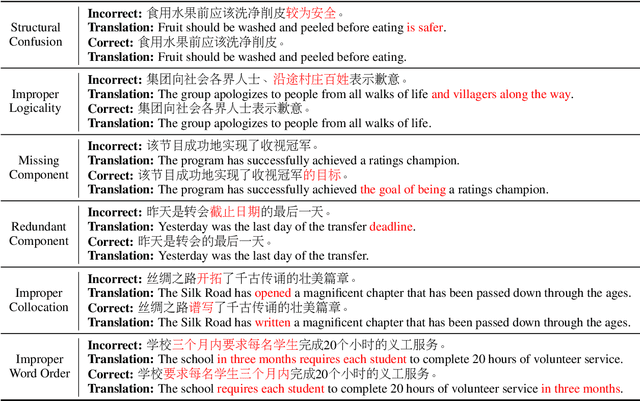
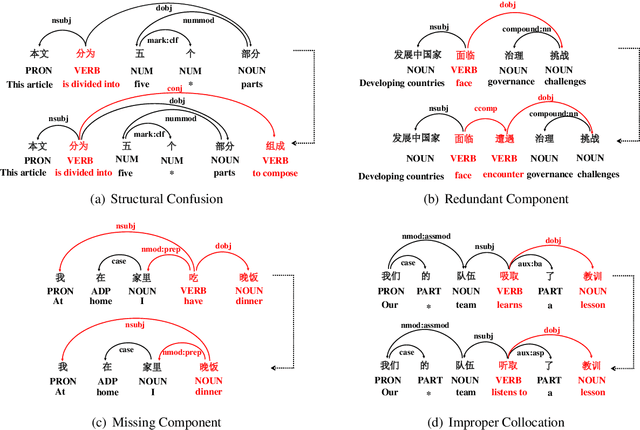
Abstract:Chinese Grammatical Error Correction (CGEC) is both a challenging NLP task and a common application in human daily life. Recently, many data-driven approaches are proposed for the development of CGEC research. However, there are two major limitations in the CGEC field: First, the lack of high-quality annotated training corpora prevents the performance of existing CGEC models from being significantly improved. Second, the grammatical errors in widely used test sets are not made by native Chinese speakers, resulting in a significant gap between the CGEC models and the real application. In this paper, we propose a linguistic rules-based approach to construct large-scale CGEC training corpora with automatically generated grammatical errors. Additionally, we present a challenging CGEC benchmark derived entirely from errors made by native Chinese speakers in real-world scenarios. Extensive experiments and detailed analyses not only demonstrate that the training data constructed by our method effectively improves the performance of CGEC models, but also reflect that our benchmark is an excellent resource for further development of the CGEC field.
Contextual Similarity is More Valuable than Character Similarity: Curriculum Learning for Chinese Spell Checking
Jul 17, 2022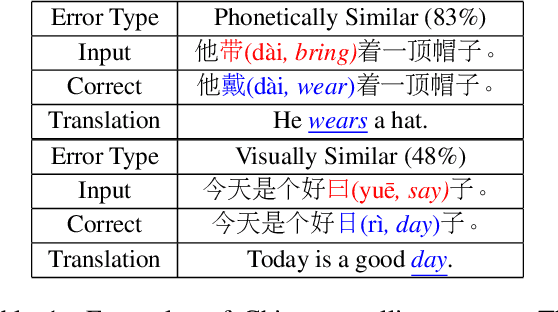
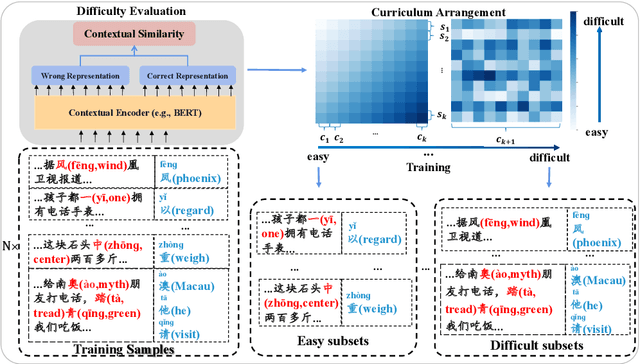
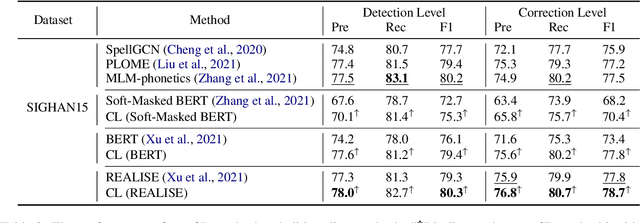
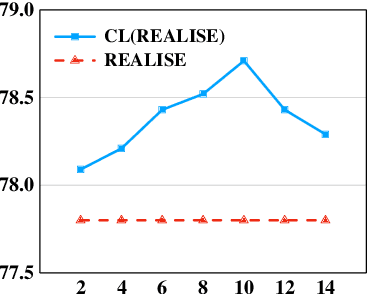
Abstract:Chinese Spell Checking (CSC) task aims to detect and correct Chinese spelling errors. In recent years, related researches focus on introducing the character similarity from confusion set to enhance the CSC models, ignoring the context of characters that contain richer information. To make better use of contextual similarity, we propose a simple yet effective curriculum learning framework for the CSC task. With the help of our designed model-agnostic framework, existing CSC models will be trained from easy to difficult as humans learn Chinese characters and achieve further performance improvements. Extensive experiments and detailed analyses on widely used SIGHAN datasets show that our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods.
Joint AP Probing and Scheduling: A Contextual Bandit Approach
Aug 13, 2021
Abstract:We consider a set of APs with unknown data rates that cooperatively serve a mobile client. The data rate of each link is i.i.d. sampled from a distribution that is unknown a priori. In contrast to traditional link scheduling problems under uncertainty, we assume that in each time step, the device can probe a subset of links before deciding which one to use. We model this problem as a contextual bandit problem with probing (CBwP) and present an efficient algorithm. We further establish the regret of our algorithm for links with Bernoulli data rates. Our CBwP model is a novel extension of the classic contextual bandit model and can potentially be applied to a large class of sequential decision-making problems that involve joint probing and play under uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge