Zhen Yang
School of Communication and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 2100023, China
Thickening-to-Thinning: Reward Shaping via Human-Inspired Learning Dynamics for LLM Reasoning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has emerged as a promising paradigm for enhancing reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, it frequently encounters challenges such as entropy collapse, excessive verbosity, and insufficient exploration for hard problems. Crucially, existing reward schemes fail to distinguish between the need for extensive search during problem-solving and the efficiency required for mastered knowledge. In this work, we introduce T2T(Thickening-to-Thinning), a dynamic reward framework inspired by human learning processes. Specifically, it implements a dual-phase mechanism: (1) On incorrect attempts, T2T incentivizes "thickening" (longer trajectories) to broaden the search space and explore novel solution paths; (2) Upon achieving correctness, it shifts to "thinning", imposing length penalties to discourage redundancy, thereby fostering model confidence and crystallizing reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments on mathematical benchmarks (MATH-500, AIME, AMC) across Qwen-series and Deepseek models demonstrate that T2T significantly outperforms standard GRPO and recent baselines, achieving superior performance.
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
UniDriveDreamer: A Single-Stage Multimodal World Model for Autonomous Driving
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:World models have demonstrated significant promise for data synthesis in autonomous driving. However, existing methods predominantly concentrate on single-modality generation, typically focusing on either multi-camera video or LiDAR sequence synthesis. In this paper, we propose UniDriveDreamer, a single-stage unified multimodal world model for autonomous driving, which directly generates multimodal future observations without relying on intermediate representations or cascaded modules. Our framework introduces a LiDAR-specific variational autoencoder (VAE) designed to encode input LiDAR sequences, alongside a video VAE for multi-camera images. To ensure cross-modal compatibility and training stability, we propose Unified Latent Anchoring (ULA), which explicitly aligns the latent distributions of the two modalities. The aligned features are fused and processed by a diffusion transformer that jointly models their geometric correspondence and temporal evolution. Additionally, structured scene layout information is projected per modality as a conditioning signal to guide the synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniDriveDreamer outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods in both video and LiDAR generation, while also yielding measurable improvements in downstream
TF-Lane: Traffic Flow Module for Robust Lane Perception
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Autonomous driving systems require robust lane perception capabilities, yet existing vision-based detection methods suffer significant performance degradation when visual sensors provide insufficient cues, such as in occluded or lane-missing scenarios. While some approaches incorporate high-definition maps as supplementary information, these solutions face challenges of high subscription costs and limited real-time performance. To address these limitations, we explore an innovative information source: traffic flow, which offers real-time capabilities without additional costs. This paper proposes a TrafficFlow-aware Lane perception Module (TFM) that effectively extracts real-time traffic flow features and seamlessly integrates them with existing lane perception algorithms. This solution originated from real-world autonomous driving conditions and was subsequently validated on open-source algorithms and datasets. Extensive experiments on four mainstream models and two public datasets (Nuscenes and OpenLaneV2) using standard evaluation metrics show that TFM consistently improves performance, achieving up to +4.1% mAP gain on the Nuscenes dataset.
Can LLMs See Without Pixels? Benchmarking Spatial Intelligence from Textual Descriptions
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in Spatial Intelligence (SI) have predominantly relied on Vision-Language Models (VLMs), yet a critical question remains: does spatial understanding originate from visual encoders or the fundamental reasoning backbone? Inspired by this question, we introduce SiT-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the SI performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) without pixel-level input, comprises over 3,800 expert-annotated items across five primary categories and 17 subtasks, ranging from egocentric navigation and perspective transformation to fine-grained robotic manipulation. By converting single/multi-view scenes into high-fidelity, coordinate-aware textual descriptions, we challenge LLMs to perform symbolic textual reasoning rather than visual pattern matching. Evaluation results of state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs reveals that while models achieve proficiency in localized semantic tasks, a significant "spatial gap" remains in global consistency. Notably, we find that explicit spatial reasoning significantly boosts performance, suggesting that LLMs possess latent world-modeling potential. Our proposed dataset SiT-Bench serves as a foundational resource to foster the development of spatially-grounded LLM backbones for future VLMs and embodied agents. Our code and benchmark will be released at https://github.com/binisalegend/SiT-Bench .
D$^3$R-DETR: DETR with Dual-Domain Density Refinement for Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Detecting tiny objects plays a vital role in remote sensing intelligent interpretation, as these objects often carry critical information for downstream applications. However, due to the extremely limited pixel information and significant variations in object density, mainstream Transformer-based detectors often suffer from slow convergence and inaccurate query-object matching. To address these challenges, we propose D$^3$R-DETR, a novel DETR-based detector with Dual-Domain Density Refinement. By fusing spatial and frequency domain information, our method refines low-level feature maps and utilizes their rich details to predict more accurate object density map, thereby guiding the model to precisely localize tiny objects. Extensive experiments on the AI-TOD-v2 dataset demonstrate that D$^3$R-DETR outperforms existing state-of-the-art detectors for tiny object detection.
SpatialBench: Can Agents Analyze Real-World Spatial Biology Data?
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics assays are rapidly increasing in scale and complexity, making computational analysis a major bottleneck in biological discovery. Although frontier AI agents have improved dramatically at software engineering and general data analysis, it remains unclear whether they can extract biological insight from messy, real-world spatial datasets. We introduce SpatialBench, a benchmark of 146 verifiable problems derived from practical spatial analysis workflows spanning five spatial technologies and seven task categories. Each problem provides a snapshot of experimental data immediately prior to an analysis step and a deterministic grader that evaluates recovery of a key biological result. Benchmark data on frontier models shows that base model accuracy remains low (20-38% across model families), with strong model-task and model-platform interactions. Harness design has a large empirical effect on performance, indicating that tools, prompts, control flow, and execution environment should be evaluated and improved as first-class objects. SpatialBench serves both as a measurement tool and a diagnostic lens for developing agents that can interact with real spatial datasets faithfully, transparently, and reproducibly.
StereoPilot: Learning Unified and Efficient Stereo Conversion via Generative Priors
Dec 18, 2025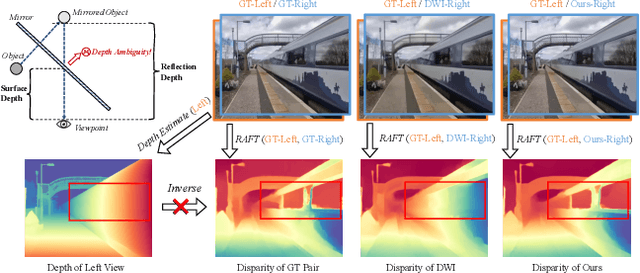
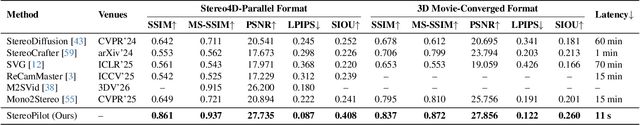
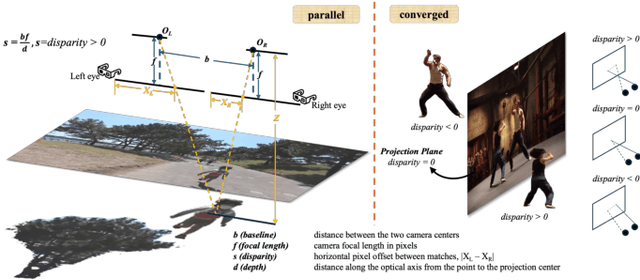

Abstract:The rapid growth of stereoscopic displays, including VR headsets and 3D cinemas, has led to increasing demand for high-quality stereo video content. However, producing 3D videos remains costly and complex, while automatic Monocular-to-Stereo conversion is hindered by the limitations of the multi-stage ``Depth-Warp-Inpaint'' (DWI) pipeline. This paradigm suffers from error propagation, depth ambiguity, and format inconsistency between parallel and converged stereo configurations. To address these challenges, we introduce UniStereo, the first large-scale unified dataset for stereo video conversion, covering both stereo formats to enable fair benchmarking and robust model training. Building upon this dataset, we propose StereoPilot, an efficient feed-forward model that directly synthesizes the target view without relying on explicit depth maps or iterative diffusion sampling. Equipped with a learnable domain switcher and a cycle consistency loss, StereoPilot adapts seamlessly to different stereo formats and achieves improved consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that StereoPilot significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual fidelity and computational efficiency. Project page: https://hit-perfect.github.io/StereoPilot/.
The FACTS Leaderboard: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Large Language Model Factuality
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce The FACTS Leaderboard, an online leaderboard suite and associated set of benchmarks that comprehensively evaluates the ability of language models to generate factually accurate text across diverse scenarios. The suite provides a holistic measure of factuality by aggregating the performance of models on four distinct sub-leaderboards: (1) FACTS Multimodal, which measures the factuality of responses to image-based questions; (2) FACTS Parametric, which assesses models' world knowledge by answering closed-book factoid questions from internal parameters; (3) FACTS Search, which evaluates factuality in information-seeking scenarios, where the model must use a search API; and (4) FACTS Grounding (v2), which evaluates whether long-form responses are grounded in provided documents, featuring significantly improved judge models. Each sub-leaderboard employs automated judge models to score model responses, and the final suite score is an average of the four components, designed to provide a robust and balanced assessment of a model's overall factuality. The FACTS Leaderboard Suite will be actively maintained, containing both public and private splits to allow for external participation while guarding its integrity. It can be found at https://www.kaggle.com/benchmarks/google/facts .
RoboTidy : A 3D Gaussian Splatting Household Tidying Benchmark for Embodied Navigation and Action
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Household tidying is an important application area, yet current benchmarks neither model user preferences nor support mobility, and they generalize poorly, making it hard to comprehensively assess integrated language-to-action capabilities. To address this, we propose RoboTidy, a unified benchmark for language-guided household tidying that supports Vision-Language-Action (VLA) and Vision-Language-Navigation (VLN) training and evaluation. RoboTidy provides 500 photorealistic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) household scenes (covering 500 objects and containers) with collisions, formulates tidying as an "Action (Object, Container)" list, and supplies 6.4k high-quality manipulation demonstration trajectories and 1.5k naviagtion trajectories to support both few-shot and large-scale training. We also deploy RoboTidy in the real world for object tidying, establishing an end-to-end benchmark for household tidying. RoboTidy offers a scalable platform and bridges a key gap in embodied AI by enabling holistic and realistic evaluation of language-guided robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge