Yushi Bai
GLM-4.5: Agentic, Reasoning, and Coding (ARC) Foundation Models
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:We present GLM-4.5, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 355B total parameters and 32B activated parameters, featuring a hybrid reasoning method that supports both thinking and direct response modes. Through multi-stage training on 23T tokens and comprehensive post-training with expert model iteration and reinforcement learning, GLM-4.5 achieves strong performance across agentic, reasoning, and coding (ARC) tasks, scoring 70.1% on TAU-Bench, 91.0% on AIME 24, and 64.2% on SWE-bench Verified. With much fewer parameters than several competitors, GLM-4.5 ranks 3rd overall among all evaluated models and 2nd on agentic benchmarks. We release both GLM-4.5 (355B parameters) and a compact version, GLM-4.5-Air (106B parameters), to advance research in reasoning and agentic AI systems. Code, models, and more information are available at https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-4.5.
LongWriter-Zero: Mastering Ultra-Long Text Generation via Reinforcement Learning
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Ultra-long generation by large language models (LLMs) is a widely demanded scenario, yet it remains a significant challenge due to their maximum generation length limit and overall quality degradation as sequence length increases. Previous approaches, exemplified by LongWriter, typically rely on ''teaching'', which involves supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on synthetic long-form outputs. However, this strategy heavily depends on synthetic SFT data, which is difficult and costly to construct, often lacks coherence and consistency, and tends to be overly artificial and structurally monotonous. In this work, we propose an incentivization-based approach that, starting entirely from scratch and without relying on any annotated or synthetic data, leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to foster the emergence of ultra-long, high-quality text generation capabilities in LLMs. We perform RL training starting from a base model, similar to R1-Zero, guiding it to engage in reasoning that facilitates planning and refinement during the writing process. To support this, we employ specialized reward models that steer the LLM towards improved length control, writing quality, and structural formatting. Experimental evaluations show that our LongWriter-Zero model, trained from Qwen2.5-32B, consistently outperforms traditional SFT methods on long-form writing tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results across all metrics on WritingBench and Arena-Write, and even surpassing 100B+ models such as DeepSeek R1 and Qwen3-235B. We open-source our data and model checkpoints under https://huggingface.co/THU-KEG/LongWriter-Zero-32B
SuperWriter: Reflection-Driven Long-Form Generation with Large Language Models
Jun 04, 2025



Abstract:Long-form text generation remains a significant challenge for large language models (LLMs), particularly in maintaining coherence, ensuring logical consistency, and preserving text quality as sequence length increases. To address these limitations, we propose SuperWriter-Agent, an agent-based framework designed to enhance the quality and consistency of long-form text generation. SuperWriter-Agent introduces explicit structured thinking-through planning and refinement stages into the generation pipeline, guiding the model to follow a more deliberate and cognitively grounded process akin to that of a professional writer. Based on this framework, we construct a supervised fine-tuning dataset to train a 7B SuperWriter-LM. We further develop a hierarchical Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) procedure that uses Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to propagate final quality assessments and optimize each generation step accordingly. Empirical results across diverse benchmarks demonstrate that SuperWriter-LM achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing even larger-scale baseline models in both automatic evaluation and human evaluation. Furthermore, comprehensive ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of hierarchical DPO and underscore the value of incorporating structured thinking steps to improve the quality of long-form text generation.
How does Transformer Learn Implicit Reasoning?
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Recent work suggests that large language models (LLMs) can perform multi-hop reasoning implicitly -- producing correct answers without explicitly verbalizing intermediate steps -- but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this paper, we study how such implicit reasoning emerges by training transformers from scratch in a controlled symbolic environment. Our analysis reveals a three-stage developmental trajectory: early memorization, followed by in-distribution generalization, and eventually cross-distribution generalization. We find that training with atomic triples is not necessary but accelerates learning, and that second-hop generalization relies on query-level exposure to specific compositional structures. To interpret these behaviors, we introduce two diagnostic tools: cross-query semantic patching, which identifies semantically reusable intermediate representations, and a cosine-based representational lens, which reveals that successful reasoning correlates with the cosine-base clustering in hidden space. This clustering phenomenon in turn provides a coherent explanation for the behavioral dynamics observed across training, linking representational structure to reasoning capability. These findings provide new insights into the interpretability of implicit multi-hop reasoning in LLMs, helping to clarify how complex reasoning processes unfold internally and offering pathways to enhance the transparency of such models.
Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Fine-Grained Geometric Understanding in Large Multimodal Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Benefiting from contrastively trained visual encoders on large-scale natural scene images, Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable performance across various visual perception tasks. However, the inherent limitations of contrastive learning upon summarized descriptions fundamentally restrict the capabilities of models in meticulous reasoning, particularly in crucial scenarios of geometric problem-solving. To enhance geometric understanding, we propose a novel hard negative contrastive learning framework for the vision encoder, which combines image-based contrastive learning using generation-based hard negatives created by perturbing diagram generation code, and text-based contrastive learning using rule-based negatives derived from modified geometric descriptions and retrieval-based negatives selected based on caption similarity. We train CLIP using our strong negative learning method, namely MMCLIP (Multimodal Math CLIP), and subsequently train an LMM for geometric problem-solving. Experiments show that our trained model, MMGeoLM, significantly outperforms other open-source models on three geometric reasoning benchmarks. Even with a size of 7B, it can rival powerful closed-source models like GPT-4o. We further study the impact of different negative sample construction methods and the number of negative samples on the geometric reasoning performance of LMM, yielding fruitful conclusions. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/THU-KEG/MMGeoLM.
An LMM for Efficient Video Understanding via Reinforced Compression of Video Cubes
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) uniformly perceive video frames, creating computational inefficiency for videos with inherently varying temporal information density. This paper present \textbf{Quicksviewer}, an LMM with new perceiving paradigm that partitions a video of nonuniform density into varying cubes using Gumbel Softmax, followed by a unified resampling for each cube to achieve efficient video understanding. This simple and intuitive approach dynamically compress video online based on its temporal density, significantly reducing spatiotemporal redundancy (overall 45$\times$ compression rate), while enabling efficient training with large receptive field. We train the model from a language backbone through three progressive stages, each incorporating lengthy videos on average of 420s/1fps thanks to the perceiving efficiency. With only 0.8M total video-text samples for training, our model outperforms the direct baseline employing a fixed partitioning strategy by a maximum of 8.72 in accuracy, demonstrating the effectiveness in performance. On Video-MME, Quicksviewer achieves SOTA under modest sequence lengths using just up to 5\% of tokens per frame required by baselines. With this paradigm, scaling up the number of input frames reveals a clear power law of the model capabilities. It is also empirically verified that the segments generated by the cubing network can help for analyzing continuous events in videos.
Shifting Long-Context LLMs Research from Input to Output
Mar 07, 2025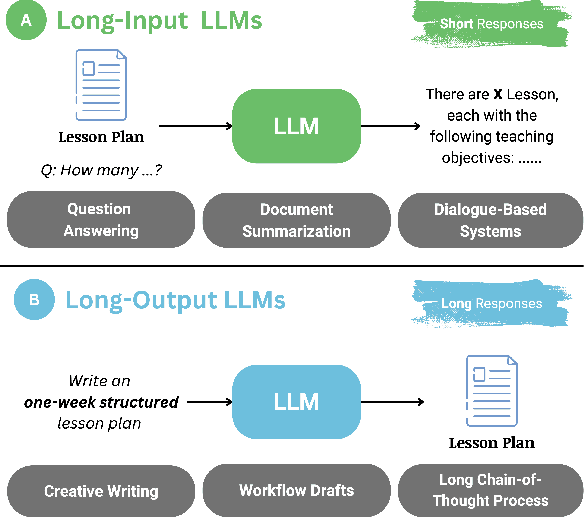
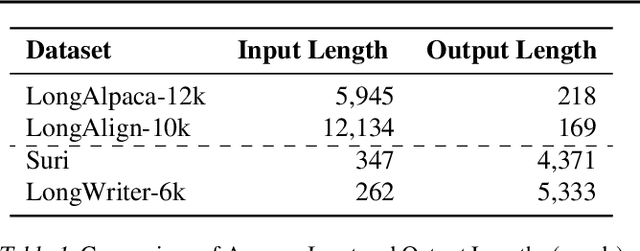
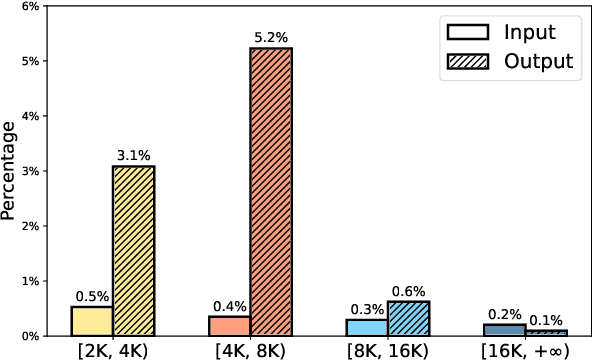
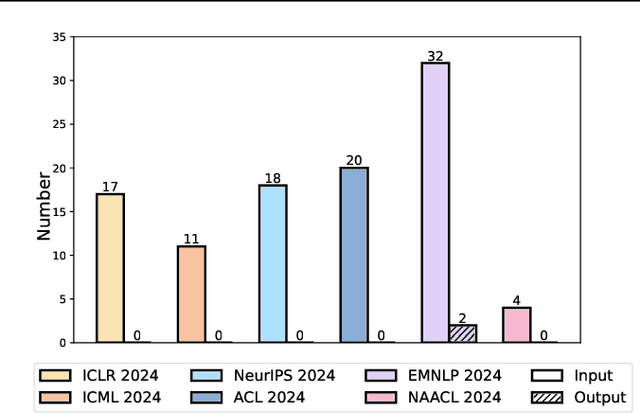
Abstract:Recent advancements in long-context Large Language Models (LLMs) have primarily concentrated on processing extended input contexts, resulting in significant strides in long-context comprehension. However, the equally critical aspect of generating long-form outputs has received comparatively less attention. This paper advocates for a paradigm shift in NLP research toward addressing the challenges of long-output generation. Tasks such as novel writing, long-term planning, and complex reasoning require models to understand extensive contexts and produce coherent, contextually rich, and logically consistent extended text. These demands highlight a critical gap in current LLM capabilities. We underscore the importance of this under-explored domain and call for focused efforts to develop foundational LLMs tailored for generating high-quality, long-form outputs, which hold immense potential for real-world applications.
LongWriter-V: Enabling Ultra-Long and High-Fidelity Generation in Vision-Language Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Existing Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) can process inputs with context lengths up to 128k visual and text tokens, yet they struggle to generate coherent outputs beyond 1,000 words. We find that the primary limitation is the absence of long output examples during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). To tackle this issue, we introduce LongWriter-V-22k, a SFT dataset comprising 22,158 examples, each with multiple input images, an instruction, and corresponding outputs ranging from 0 to 10,000 words. Moreover, to achieve long outputs that maintain high-fidelity to the input images, we employ Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to the SFT model. Given the high cost of collecting human feedback for lengthy outputs (e.g., 3,000 words), we propose IterDPO, which breaks long outputs into segments and uses iterative corrections to form preference pairs with the original outputs. Additionally, we develop MMLongBench-Write, a benchmark featuring six tasks to evaluate the long-generation capabilities of VLMs. Our 7B parameter model, trained with LongWriter-V-22k and IterDPO, achieves impressive performance on this benchmark, outperforming larger proprietary models like GPT-4o. Code and data: https://github.com/THU-KEG/LongWriter-V
LongBench v2: Towards Deeper Understanding and Reasoning on Realistic Long-context Multitasks
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces LongBench v2, a benchmark designed to assess the ability of LLMs to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across real-world multitasks. LongBench v2 consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions, with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, across six major task categories: single-document QA, multi-document QA, long in-context learning, long-dialogue history understanding, code repository understanding, and long structured data understanding. To ensure the breadth and the practicality, we collect data from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds. We employ both automated and manual review processes to maintain high quality and difficulty, resulting in human experts achieving only 53.7% accuracy under a 15-minute time constraint. Our evaluation reveals that the best-performing model, when directly answers the questions, achieves only 50.1% accuracy. In contrast, the o1-preview model, which includes longer reasoning, achieves 57.7%, surpassing the human baseline by 4%. These results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2. The project is available at https://longbench2.github.io.
AlphaTablets: A Generic Plane Representation for 3D Planar Reconstruction from Monocular Videos
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:We introduce AlphaTablets, a novel and generic representation of 3D planes that features continuous 3D surface and precise boundary delineation. By representing 3D planes as rectangles with alpha channels, AlphaTablets combine the advantages of current 2D and 3D plane representations, enabling accurate, consistent and flexible modeling of 3D planes. We derive differentiable rasterization on top of AlphaTablets to efficiently render 3D planes into images, and propose a novel bottom-up pipeline for 3D planar reconstruction from monocular videos. Starting with 2D superpixels and geometric cues from pre-trained models, we initialize 3D planes as AlphaTablets and optimize them via differentiable rendering. An effective merging scheme is introduced to facilitate the growth and refinement of AlphaTablets. Through iterative optimization and merging, we reconstruct complete and accurate 3D planes with solid surfaces and clear boundaries. Extensive experiments on the ScanNet dataset demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in 3D planar reconstruction, underscoring the great potential of AlphaTablets as a generic 3D plane representation for various applications. Project page is available at: https://hyzcluster.github.io/alphatablets
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge